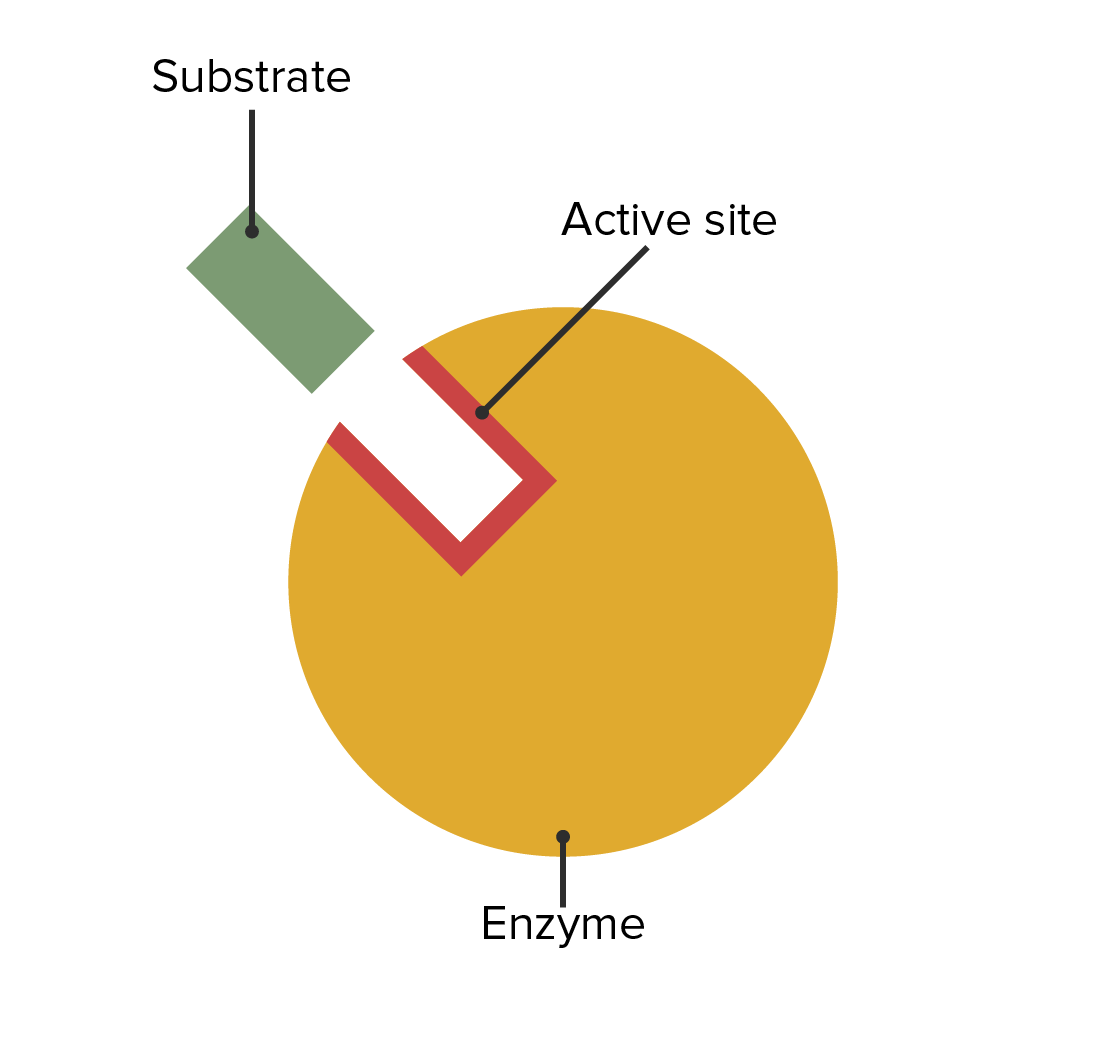
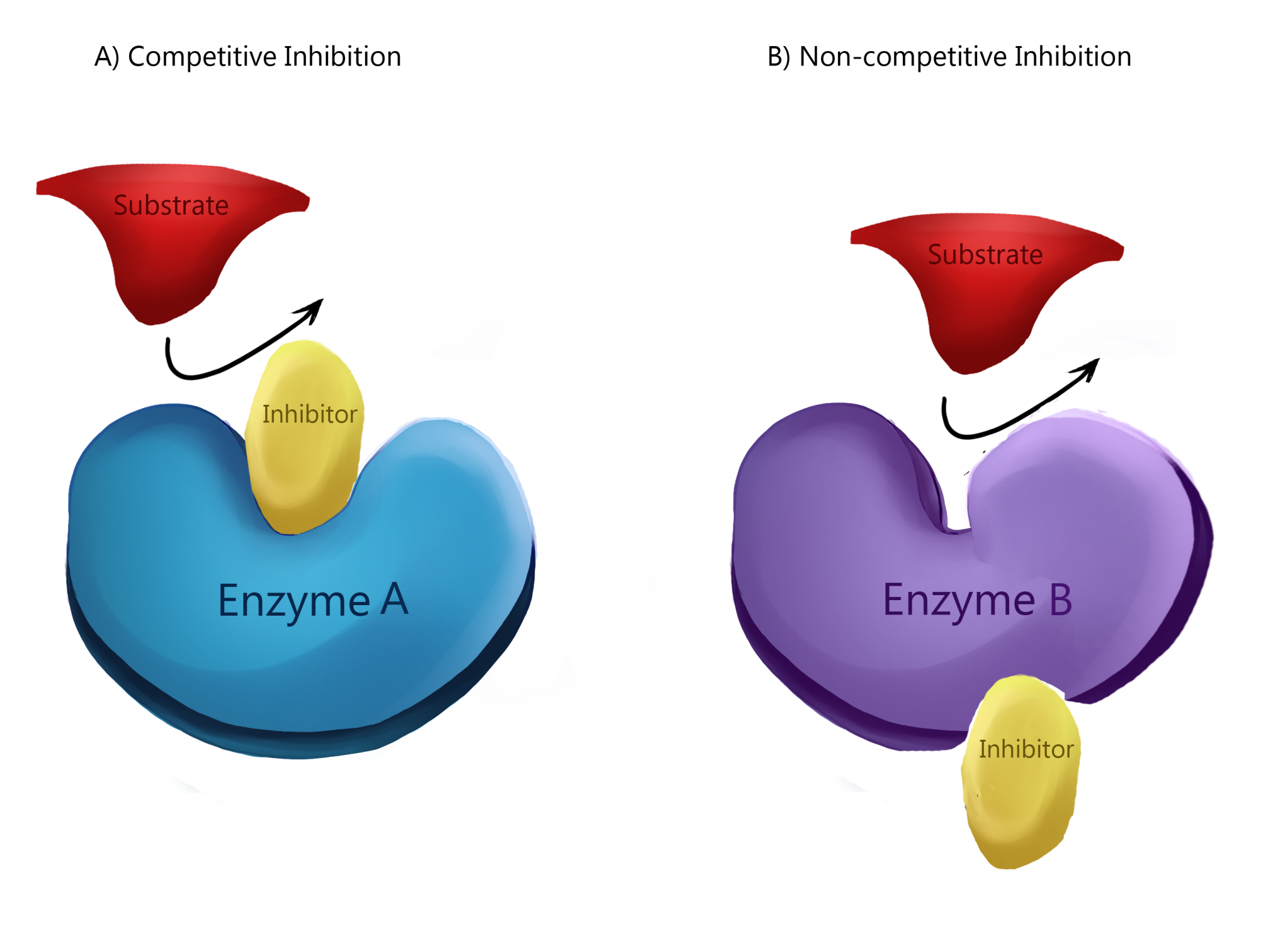
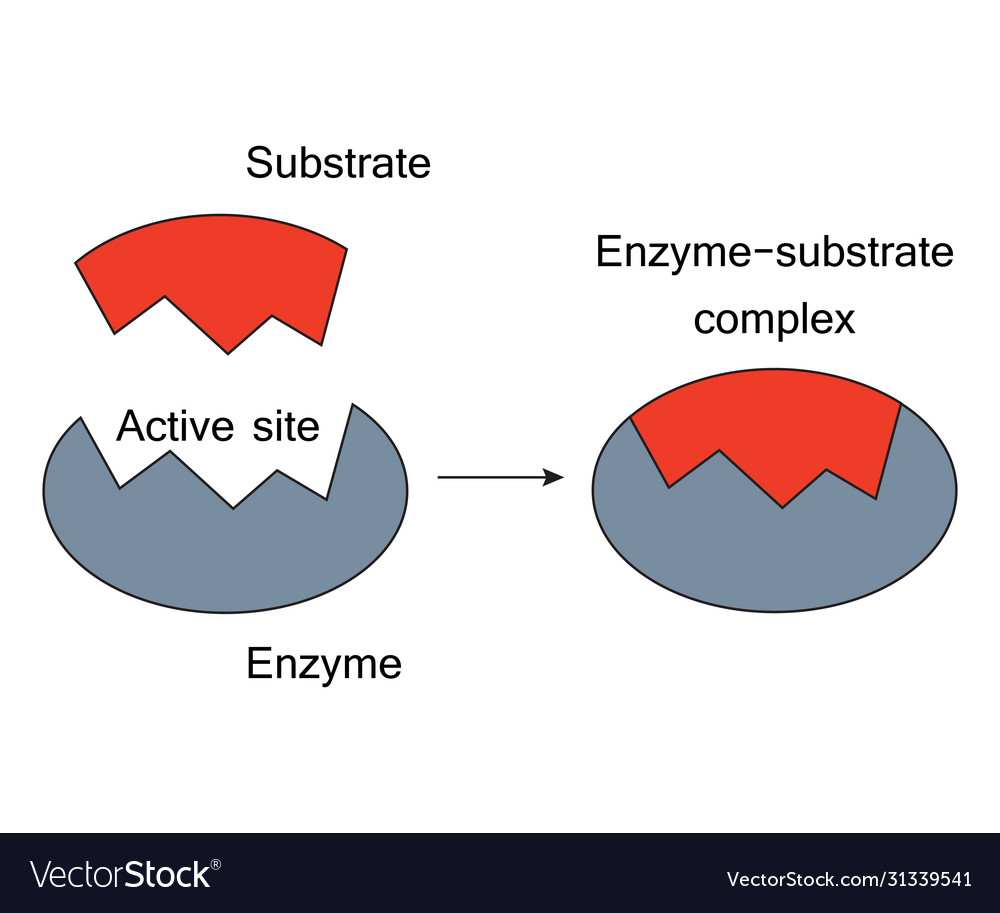
Drawing Of An Enzyme
Drawing Of An Enzyme - Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. Enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. Web enzymes can be described at four levels: Some situations have more than one substrate molecule that the enzyme will change. We will see that enzymes employ various chemical strategies to increase the rates of reactions, in addition to physical ones like reactant proximity and the introduction of strain. Web what are enzymes? Enzymes can be used multiple times and are affected by factors such as temperature and ph. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. Web enzymes bring reactants together so they don’t have to expend energy moving about until they collide at random. Some enzymes reduce the activation energy to such low levels that they actually reverse cellular reactions. Web what are enzymes? We will see that enzymes employ various chemical strategies to increase the rates of reactions, in addition to physical ones like reactant proximity and the introduction of strain. Web enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. Web describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. The enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. Web an enzymes is a protein that facilitates a cellular metabolic process by lowering activation energy (ea) levels in order to catalyze the chemical reactions between biomolecules. They can also be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. For example, they perform a necessary function for metabolism, the process of breaking down food and drink into energy. The active site is where substrates bind to the enzyme. Enzymes are usually proteins, though some ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules act as enzymes too. They can also be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. Web enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes can be used multiple times and are affected by factors such as temperature and ph. Web basic enzyme kinetics graphs. Web enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. Web four steps of enzyme action 1. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Web enzyme activity can be analyzed quantitatively. The catalysts for biochemical reactions that happen in living organisms are called enzymes. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. Web enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions without itself being altered in the process.. Web enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. Web enzyme activity can be analyzed quantitatively. In most cases, the forces that hold the substrate in the active site of the enzyme are noncovalent, an assortment of hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Web enzymes can be regulated in ways that either promote or reduce their activity. For example, they perform a necessary function for metabolism, the process of breaking down food and drink into energy. Web enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions. Web an enzymes is a protein that facilitates a cellular metabolic process by lowering activation energy (ea) levels in order to catalyze the chemical reactions between biomolecules. Web enzymes can be described at four levels: The single most important property of enzymes is the ability to increase the rates of reactions occurring in living organisms, a property known as catalytic. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. Web what are enzymes? In most cases, the forces that hold the substrate in the active site of the enzyme are noncovalent, an assortment of hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. Graphs. The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active site. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. They are usually proteins, though some rna molecules act as enzymes too. Web to describe how ph, temperature, and the concentration of an enzyme and its substrate influence enzyme activity. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Web enzymes help with the chemical reactions that keep a person alive and well. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. The primary structure of an enzyme is the linear sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain(s), which are linked by peptide bonds. Enzymes bind both reactant molecules (called the substrate), tightly and specifically, at a site on the enzyme molecule called the active site (figurebelow). The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. Web enzymes help with the chemical reactions that keep a person alive and well. Induced fit occurs when the enzyme changes shape to better accommodate substrates, facilitating the reaction. The primary structure of an enzyme is the linear sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain(s), which are linked by peptide bonds. An. Web basic enzyme kinetics graphs. The enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. The catalysts for biochemical reactions that happen in living organisms are called enzymes. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Enzymes can be used multiple times and are affected by factors such as temperature and ph. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. The catalysts for biochemical reactions that happen in living organisms are called enzymes. Web to describe the interaction between an enzyme and its substrate. The area in which bonds of the reactant(s) are broken is known as the active site. Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Enzymes are very, very specific. Web enzymes bring reactants together so they don’t have to expend energy moving about until they collide at random. Enzymes bind both reactant molecules (called the substrate), tightly and specifically, at a site on the enzyme molecule called the active site (figurebelow). To do its work, an enzyme must unite — even if ever so briefly — with at least one of the reactants. The primary structure of an enzyme is the linear sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain(s), which are linked by peptide bonds. Web in this section, we will explore chemical and physical factors that speed up reactions, and begin to relate these effects to reactions catalyzed by enzymes. We will see that enzymes employ various chemical strategies to increase the rates of reactions, in addition to physical ones like reactant proximity and the introduction of strain. The enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. Web enzymes can be described at four levels: Web enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions.Enzyme
Enzyme & Their Substrates Mode of Action Plantlet
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki
Structure and Function of an Enzyme
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions
Basics of Enzymes Concise Medical Knowledge
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions
Enzymes AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io
Enzyme vector illustration Full labeled cycle and diagram with
What is the substrate of an enzyme
Enzymes Can Be Used Multiple Times And Are Affected By Factors Such As Temperature And Ph.
They Are Usually Proteins, Though Some Rna Molecules Act As Enzymes Too.
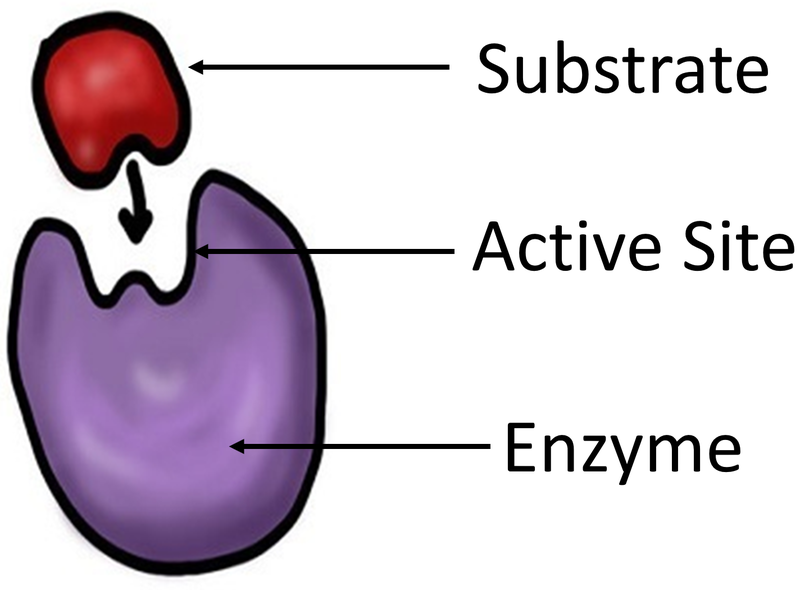
The Enzyme Grabs On To The Substrate At A Special Area Called The Active Site.
An Enzyme Is A Protein Biomolecule That Acts As A Biocatalyst By Regulating The Rate Of Various Metabolic Reactions Without Itself Being Altered In The Process.
Related Post:
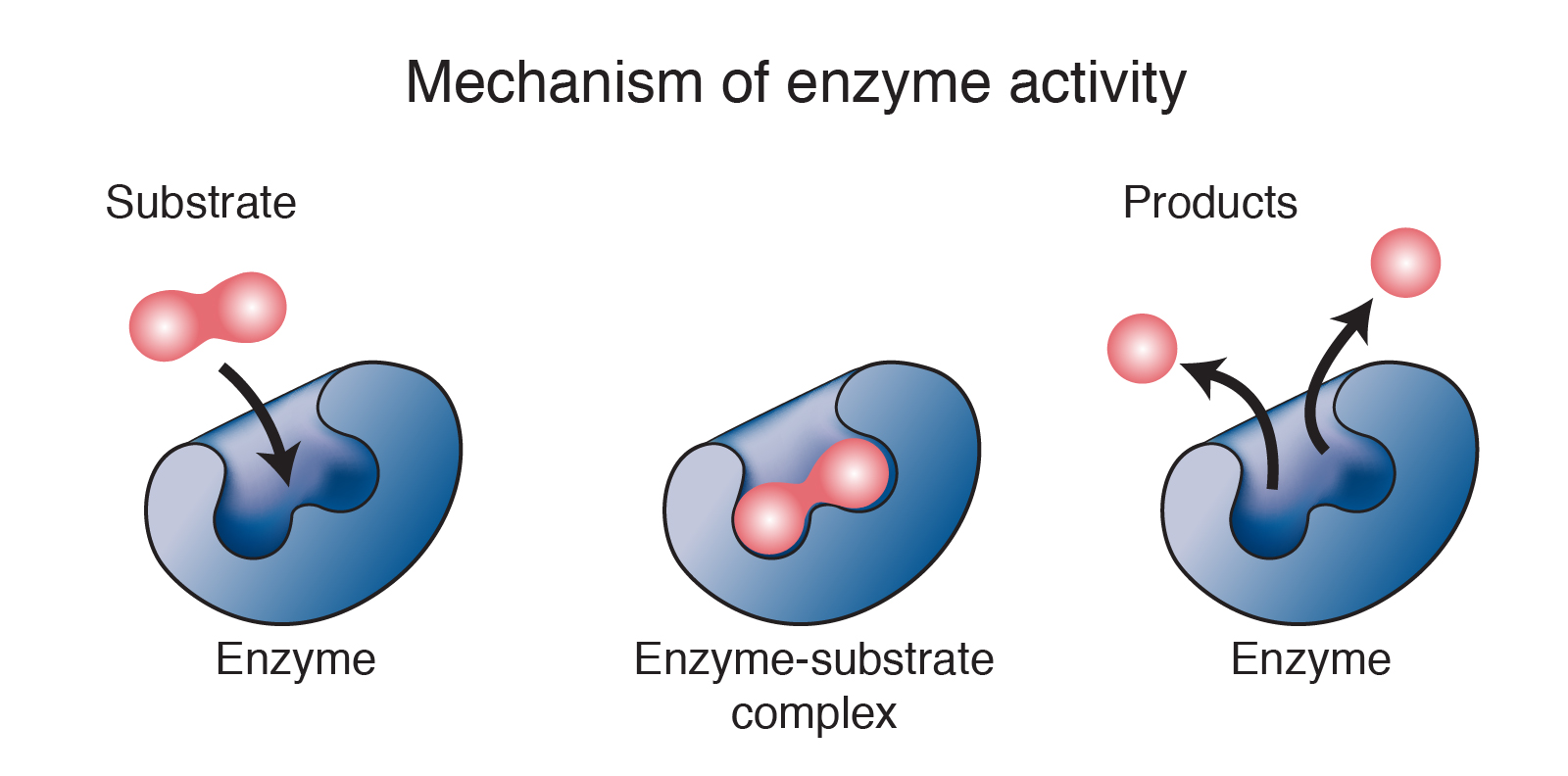

/what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)