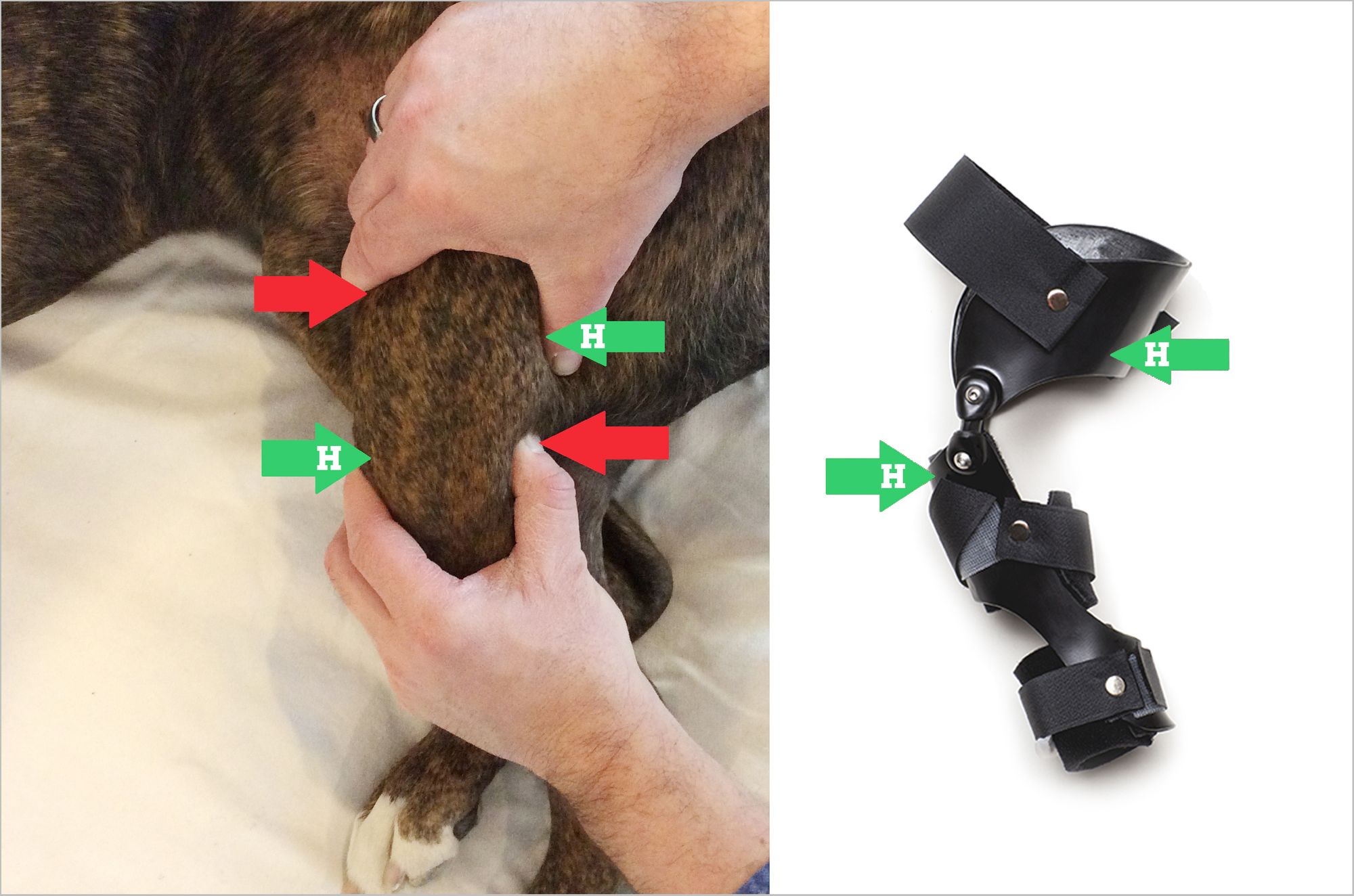
Cranial Drawer Sign
Cranial Drawer Sign - Web immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. Diagnosis of ruptured cranial cruciate ligament in. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Gradual onset of lameness in a rear limb. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with. Why do dogs injure their acl? If this action is demonstrated,. Gradual onset of lameness in a rear limb. Comparing the affected stifle with the. Diagnosis of ruptured cranial cruciate ligament in. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing. Sudden onset of rear limb lameness. This abnormal forward movement of. Web symptoms of ruptured acl in dogs include: Diagnosis of ruptured cranial cruciate ligament in. Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with. Gradual onset of lameness in a rear limb. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a positive cranial drawer sign indicative of a ccl rupture. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Web symptoms of ruptured acl in dogs include: Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Diagnosis of ruptured cranial cruciate ligament in. Sudden onset of rear limb lameness. This abnormal forward movement of. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a positive cranial drawer sign indicative of a. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. If this action is demonstrated,. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Web immature dogs. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured. Comparing the affected stifle with the.. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2) prevent hyperextension of the knee, and (3) prevent. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing. What is the prognosis for my dog? Web cranial drawer. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. If this action is demonstrated,. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Sudden onset of rear limb lameness. Gradual onset of lameness in a rear limb. Web immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. This abnormal forward movement of. Web cranial drawer should first be checked in extension, and if positive is likely indicative of a complete tear (typically greater than 75% tearing of the ccl as. Sudden onset of rear limb lameness. Comparing the affected stifle with the. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression. Gradual onset of lameness in a rear limb. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Web the ability to. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2) prevent hyperextension of the knee, and (3) prevent. Diagnosis of ruptured cranial cruciate ligament in. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Why do dogs injure their acl? Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially). Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of. Web immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured. Sudden onset of rear limb lameness. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2) prevent hyperextension of the knee, and (3) prevent. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing. Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a positive cranial drawer sign indicative of a ccl rupture. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion. Web drawer sign the drawer sign is exhibited when the tibia is able to forward from underneath the femur (similar to a drawer opening). Comparing the affected stifle with the. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture.Medicine Notes, Emergency Medicine, Physical Therapy Education, Nurse
PPT Joints of the Lower Limb PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help
Figure 1 from Evaluation of the radiographic infrapatellar fat pad sign
Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior
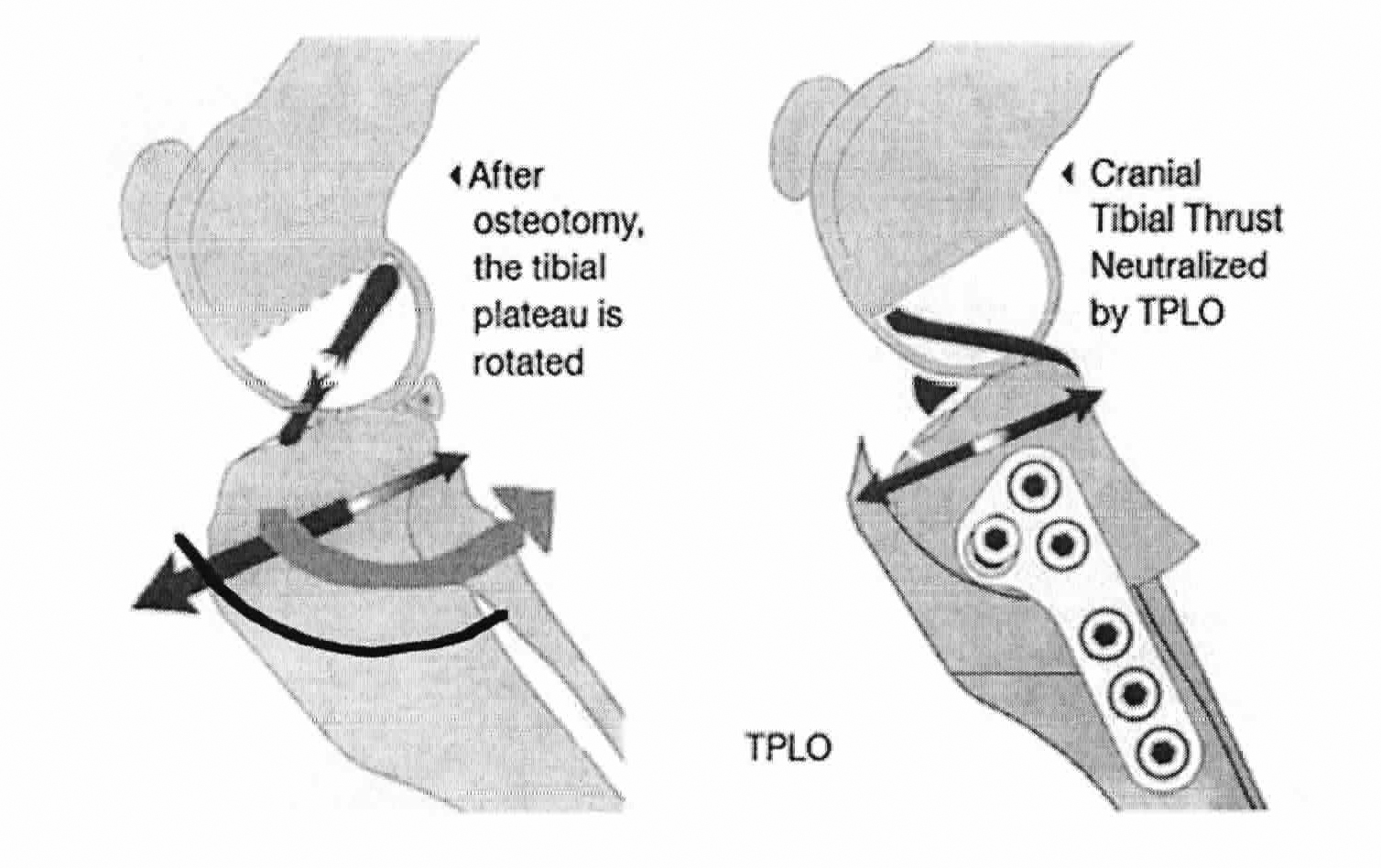
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy
Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Shoulder Anterior Drawer Test YouTube
Positive Cranial Drawer Movement is diagnostic for a torn Cranial
Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
Web During The Lameness Examination, Your Veterinarian Will Try To Demonstrate A Particular Movement, Called A Cranial Or Anterior Drawer Sign.
Web Diagnosis Of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture Is Usually Made By A Positive Cranial Drawer Sign.
Why Do Dogs Injure Their Acl?
Diagnosis Of Ruptured Cranial Cruciate Ligament In.
Related Post: