Autotroph Drawing
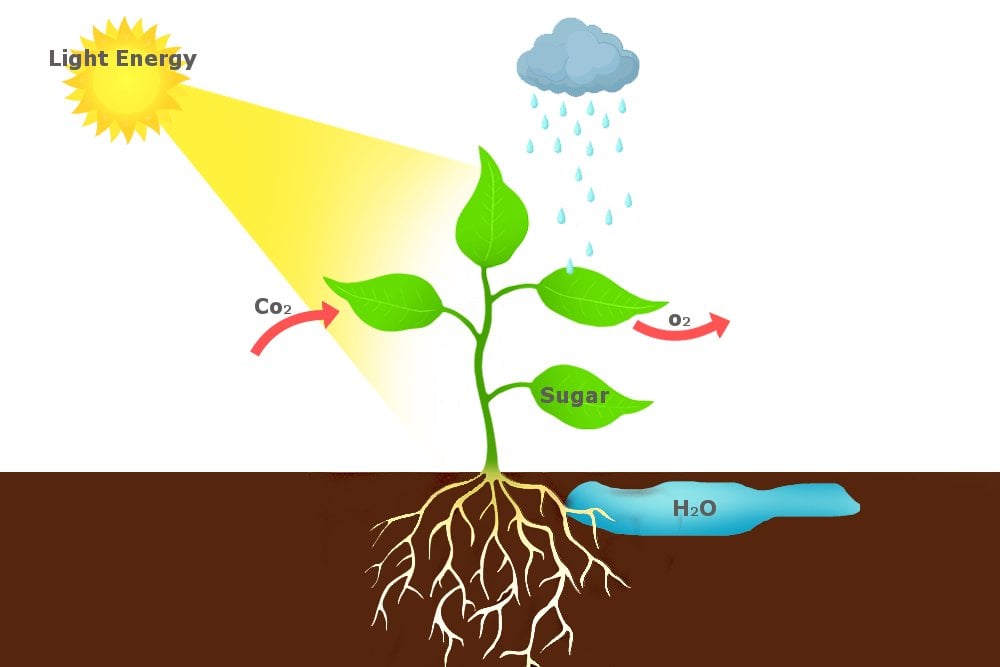
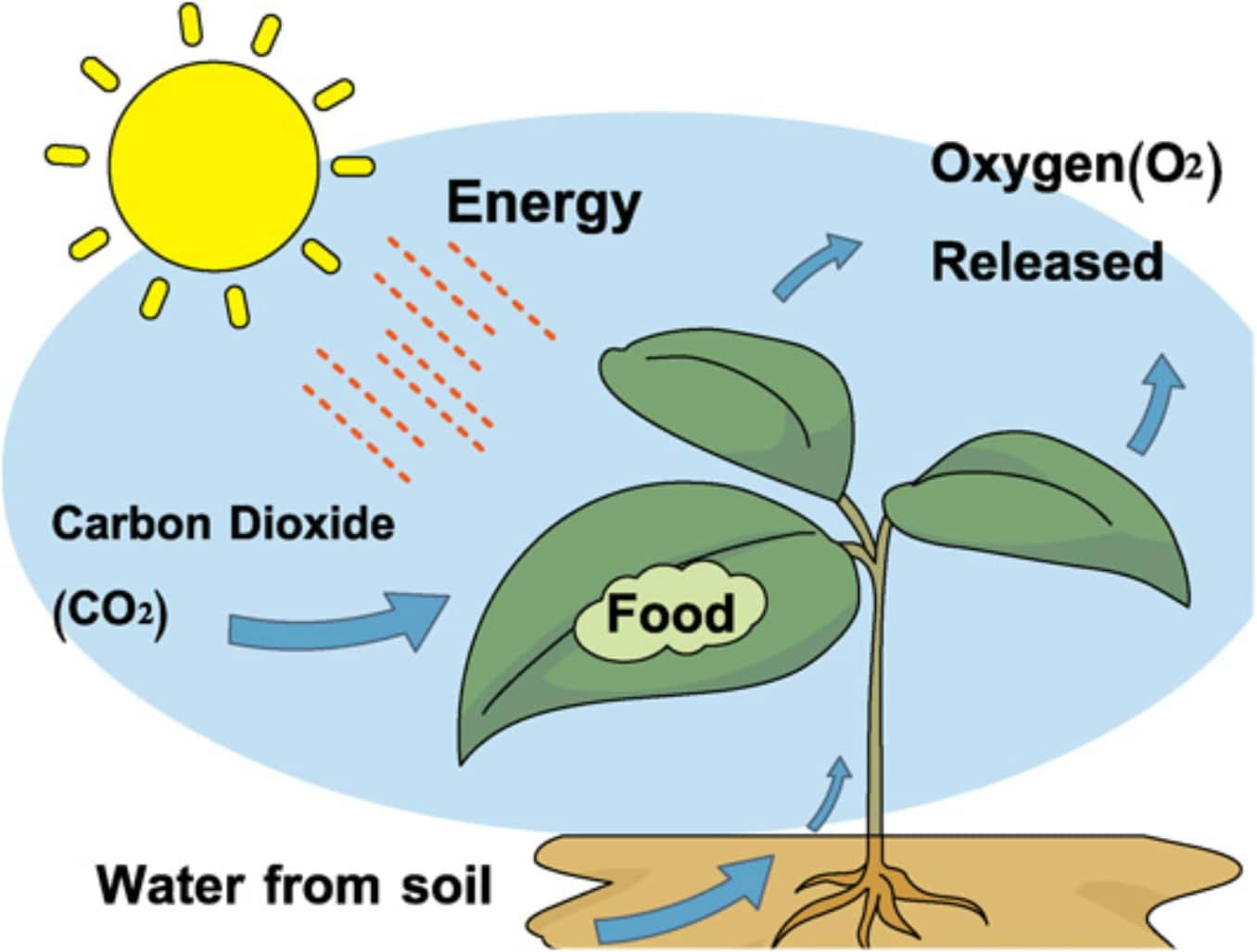
Autotroph Drawing - Examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, plankton and bacteria. The word “autotroph” comes from the root words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food.” an autotroph is an organism that feeds itself, without the assistance of any other organisms. Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates , fats , and proteins ) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, [1] generally using energy from light or. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producers. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process known as photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. There are two basic types of autotrophs: Web autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food, using materials from inorganic sources. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates , fats , and proteins ) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, [1] generally using energy from light or. Web an autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. The word “autotroph” comes from the root words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food.” an autotroph is an organism that feeds itself, without the assistance of any other organisms. Examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, plankton and bacteria. The food chain is comprised of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. Another name for primary producers in ecosystems is autotrophs. Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms. Web autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food, using materials from inorganic sources. Web for example, if you are drawing a food web of the desert, you might include cacti as a producer. The food chain is comprised of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms. Another name for primary producers in ecosystems is autotrophs. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process known as photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Web an autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. There are two basic types of autotrophs: It survives by using photosynthesis to convert sunlight to energy. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producers. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. The word “autotroph” comes from the root words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food.” an autotroph is an organism that feeds itself, without the assistance of any other organisms. Web an autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either. Web autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food, using materials from inorganic sources. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, plankton and bacteria. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process. Web autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food, using materials from inorganic sources. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producers. It survives by using photosynthesis to convert sunlight to energy. There are two basic types of autotrophs: Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates , fats , and proteins ) using carbon from. Web for example, if you are drawing a food web of the desert, you might include cacti as a producer. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process known as photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Web an autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. There are two basic types of autotrophs: Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Web an autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains,. There are two basic types of autotrophs: Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. It survives by using photosynthesis to convert sunlight to energy. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process known as photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Autotrophs produce. There are two basic types of autotrophs: Web an autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates , fats , and proteins ) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, [1] generally using energy. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. Web an autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. The word “autotroph” comes from the root words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food.” an autotroph is an organism that feeds itself, without the. The food chain is comprised of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. Web autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water. Web for example, if you are drawing a food web of the desert, you might include cacti as a producer. The word “autotroph” comes from the root words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food.” an autotroph is an organism that feeds itself, without the assistance of any other organisms. Web autotrophs use inorganic material to produce food through either a process known as photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Web an autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Another name for primary producers in ecosystems is autotrophs. Web when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call autotrophs producers. Plants are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms. Examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, plankton and bacteria. Web an autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates , fats , and proteins ) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, [1] generally using energy from light or. The food chain is comprised of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. There are two basic types of autotrophs:Autotrophs Examples
Autotroph Definition & Examples Lesson
Шта је аутотроф? Дефиниција и примери
What is Autotrophic Nutrition? Types and Examples of Autotrophic
Photosynthesis Presentation Biology
Autotrophs Examples
Autotroph Definition, Classification, And Examples
SONU ACADEMY AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITIONTEXT
Fill in the blanks Questions Class 6 Science Teachoo
Autotrophs or producers and heterotrophs or consumers as nature energy
It Survives By Using Photosynthesis To Convert Sunlight To Energy.
Web Autotrophs Capture Carbon Dioxide From The Air Or Bicarbonate Ions From The Water And Use Them To Make Organic Compounds Such As Glucose.
Web Autotrophs Are Organisms That Can Produce Their Own Food, Using Materials From Inorganic Sources.
Because Autotrophs Produce Their Own Food, They Are Sometimes Called Producers.
Related Post:


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/heterotroph-and-autotroph-vector-illustration--labeled-biological-division--1197028175-d0873313a374439691bf1e333af1b588.jpg)
.PNG)