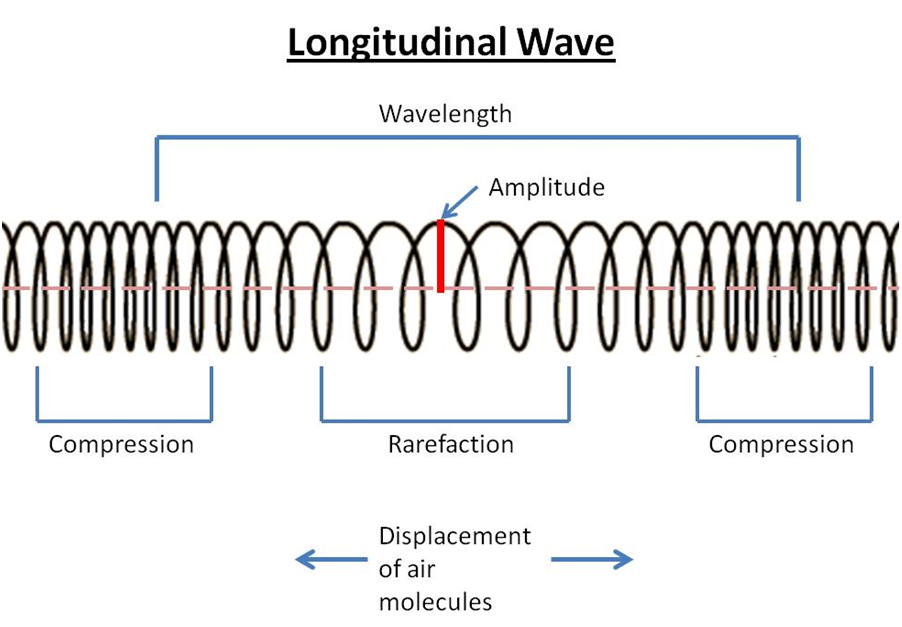
Draw A Longitudinal Wave
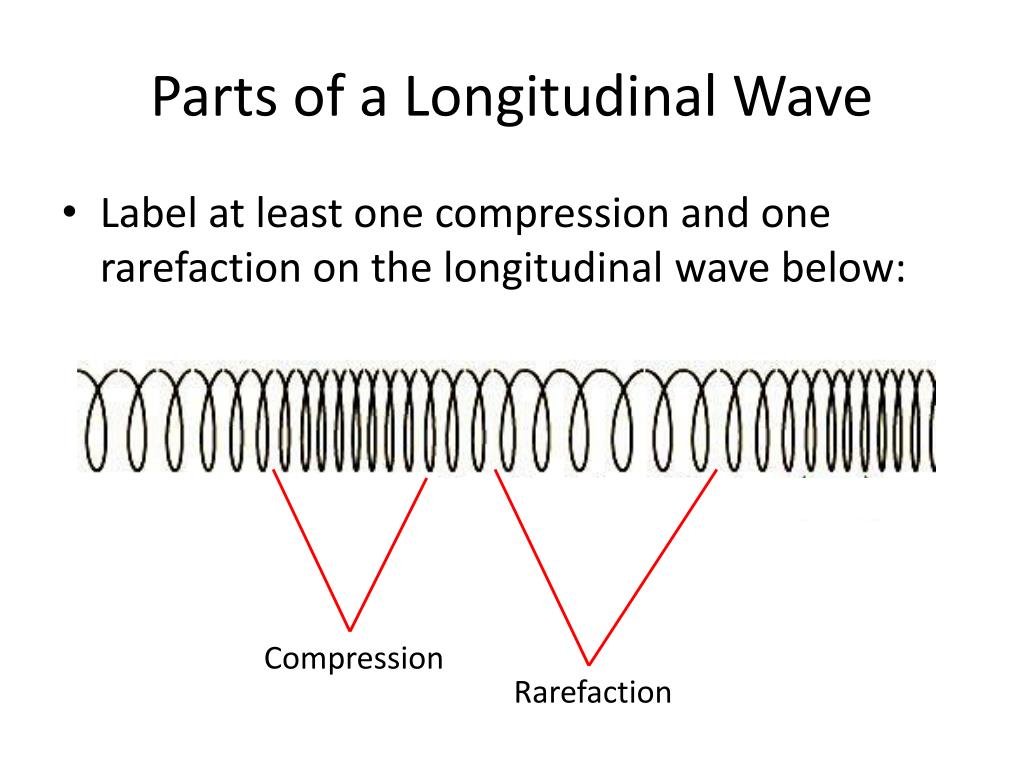
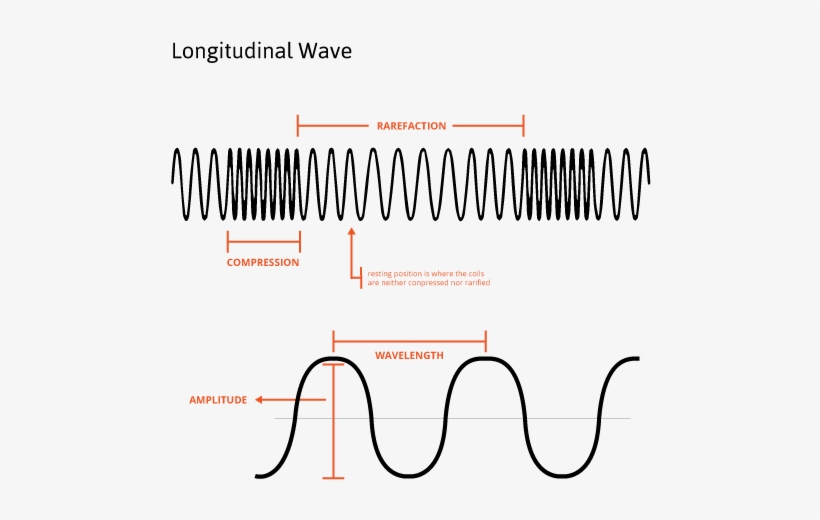
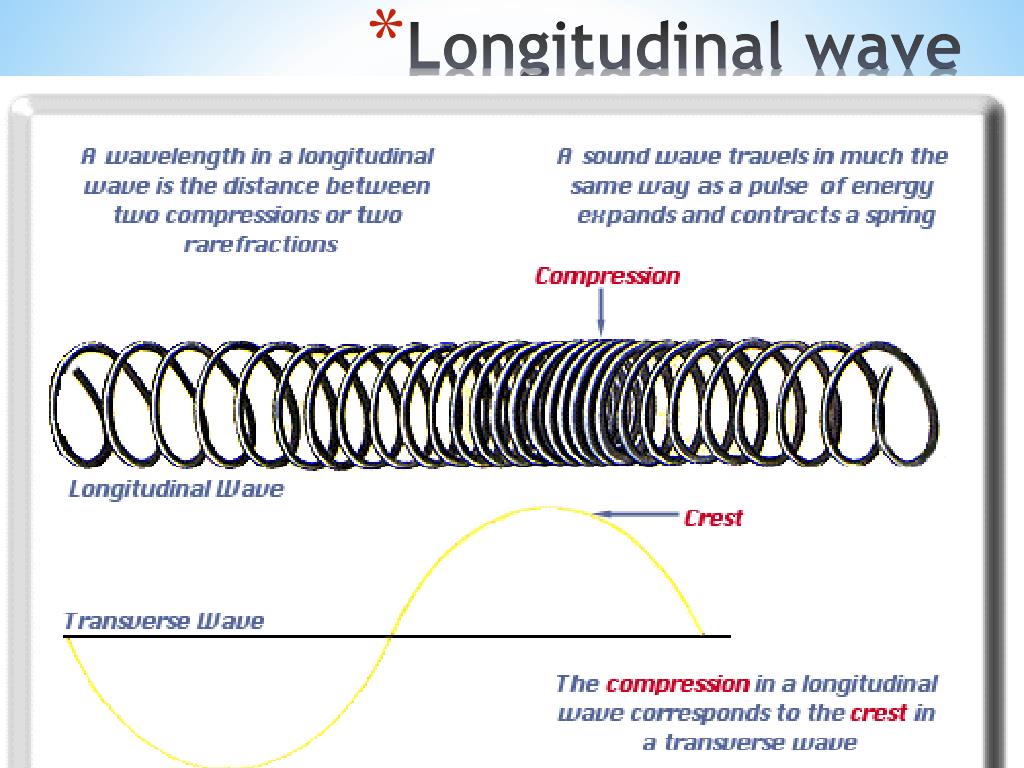
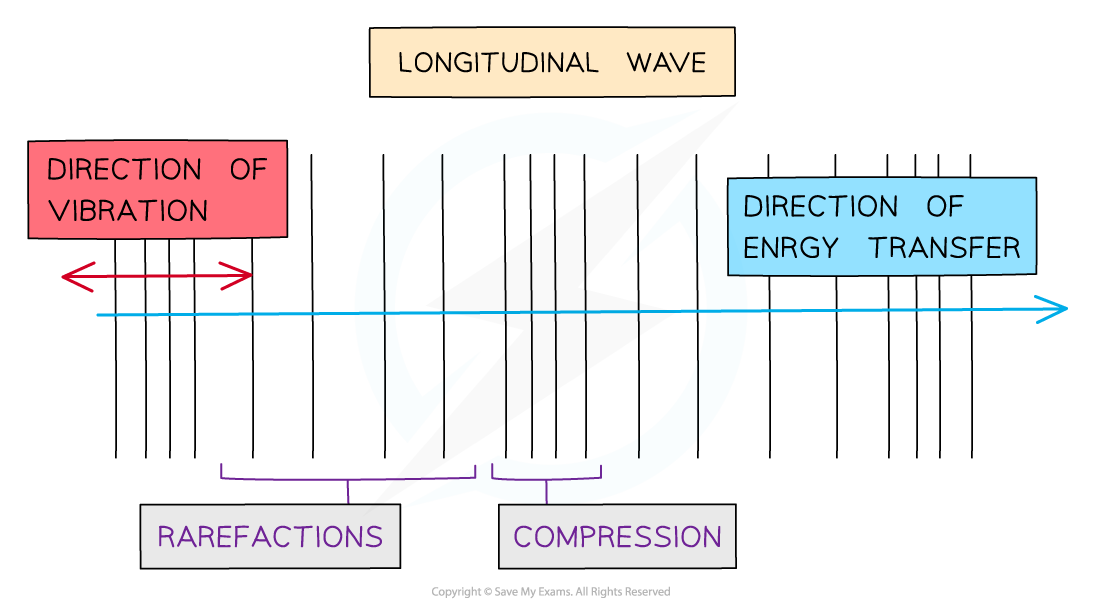
Draw A Longitudinal Wave - Draw a sketch of a longitudinal wave. Web longitudinal wave, wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave. The rarefactions are areas of low pressure due to the particles spread further apart Web in a longitudinal wave, the displacement of the particle is parallel to the direction of the wave propagation. Web what a longitudinal wave is, its compressions and rarefactions and what a p wave is. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Web longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. Web earthquakes cause longitudinal waves called p waves, which pass through underground rocks. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Web a longitudinal wave occurs when the disturbance moves in the same direction as the wave itself. Another type, an s wave, is a transverse wave and cannot pass through the outer core. In a light wave, $q$ can be any of the components of the electromagnetic field, or any of the components of the em potential. We can make a horizontal longitudinal wave by pushing and pulling the slinky horizontally. Models based on known or potential confounders and directed acyclic graphs. Web sound waves in air (and any fluid medium) are longitudinal waves because particles of the medium through which the sound is transported vibrate parallel to the direction that the sound wave moves. Web we analyzed survey responses from waves 1 to 5 of the national longitudinal study of adolescent to adult health (add health), coupled with new epigenetic data from wave 5. Add labels to identify the compressions and rarefactions. An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. Web earthquakes cause longitudinal waves called p waves, which pass through underground rocks. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Another type, an s wave, is a transverse wave and cannot pass through the outer core. Web what a longitudinal wave is, its compressions and rarefactions and what a p wave is. Longitudinal waves are made of compressions and rarefactions, while transverse waves are made of crests and troughs. The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. Web we analyzed survey responses from waves 1 to 5 of the national longitudinal study of adolescent to adult health (add health), coupled with new epigenetic data. Another type, an s wave, is a transverse wave and cannot pass through the outer core. Web in a sound wave, $q$ could be pressure or density or longitudinal displacement. In most examples of longitudinal waves that we explore, this displacement occurs as periodic compressions (region of more dense medium) and rarefactions (regions of less dense. Diagram of a longitudinal. In chapter 4 we discussed transverse waves, in particular transverse waves on a string. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. We'll now move on to longitudinal waves. Web learn about and revise transverse, longitudinal and electromagnetic waves with gcse bitesize physics. In a light wave, $q$ can be any of the components of the electromagnetic field, or any. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Web there are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; Use arrows to show the direction of the wave and the. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Parts of a longitudinal wave. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released. The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. We'll now move on to longitudinal. We'll now move on to longitudinal waves. The rarefactions are areas of low pressure due to the particles spread further apart Web in a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. A material wave is longitudinal if the medium displacement from equilibrium is in the same direction that the wave is traveling. Longitudinal waves. Web longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Web learn about and revise transverse, longitudinal and electromagnetic waves with gcse bitesize physics. Longitudinal waves are made of compressions and rarefactions, while transverse. Web longitudinal sound waves are used in ultrasound to do prenatal screening. Web a longitudinal wave occurs when the disturbance moves in the same direction as the wave itself. An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky. Diagram of a longitudinal wave. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is. Models based on known or potential confounders and directed acyclic graphs. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; What you see in the picture is the wavefront progressing forward and the particles compressing and expanding in the same direction. Use arrows to show the direction of the wave and the direction of the vibrating particles of the medium. Longitudinal waves show areas of compressions and rarefactions; Web earthquakes cause longitudinal waves called p waves, which pass through underground rocks. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. The rarefactions are areas of low pressure due to the particles spread further apart The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. Add labels to identify the compressions and rarefactions. Web sound waves in air (and any fluid medium) are longitudinal waves because particles of the medium through which the sound is transported vibrate parallel to the direction that the sound wave moves. Web there are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: Web a longitudinal wave occurs when the disturbance moves in the same direction as the wave itself. In chapter 4 we discussed transverse waves, in particular transverse waves on a string. Also, you can clean teeth using ultrasound, knock out small cancers, and obliterate kidney stones, all using ultrasound, which is sounds at a frequency in excess of 20,000 hz. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together.PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID
Longitudinal and Transverse wave type, vector illustration scientific
Diagram Of A Longitudinal Wave
Drawing & Labeling Transverse and Longitudinal Waves YouTube
Waves Class 11 Notes, Formulas, NCERT, For NEET Leverage Edu
PPT Wave Top 12! PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2622129
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 复习笔记 3.1.1 Transverse & Longitudinal Waves翰林国际教育
Longitudinal Wave Anatomy ANATOMY STRUCTURE
Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
Web A Longitudinal Wave Is A Wave In Which The Particles Of The Medium Are Displaced In A Direction Parallel To The Direction Of Energy Transport.
Web Longitudinal Waves Are Waves Where The Motion Of The Material In The Wave Is Back And Forth In The Same Direction That The Wave Moves.
Web In A Longitudinal Wave, The Displacement Of The Particle Is Parallel To The Direction Of The Wave Propagation.
Web What A Longitudinal Wave Is, Its Compressions And Rarefactions And What A P Wave Is.
Related Post: