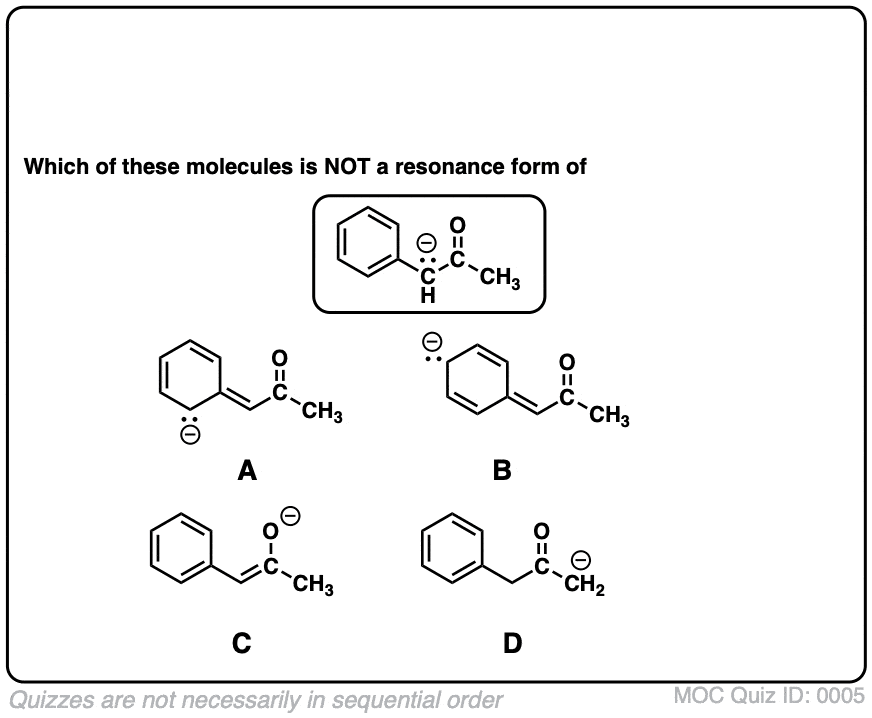
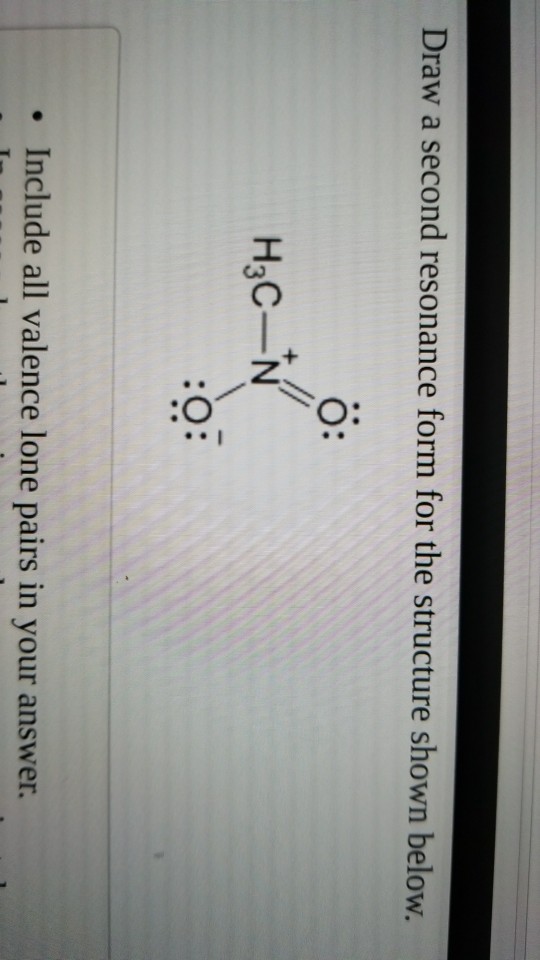
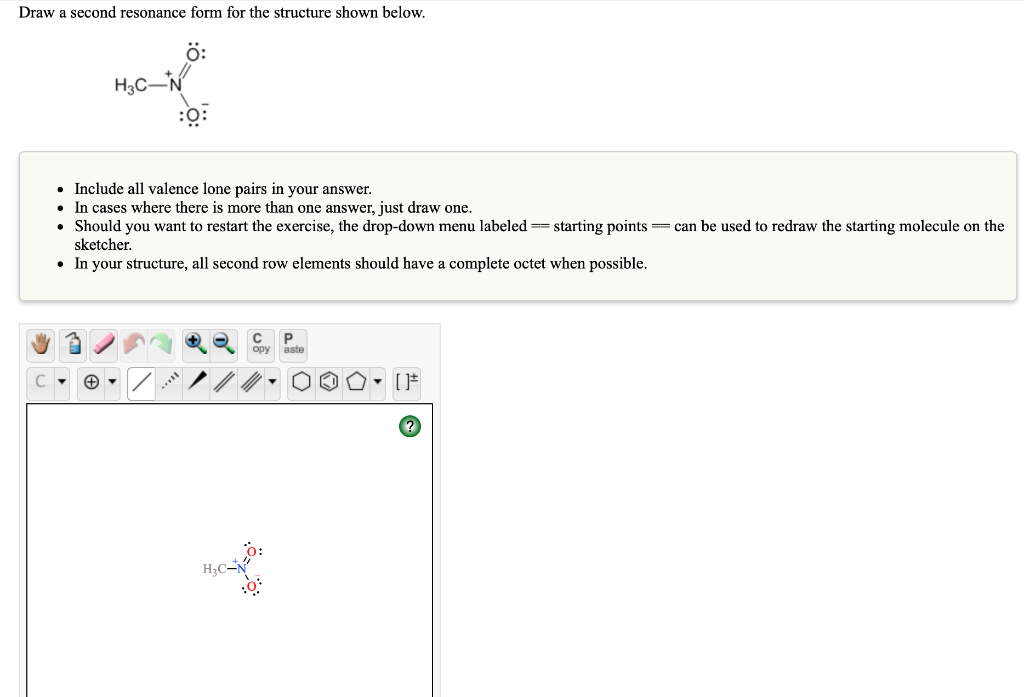
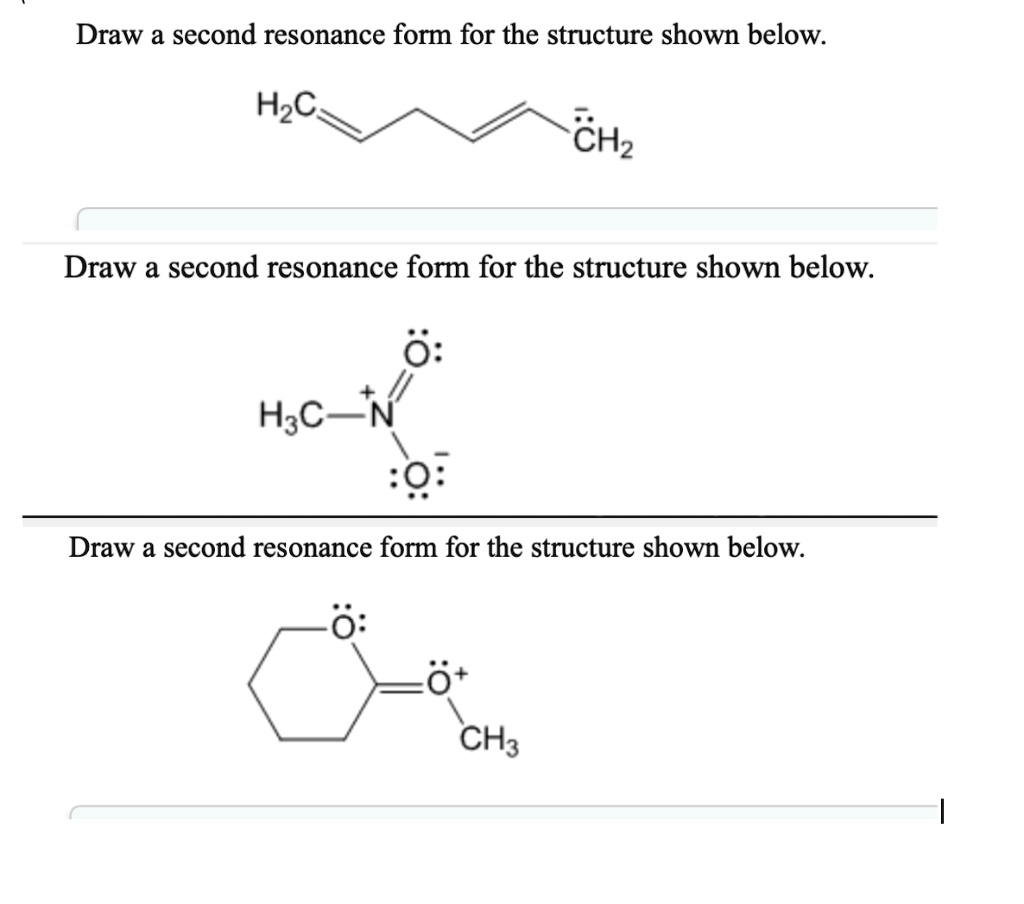
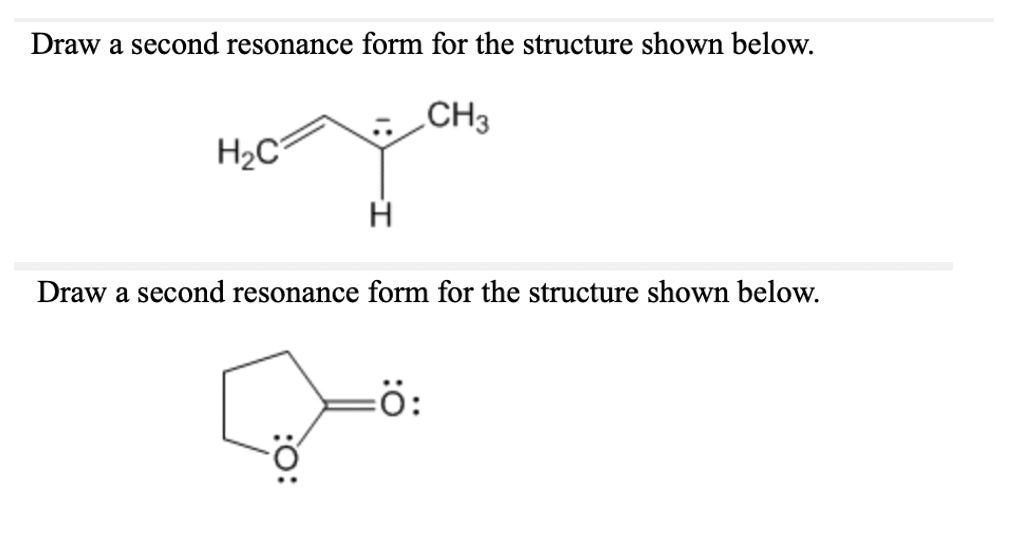
Draw A Second Resonance Form For The Structure Shown Below
Draw A Second Resonance Form For The Structure Shown Below - A negative charge will be formed when this lone pair arrives here. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. We can convert one resonance form into another by showing the movement of electrons between bonds and lone pairs (or vice versa). H3c nh2 your solution’s ready to go! Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. If you've ever had a negative charge next to a double bond, i don't think you should. Draw the lewis structure & resonance. Explain why your contributor is the major one. Web a resonance form is another way of drawing a lewis dot structure for a given compound. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: Web draw the major resonance contributor of the structure below. We need to match each linear system with a face plane direction. Web first, we need to identify the atoms that can move their electrons to form a double bond or a lone pair. I can do this pattern for residents. In the first question, the dash is equal to 2225 times of the s vector. H3c nh2 your solution’s ready to go! Web the second resonance structure of ozone is very similar, as it has one positively charged oxygen, one negatively charged oxygen, and one neutral oxygen with two bonds again. Web indicate whether the pair of structures shown represent stereoisomers, constitutional isomers, different H ch3 h3c n ch3 • include all valence lone pairs in your answer. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. Web a resonance form is another way of drawing a lewis dot structure for a given compound. Move one of the lone pairs from the neighboring atom to form a double bond with the atom that initially had a double bond. Explain why your contributor is the major one. Equivalent lewis structures are called resonance forms. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. • in cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. We can convert one resonance form into another by showing the movement of electrons between bonds and lone pairs (or vice versa). The lone pair will form a negative Web draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. Web first, we need to identify the atoms that can move their electrons to form a double bond or a lone pair. Web draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. Ö+ ch3 draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. This is. Web draw the major resonance contributor of the structure below. This is what the system looks like. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. I hopped the neighboring double bond onto the carbon and turned it into a double bond. We just need a graphical tool to do it. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. Ö+ ch3 draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: We can see the resonal structure here. We need to. We need to match each linear system with a face plane direction. Web identify the positions of the atoms and the location of the pi bonds and lone pairs in the given structure to determine which electrons can be delocalized in creating a new resonance form. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds. We can say that this is a compound here, or this is a double bond oxygen, or this is a lone pair. This is where we can see the structure. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. They are used when there. Web identify the positions of the atoms and the location of the pi bonds and lone pairs in the given structure to determine which electrons can be delocalized in creating a new resonance form. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. Here we can say the resonance Web a resonance form is another way. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. We will try to find out what our equation is. We can convert one resonance form into another by showing the movement of electrons between bonds and lone pairs (or vice versa). Web identify the positions of the atoms and the location of the pi bonds and. Web introducing curved arrows, a tool for showing the movement of electrons between resonance structures. I can do this pattern for residents. However, in this structure, the right oxygen atom has the negative charge and the left oxygen atom is neutral. Ö+ ch3 draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. If we see that compound, we can. Explain why your contributor is the major one. • in cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. If we see that compound, which is here, we can say that this is a thing here here, or this is the oxygen here, and this is a long pair like this,… We can see the resonal structure here.. Web draw the major resonance contributor of the structure below. If we see that compound, which is here, we can say that this is a thing here here, or this is the oxygen here, and this is a long pair like this,… I hopped the neighboring double bond onto the carbon and turned it into a double bond. Web draw. The lone pair will form a negative Web draw the major resonance contributor of the structure below. Web indicate whether the pair of structures shown represent stereoisomers, constitutional isomers, different Here we can say the resonance In the first question, the dash is equal to 2225 times of the s vector. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: However, in this structure, the right oxygen atom has the negative charge and the left oxygen atom is neutral. We will try to find out what our equation is. Ö+ ch3 draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Use the concept of resonance to explain structural features of molecules and ions. If you've ever had a negative charge next to a double bond, i don't think you should. We can see the resonal structure here. This is where we can see the structure. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization.Resonance Structures Practice Master Organic Chemistry
Solved Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown
[Solved] Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below. H
Solved Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown
Solved Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown
SOLVEDDraw a second resonance form for the structure shown below 0
SOLVED Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below H3C
SOLVED Draw a second resonance form for the structure shown below CH3
[Solved] Draw a second resonance form for the structures shown below
Resonance Structures Easy Hard Science
Equivalent Lewis Structures Are Called Resonance Forms.
Use The Concept Of Resonance To Explain Structural Features Of Molecules And Ions.
I Can Do This Pattern For Residents.
Add Only The Lone Pairs Found On All Resonance Structures.
Related Post: