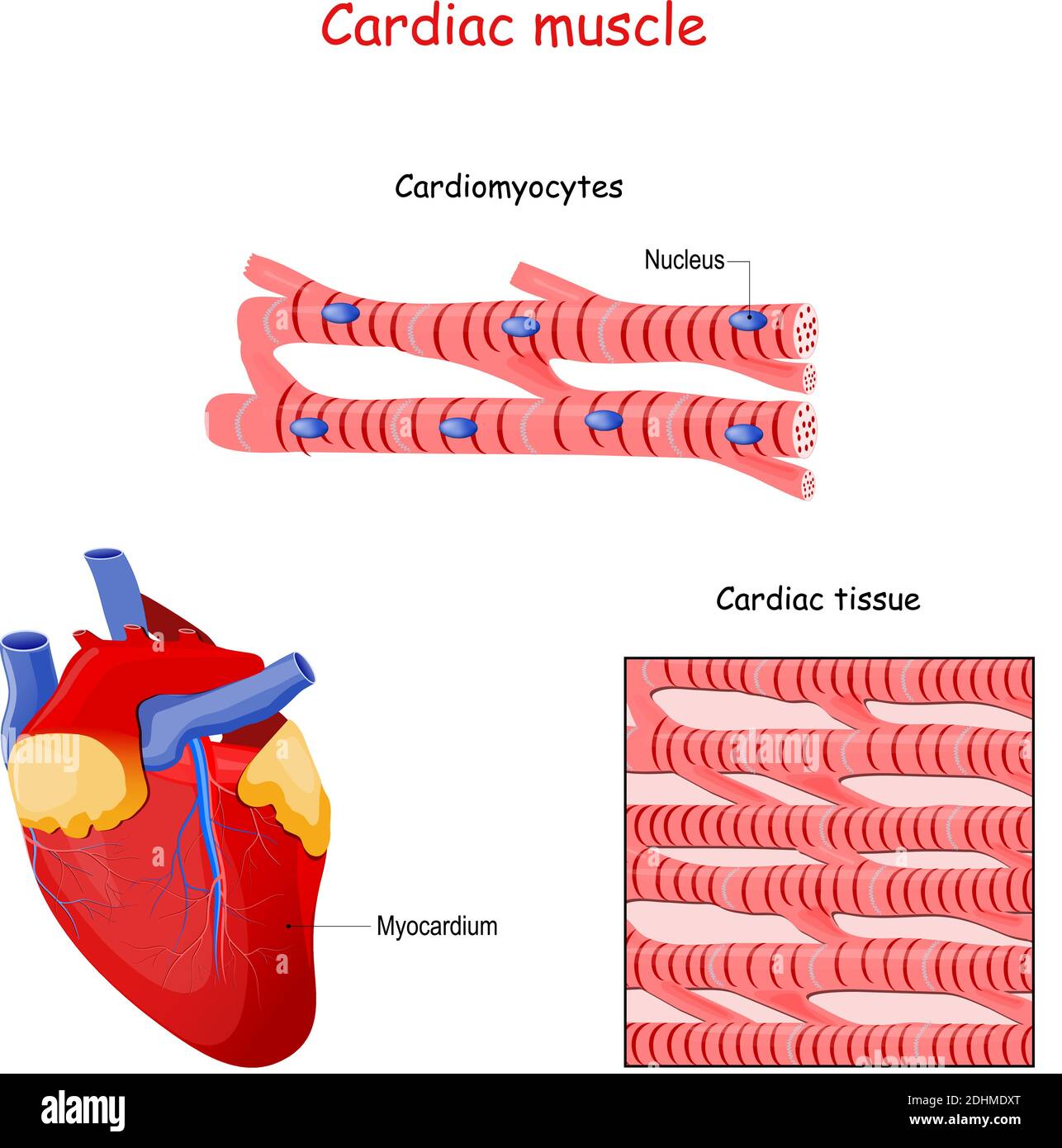
Drawing Of Cardiac Muscle
Drawing Of Cardiac Muscle - Web cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. Web cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. It is responsible for keeping the heart pumping and blood circulating. These inner and outer layers of. The outermost layer protects the heart and reduces. Web cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. The other two types are skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical impulses through the heart; The rhythmic contraction of cardiac. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass. The outermost layer protects the heart and reduces. Web cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. Web cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart. You will find some unique features in cardiac muscle. Web cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. Learn this topic now at kenhub! The middle layer, composed of muscle tissue that enables heart contractions. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Web cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. The myocardium is the muscular middle layer of the heart wall that contains the cardiac muscle tissue. It is responsible for keeping the heart pumping and blood circulating. Learn this topic now at kenhub! Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical impulses through the heart; Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. Web for instance, the risk of major complications during lateral trans iliac (lti) si joint fusion (cpt code 27279) is lower than the risks associated with other obl. Web cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. Web the cardiac muscle under a microscope shows a short cylindrical fiber with a centrally placed oval nucleus. Web cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Web for instance, the risk of major complications during lateral trans iliac (lti) si joint fusion (cpt code 27279) is lower than the risks associated with other obl. Web review the cardiac muscle cells. Web describe the structure of cardiac muscle; Web cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. Web cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass. Web this article describes the characteristics, components. The myocardium is the muscular middle layer of the heart wall that contains the cardiac muscle tissue. The other two types are skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Learn this topic now at kenhub! Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. The myocardium is the muscular middle layer of the heart wall that contains the cardiac muscle tissue. These inner and outer layers of. Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. Web review the cardiac muscle cells which make up the myocardium portion of the heart wall in this interactive tutorial, and test yourself in. Web describe the structure of cardiac muscle; These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic nerve fibres. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass. The rhythmic contraction of cardiac. The outermost layer protects the heart and reduces. The video describes the summary of the whole topic of the muscle. Web cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. Web cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart.. Web for instance, the risk of major complications during lateral trans iliac (lti) si joint fusion (cpt code 27279) is lower than the risks associated with other obl. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Web the cardiac muscle under a microscope shows a short cylindrical fiber with a centrally placed oval. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass. The outermost layer protects the heart and reduces. Web cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart. The middle layer, composed of muscle tissue that enables heart contractions. Web cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and. Web cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic nerve fibres. The rhythmic contraction of cardiac. It is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth. The outermost layer protects the heart and. The other two types are skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Web review the cardiac muscle cells which make up the myocardium portion of the heart wall in this interactive tutorial, and test yourself in the quiz. The middle layer, composed of muscle tissue that enables heart contractions. These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic. Myocardium makes up the majority of the thickness and mass. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. The rhythmic contraction of cardiac. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Web the cardiac muscle under a microscope shows a short cylindrical fiber with a centrally placed oval nucleus. It is responsible for keeping the heart pumping and blood circulating. Web cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic nerve fibres. Web this article describes the characteristics, components and function of the cardiac muscle tissue, including clinical points. Web describe the structure of cardiac muscle; The video describes the summary of the whole topic of the muscle. The middle layer, composed of muscle tissue that enables heart contractions. Web cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart. Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical impulses through the heart; It is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth.Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
Stockvector Heart anatomy colored sketch. Anatomic human cardiac muscle
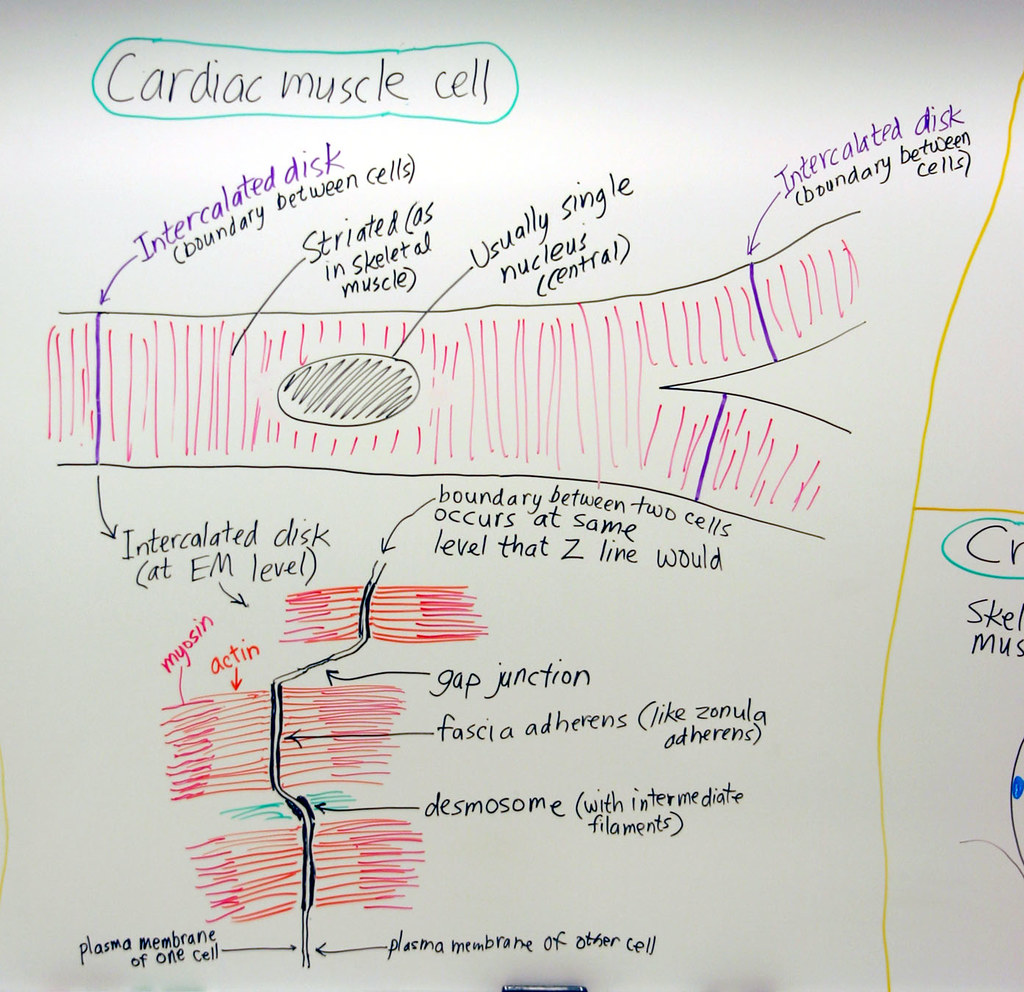
Muscle Cardiac Muscle Cell A hand drawn sketch by Dr. Chr… Flickr
Cardiac muscle fibers' structure. Heart muscle tissue, anatomy Stock
Cardiac Muscle Vector Illustration Diagram, Anatomical Scheme with
Example of a cardiac muscle
How to draw " Cardiac Muscles" step by step in a very easy way Type
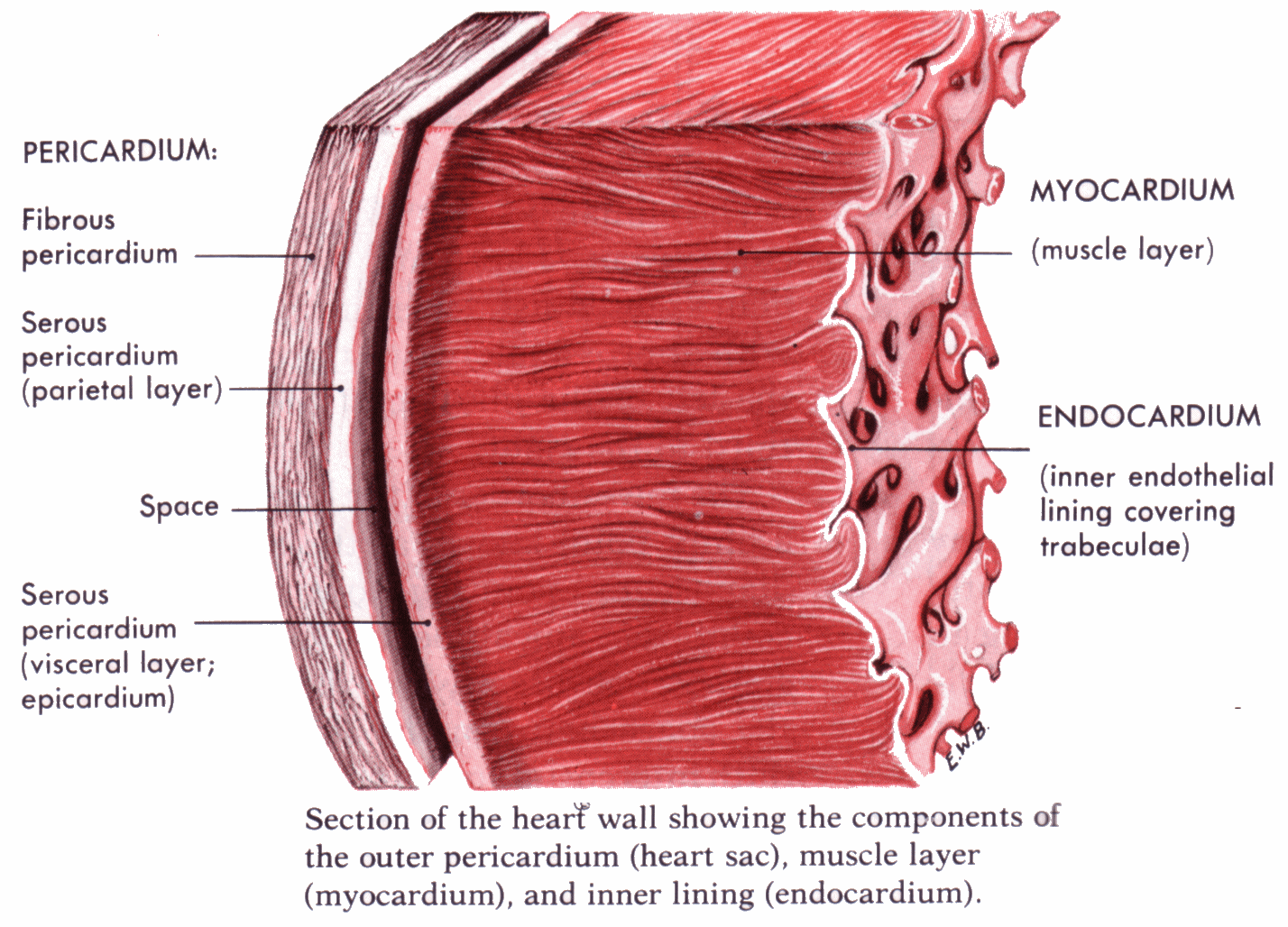
Which is the cardiac muscle layer of the heart? Socratic
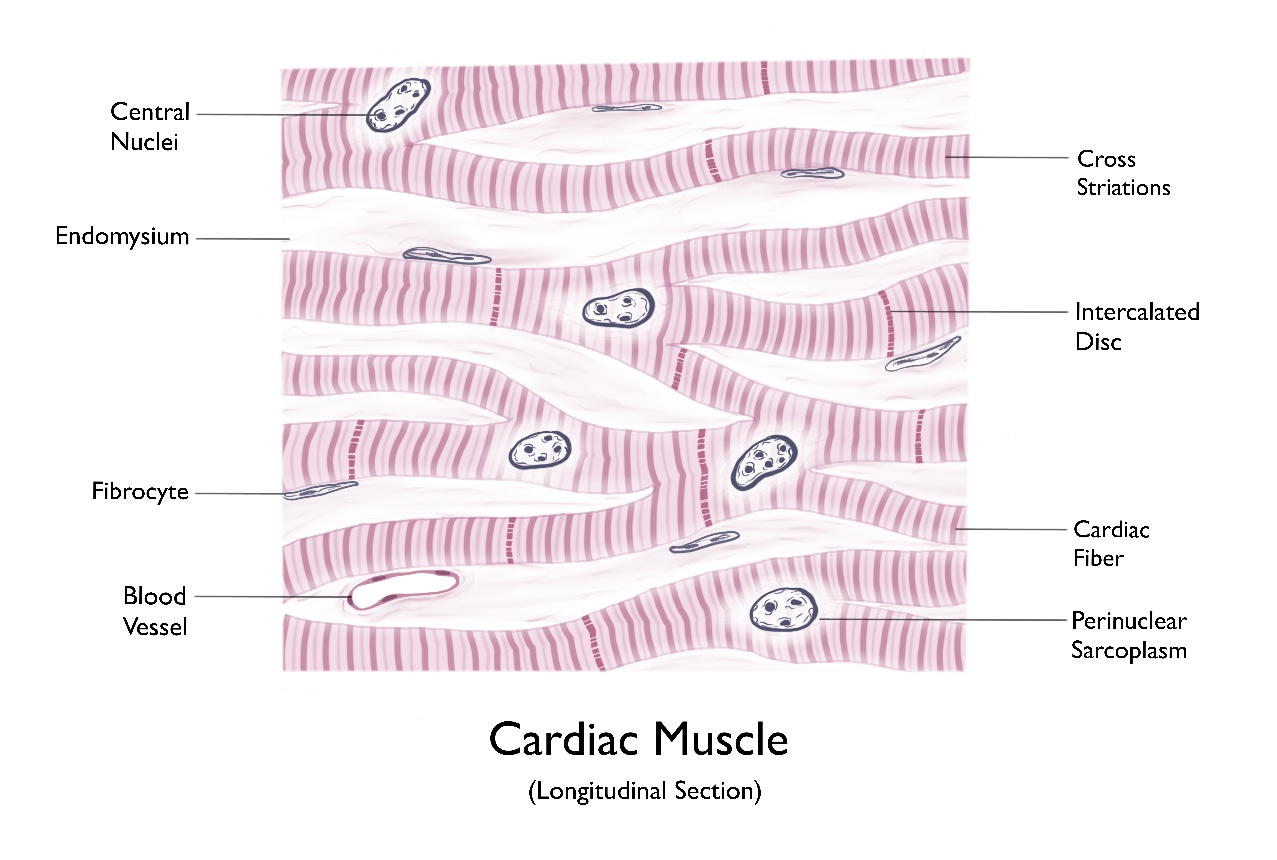
Cardiac Muscle (longitudinal section)
Cardiac Muscle Structure
Highly Coordinated Contractions Of Cardiac Muscle Pump Blood Into The Vessels Of The Circulatory System.
Web Cardiac Muscle Tissue Is One Of The Three Types Of Muscle Tissue In Your Body.
You Will Find Some Unique Features In Cardiac Muscle.
Web For Instance, The Risk Of Major Complications During Lateral Trans Iliac (Lti) Si Joint Fusion (Cpt Code 27279) Is Lower Than The Risks Associated With Other Obl.
Related Post: