Auxiliary View Engineering Drawing
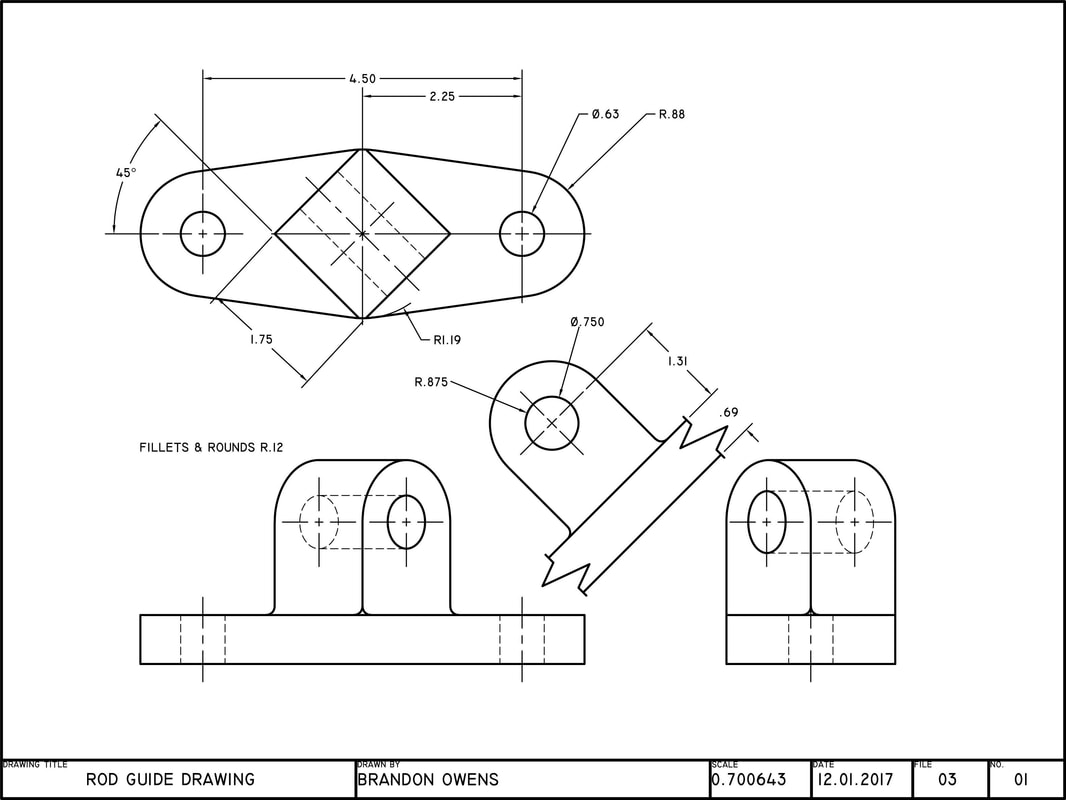
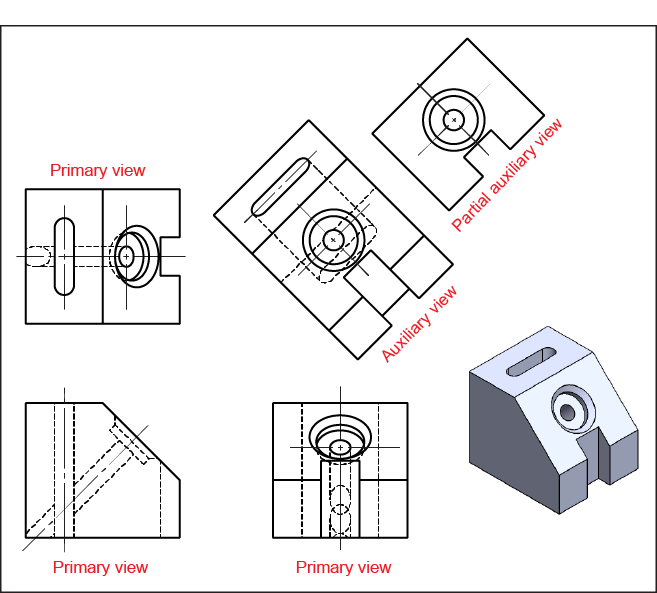
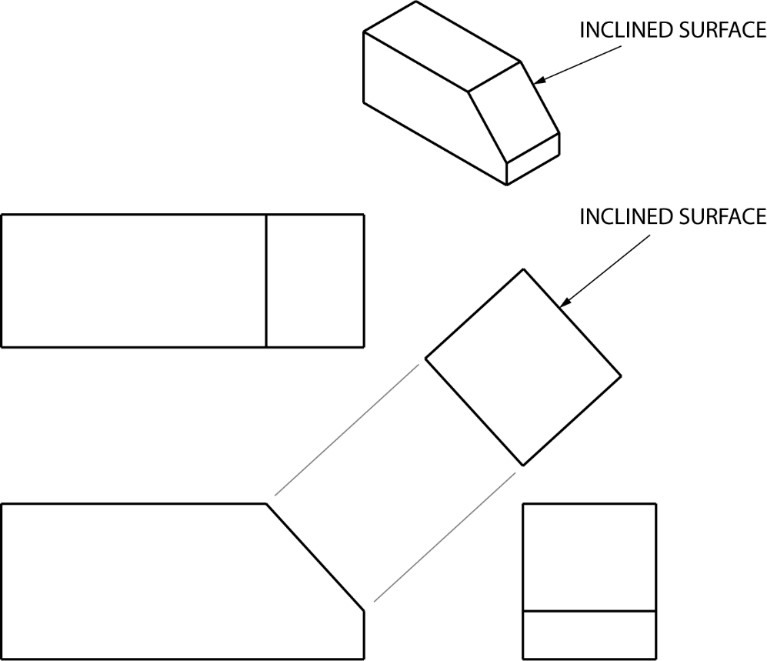
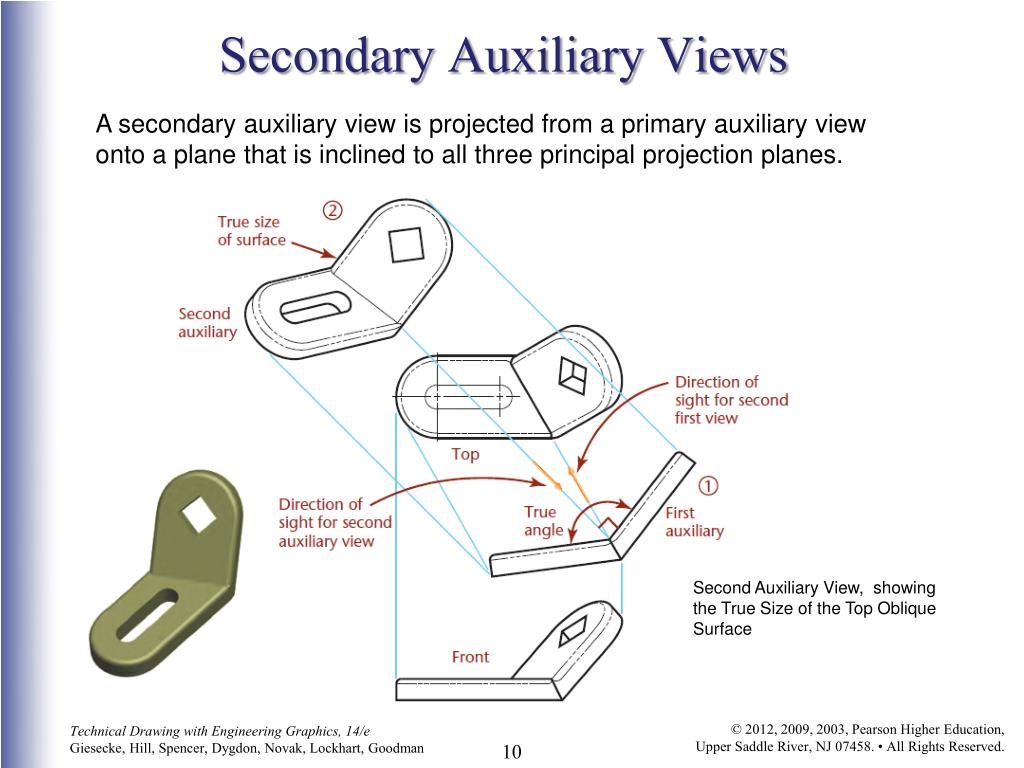
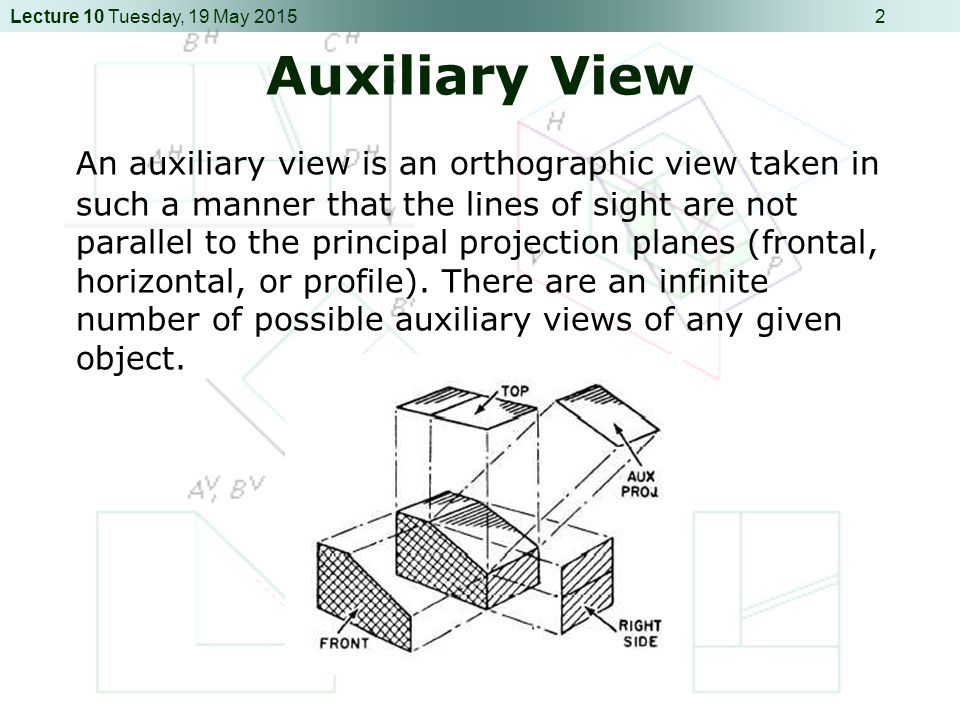
Auxiliary View Engineering Drawing - Web auxiliary drawings are used to help visualize a structure more clearly. Draw apparent shapes of surfaces in either the principal views or auxiliary views, if at least one of the views represents the true shape. Whereas, breadth and other detail are obtained from other views like side view, top view, for the completion of the auxiliary views. Web an auxiliary view is an orthographic view that is projected into any plane other than one of the six primary views. Web draw primary auxiliary views representing the true shapes of surfaces that are perpendicular to one of the reference planes and inclined to the other two. Ideally, the view that is created should be shown in line with the direction of view. Make a rough sketch of the structure on paper. Web create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. It is typically used in technical drawings and engineering to show details that are not easily visible in standard orthographic views. Using the auxiliary view allows for that inclined plane (and any other significant features) to be projected in their true size and shape. Web auxiliary views are used when showing true dimensions of parts that are on an inclined angle. Web create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. Web view of the object projected on the auxiliary plane is called auxiliary top view and the auxiliary plane is called auxiliary inclined plane and denoted as aip. Web construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Web an auxiliary view is a 2d representation of a 3d object that provides additional information about the object's shape and features. For many objects the six principle views do not always describe an object’s true shape. In the second and third types of drawings, the auxiliary views are projected from the top and side views. There are an infinite number of possible auxiliary views of any given object. To construct an auxiliary drawing, you will need to: Make a rough sketch of the structure on paper. Web an auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection. Web create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. For many objects the six principle views do not always describe an object’s true shape. Understand the problem and what you are trying to draw. Web this exercise takes you through the steps required to construct an auxiliary view. Plot curves in auxiliary views. Make a rough sketch of the structure on paper. Web understanding the types, principles, and significance of engineering drawing views empowers engineers and designers to communicate design intent effectively, visualize complex geometries accurately, and ensure manufacturability and compliance with industry standards. An auxiliary view is used to show the true size and shape of an inclined or oblique surface that can not be otherwise seen from any of the six principal views discussed in the previous chapter. Ideally, the view that is created should be shown in line with the direction of view. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Web draw primary auxiliary views representing the true shapes of surfaces that are perpendicular to one of the reference planes and inclined to the other two. Web understanding the types, principles, and significance of engineering drawing views empowers engineers and designers to communicate design intent effectively, visualize complex geometries accurately, and ensure manufacturability. Plot curves in auxiliary views. An auxiliary view is used to show the true size and shape of an inclined or oblique surface that can not be otherwise seen from any of the six principal views discussed in the previous chapter. Web there are three basic type of auxiliary views. In the second and third types of drawings, the auxiliary. The below example demonstrates the auxiliary view and its purpose: Understand the problem and what you are trying to draw. An arrow is used to identify the surface that is looked at. Web draw primary auxiliary views representing the true shapes of surfaces that are perpendicular to one of the reference planes and inclined to the other two. For many. Web an auxiliary view is an ortographic view taken in such a manner that the lines of sight are not parallel to the principal projection planes (frontal, horizontal, or profile). An arrow is used to identify the surface that is looked at. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. If the object contains an inclined surface, you need an additional. Web there are three basic type of auxiliary views. Web an auxiliary view is an orthographic view on a plane that is not one of the principal planes of projection. In the second and third types of drawings, the auxiliary views are projected from the top and side views. There are an infinite number of possible auxiliary views of any. Web understanding the types, principles, and significance of engineering drawing views empowers engineers and designers to communicate design intent effectively, visualize complex geometries accurately, and ensure manufacturability and compliance with industry standards. Use a ruler and other geometry tools to create a more accurate drawing. Visualizing a primary auxiliary view: An auxiliary view is used to show the true size. Web this exercise takes you through the steps required to construct an auxiliary view. Web understanding the types, principles, and significance of engineering drawing views empowers engineers and designers to communicate design intent effectively, visualize complex geometries accurately, and ensure manufacturability and compliance with industry standards. The below example demonstrates the auxiliary view and its purpose: If the object contains. Using the auxiliary view allows for that inclined plane (and any other significant features) to be projected in their true size and shape. This is a type of orthographic view used to represent planes that are horizontal or vertical. The below example demonstrates the auxiliary view and its purpose: Plot curves in auxiliary views. Web to present a more accurate. Web construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. The below example demonstrates the auxiliary view and its purpose: Web there are three basic type of auxiliary views. Construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Understand the problem and what you are trying to draw. Web construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Web an auxiliary view is a 2d representation of a 3d object that provides additional information about the object's shape and features. This is a type of orthographic view used to represent planes that are horizontal or vertical. Web an auxiliary view is an ortographic view taken in such a manner that. Web to present a more accurate description of any inclined surface, an additional view, known as an auxiliary view, is usually required. An arrow is used to identify the surface that is looked at. Web this exercise takes you through the steps required to construct an auxiliary view. Web to prepare an auxiliary view, the length and other detail about auxiliary views are obtained by taking projections from the inclined surface. In the second and third types of drawings, the auxiliary views are projected from the top and side views. An auxiliary view is used to show the true size and shape of an inclined or oblique surface that can not be otherwise seen from any of the six principal views discussed in the previous chapter. Use a ruler and other geometry tools to create a more accurate drawing. Web auxiliary drawings are used to help visualize a structure more clearly. Web construct depth, height, or width auxiliary views. Whereas, breadth and other detail are obtained from other views like side view, top view, for the completion of the auxiliary views. Web there are three basic type of auxiliary views. Web create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. Draw apparent shapes of surfaces in either the principal views or auxiliary views, if at least one of the views represents the true shape. Web auxiliary views are used when showing true dimensions of parts that are on an inclined angle. Using the auxiliary view allows for that inclined plane (and any other significant features) to be projected in their true size and shape. Plot curves in auxiliary views.AUXILIARY DRAWINGS BRANDON OWENS' PORTFOLIO
Introduction to Engineering Drawings
What Is Auxiliary Plane Types of Auxiliary Plane Types of Auxiliary
Auxiliary Views Basic Blueprint Reading
Drawing 04_01 Primary Auxiliary View YouTube
Auxiliary View
AUXILIARY VIEW IN ENGINEERING DRAWING YouTube
Auxiliary view in engineering drawing YouTube
Auxiliary Views FREEMAN'S TECH ED SITE
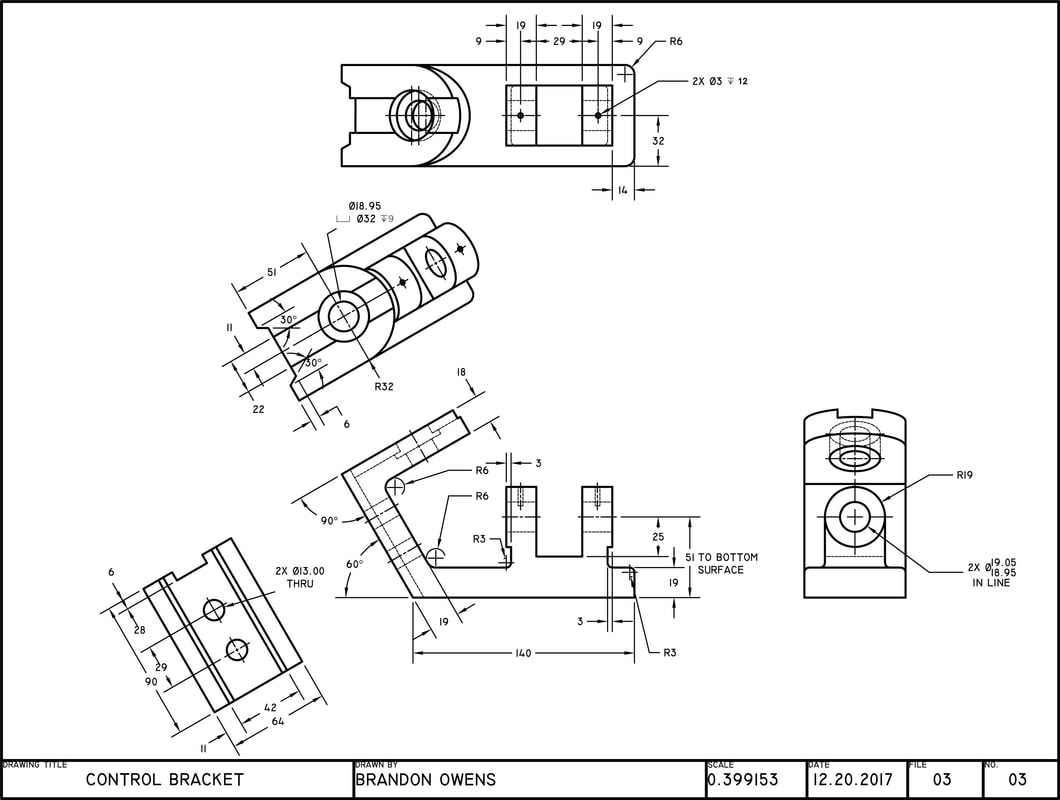
AUXILIARY DRAWINGS BRANDON OWENS' PORTFOLIO
The Below Example Demonstrates The Auxiliary View And Its Purpose:
Construct Depth, Height, Or Width Auxiliary Views.
Plot Curves In Auxiliary Views.
It Helps Exhibit Inclined Surfaces Without Distortion.
Related Post: