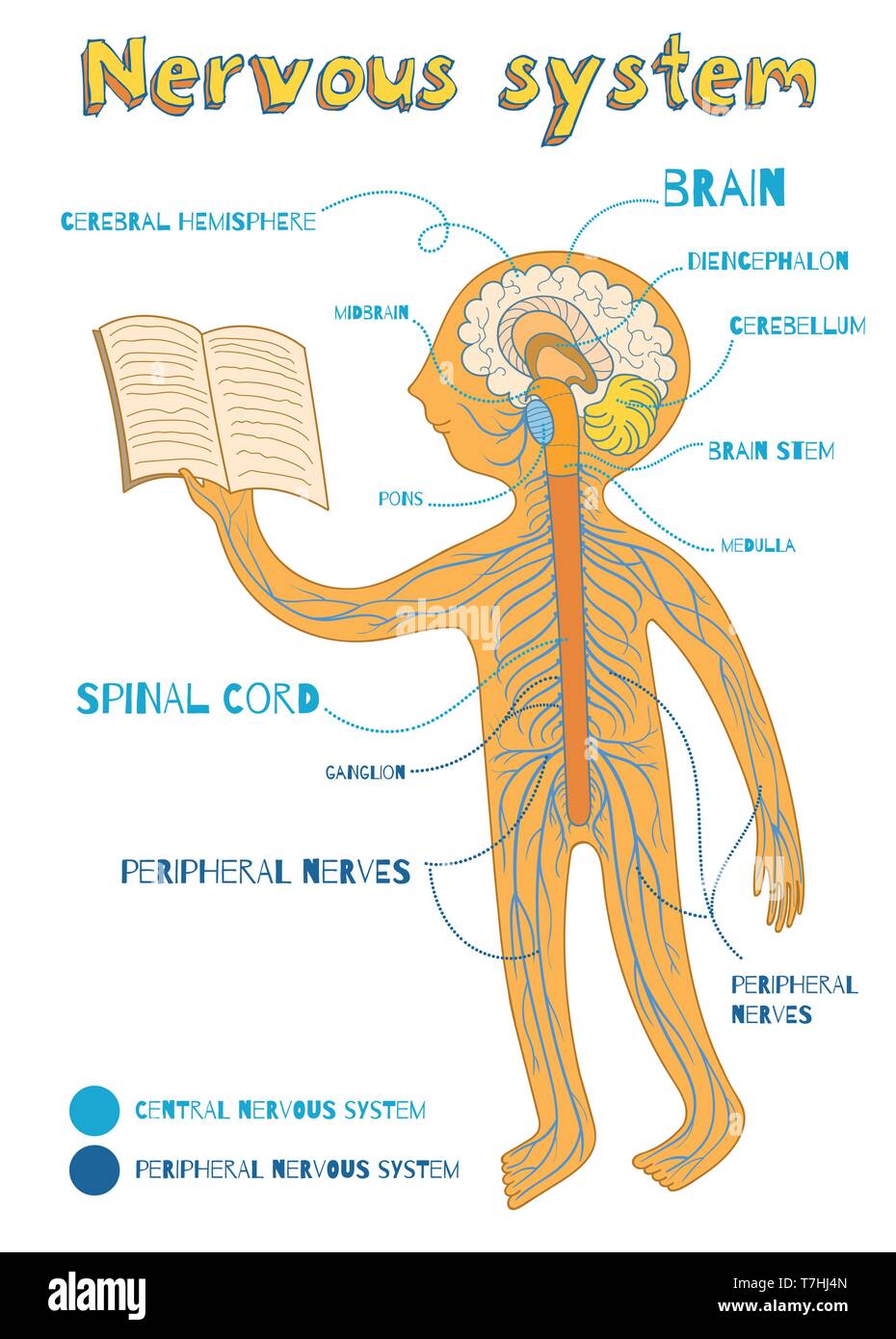
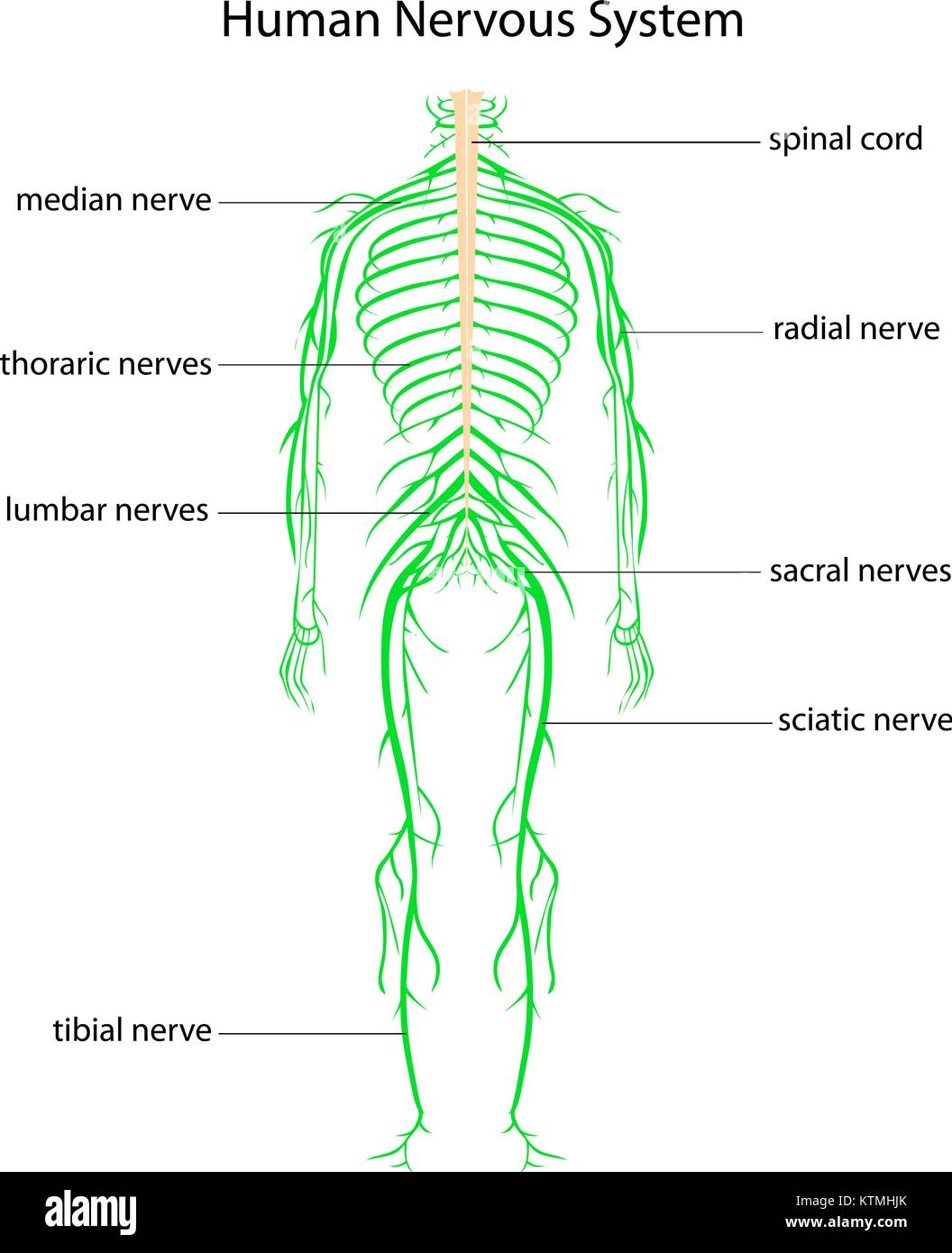
Draw The Nervous System
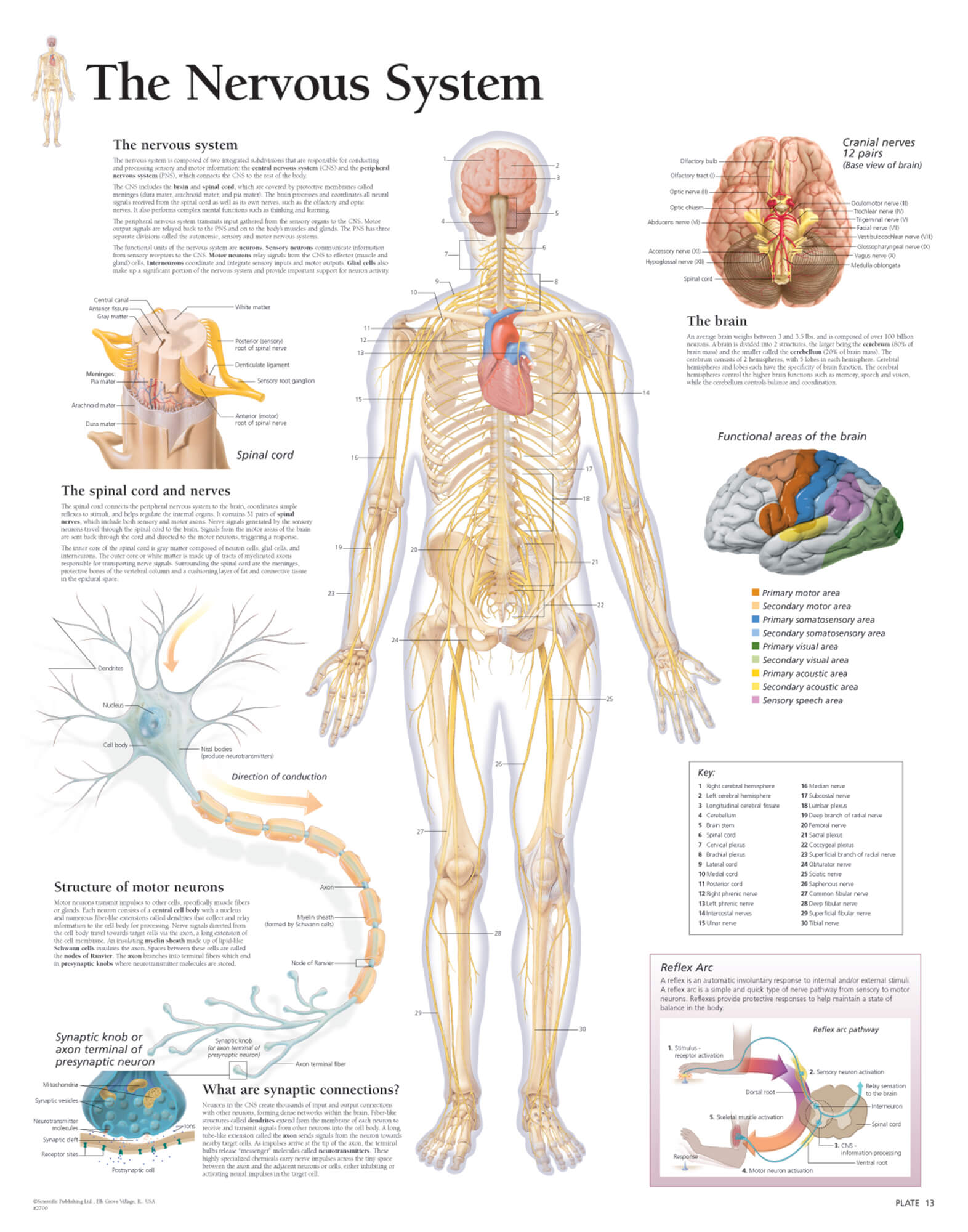
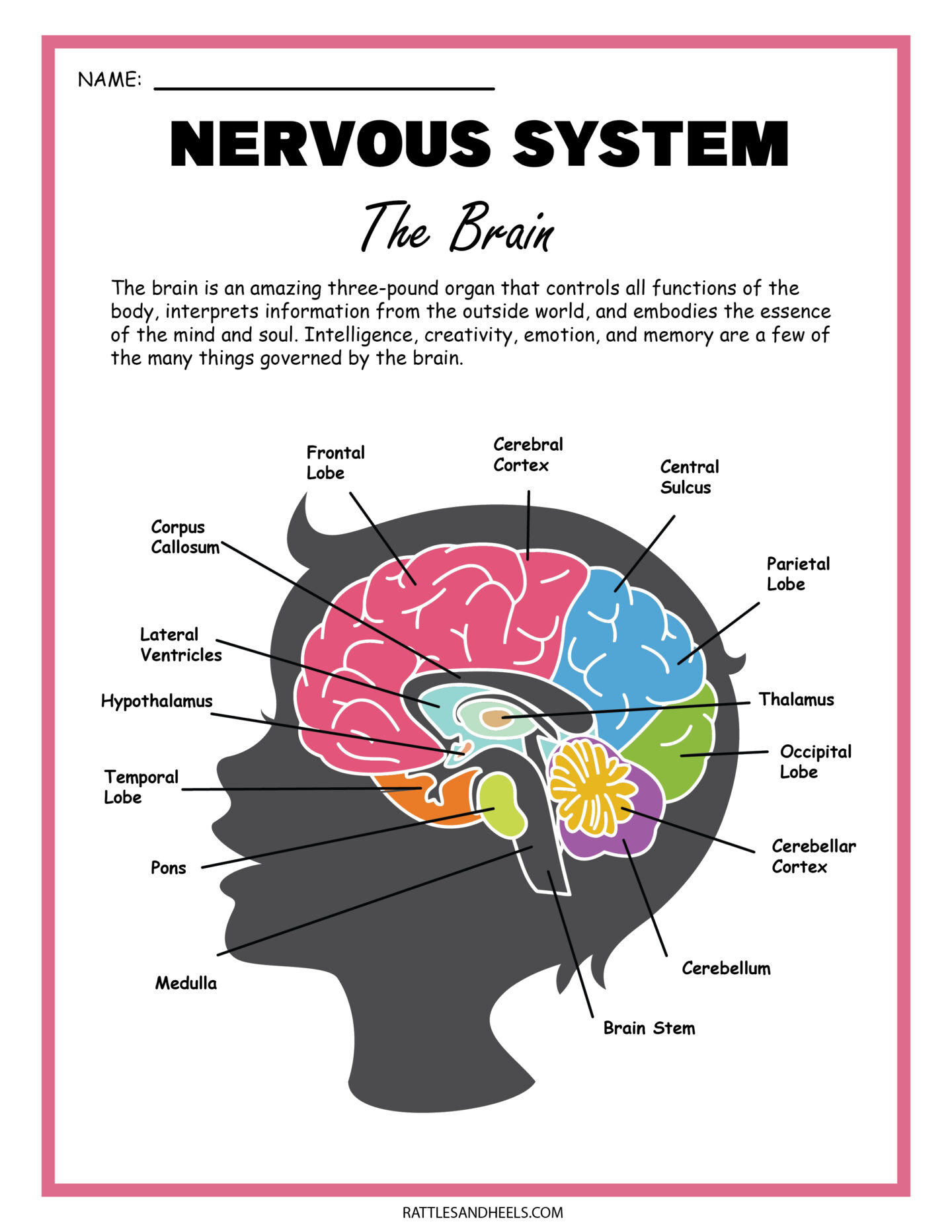
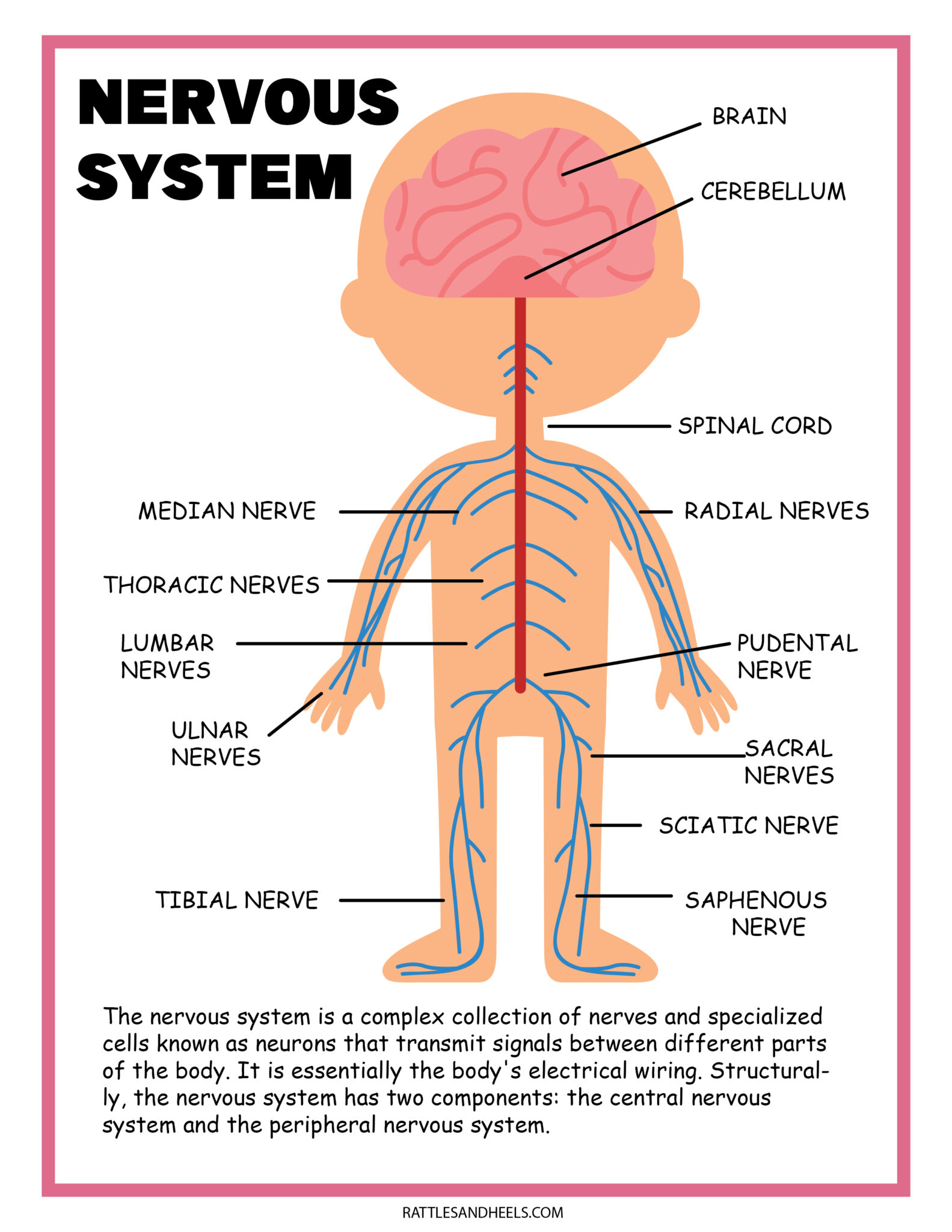
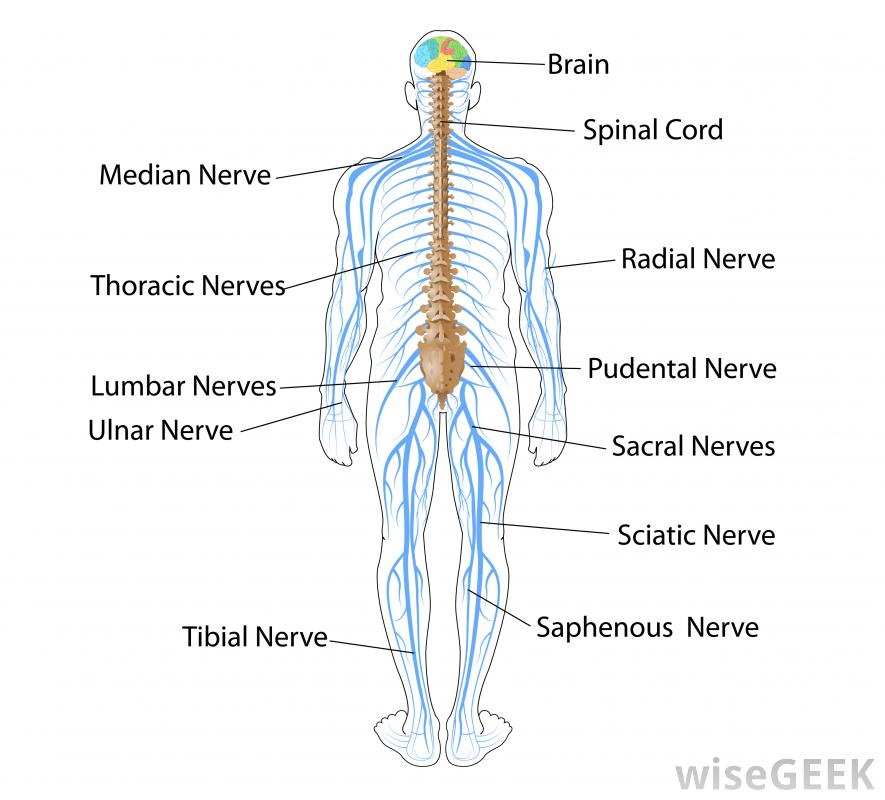
Draw The Nervous System - So in order to understand why a myelinated axon propagates a signal faster than an umyelinated axon you have to understand that passive current flow (electrotonic spread or electrotonic potential) travels much faster than a propagation of action potentials. Relate the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures of the nervous system to the structure of neurons. The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is. The central and peripheral nervous systems. Neurons are the information processing units of the brain responsible for sending, receiving, and transmitting electrochemical signals. It generates, modulates and transmits information in the human body. Web the nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. Web neurons (nerve cells): Web neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. Identify the anatomical and functional divisions of the nervous system. Neurons are information carrier cells within the central nervous system (cns) and peripheral nervous system (pns). So in order to understand why a myelinated axon propagates a signal faster than an umyelinated axon you have to understand that passive current flow (electrotonic spread or electrotonic potential) travels much faster than a propagation of action potentials. There are three main categories of neurons: Neuron, glia, ganglion, nerve, gray matter, tract, white matter, sensory neuron, motor neuron. Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. Glia are also essential to nervous system function, but they work mostly by supporting the neurons. Web the nervous system consists of the central and the peripheral nervous system. Web the brain is the command center that controls the nervous system. The central nervous system (cns) is the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (pns) is everything else ( [link] ). Web neurons can send more than 100 signals a second! Web neurons can send more than 100 signals a second! Web the nervous system can be divided into two major regions: At the end of this unit, you should be able to: Web the nervous system has two major parts: Web neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. Web the brain is the command center that controls the nervous system. Thoughts, memory, learning and feelings. The central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). Glia are also essential to nervous system function, but they work mostly by supporting the neurons. Web the peripheral nervous system has two parts: Relate the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures of the nervous system to the structure of neurons. Web neurons (nerve cells): The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is. Put simply, the cns is the supreme command center of the body. Neurons are information carrier cells within the central nervous. The central and peripheral nervous systems. The central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. The central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, made up of nerves. The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is. Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. Cranial nerves originate from the brainstem, predominantly innervating the head and neck region. Web the nervous system can be divided into two major regions: Web the nervous system in a human is made of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs and. Relate the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures of the nervous system to the structure of neurons. Web the nervous system is the human organ system that coordinates all of the body's voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical signals to and from different parts of the body. Web the human nervous system controls all. Put simply, the cns is the supreme command center of the body. The motor ( efferent) branch of the pns carries signals away from the cns to the effector organs. Web the nervous system is the human organ system that coordinates all of the body's voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical signals to and from different parts of the. The central nervous system (cns) is the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (pns) is everything else ( figure 12.2 ). It generates, modulates and transmits information in the human body. Describe the structure of the following: Web neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which. Describe the structure of the following: Web the nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. Web your nervous system’s main function is to send messages from various parts of your body to your brain, and from your brain back out to your body to tell your body what to. Neurons are the information processing units of the brain responsible for sending, receiving, and transmitting electrochemical signals. It generates, modulates and transmits information in the human body. The central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). Neurons are information carrier cells within the central nervous system (cns) and peripheral nervous system (pns). Cranial nerves originate from the brainstem,. The central nervous system (cns) is the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (pns) is everything else ( [link] ). Web the nervous system can be divided into two major regions: Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. Web in biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory. Web the nervous system can be divided into two major regions: Web the nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. So in order to understand why a myelinated axon propagates a signal faster than an umyelinated axon you have to understand that passive current flow (electrotonic spread or electrotonic. Thoughts, memory, learning and feelings. Neuron, glia, ganglion, nerve, gray matter, tract, white matter, sensory neuron, motor neuron. When people damage different parts of the brain, they may notice changes in their personality, movement, vision, sleep, and. The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is. The central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Web the nervous system has two major parts: Web the nervous system is the human organ system that coordinates all of the body's voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical signals to and from different parts of the body. Describe the structure of the following: Glia are also essential to nervous system function, but they work mostly by supporting the neurons. Web the peripheral nervous system has two parts: Neurons are the information processing units of the brain responsible for sending, receiving, and transmitting electrochemical signals. Web your nervous system’s main function is to send messages from various parts of your body to your brain, and from your brain back out to your body to tell your body what to do. Web neurons (nerve cells): Web the human nervous system controls all activities of the body in a quicker fashion. Web the nervous system can be divided into two major regions:The Nervous System Scientific Publishing
Human Nervous System Structure and Functions Explained With Diagrams
Draw The Nervous System
Free Science Worksheets The Nervous System Adanna Dill
Components of the Nervous System Biology for Majors II
Nervous System Body systems
Human nervous system for kids. Vector color cartoon illustration. Human
How to draw the Human Nervous System YouTube
Central Nervous System Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Illustration of human nervous system with labels Stock Vector Image
Identify The Anatomical And Functional Divisions Of The Nervous System.
Web The Peripheral Nervous System Consists Of 12 Pairs Of Cranial Nerves, 31 Pairs Of Spinal Nerves, And All Their Branches.
Describe The Organization Of The Nervous System And Explain The Functions Of Its Principal Components.
Download A Free Printable Outline Of This Video And Draw Along With Us.
Related Post: