Drawing Of Cations
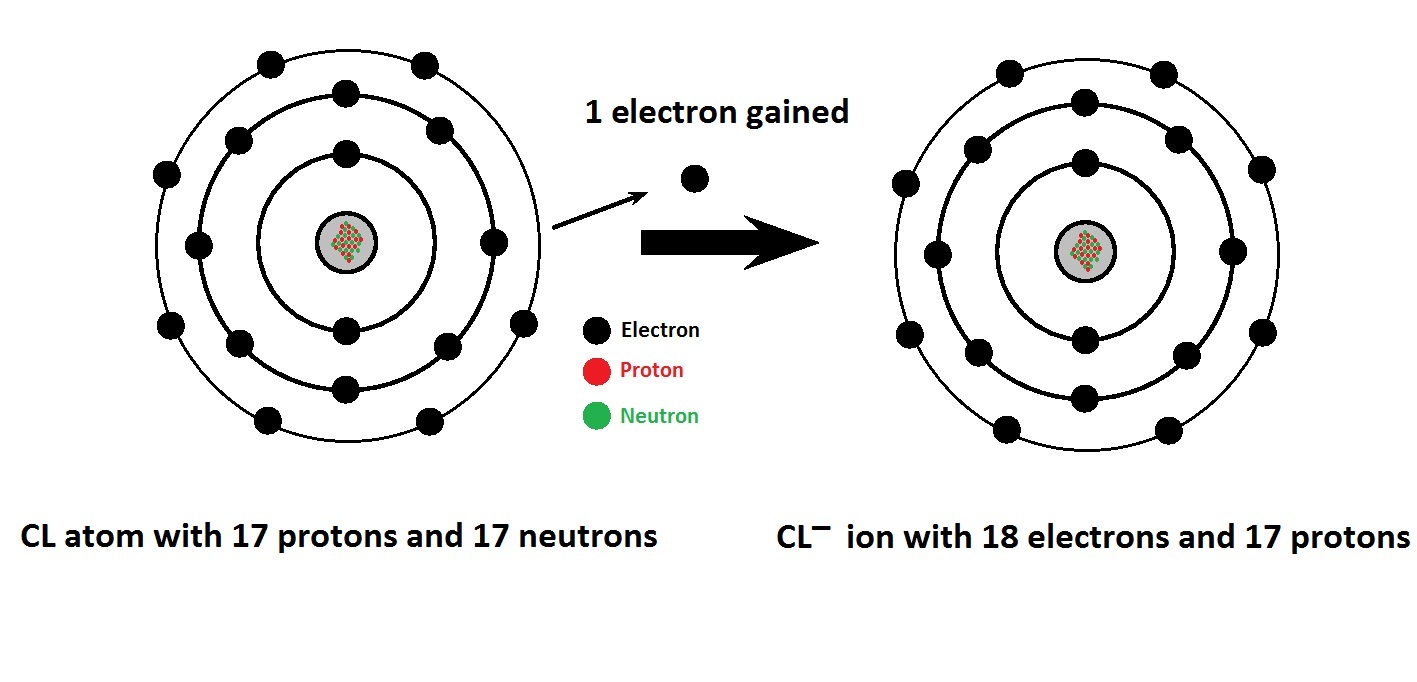
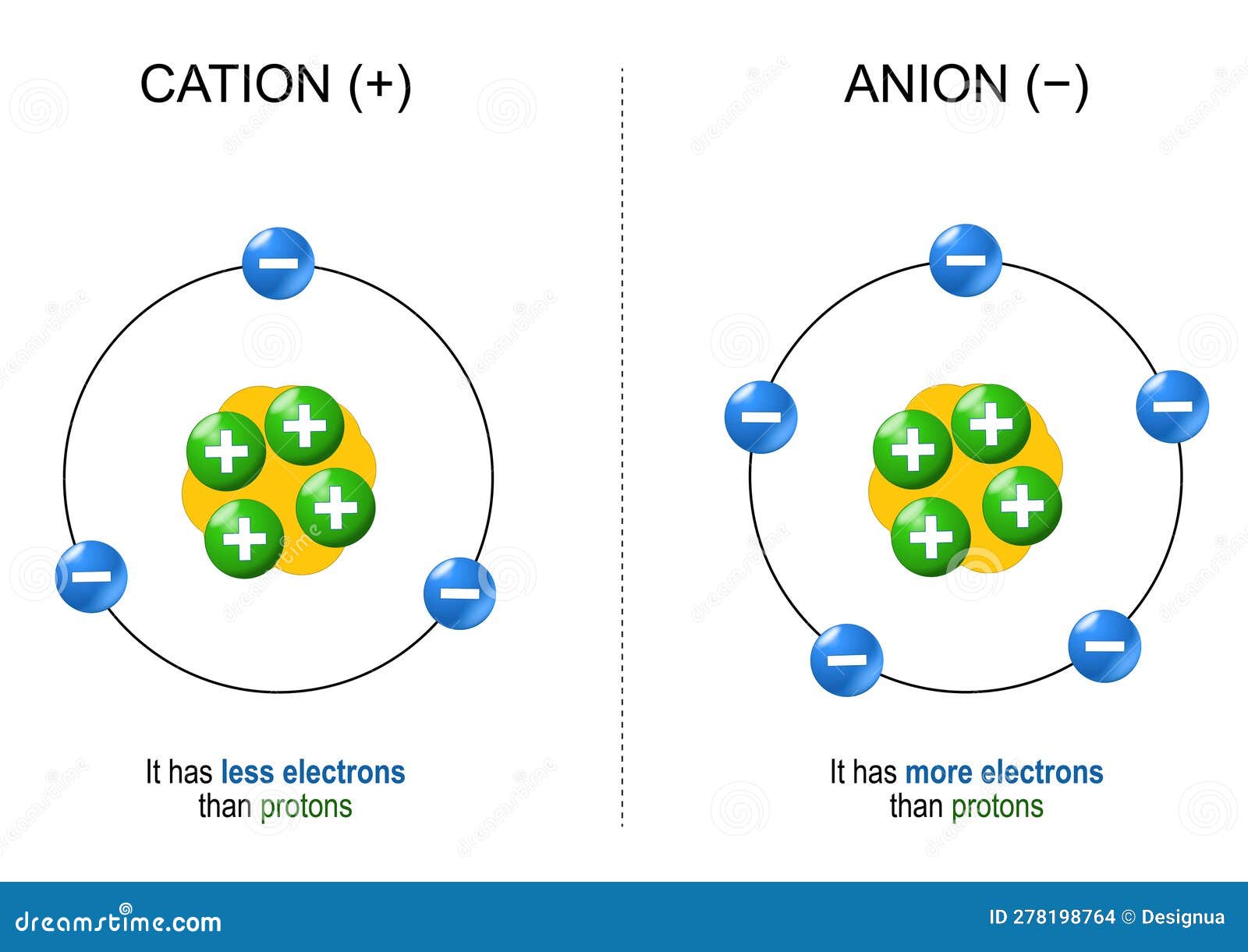
Drawing Of Cations - Web principles of the qualitative analysis of cations. Writing lewis dot symbols of elements. Explain the relative stability of methyl, primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations in terms of hyperconjugation and inductive effects. Web draw a perpendicular line toward the diamond from the sample point in the cation triangle: Web a cation is an ionic species with a positive charge. The process of finding out what compounds are contained in a sample is called. The flow of electrons b. One with a +3 charge is a. Web for cations, subtract one electron for each positive charge. The word “cation” comes from the greek word ánō, which means “up.” examples of cations include: Web draw lewis structures for ionic compounds. Web the cations (cu +1 and hg +2) fill the tetrahedral holes in two adjacent cubic cells to provide a neutral compound with the correct molecular formula (cu 2 hgi 4). The astute reader may have noticed something: The process of finding out what compounds are contained in a sample is called. Writing lewis dot symbols of elements. A negatively charged ion (an anion) has more electrons than protons. Web the purpose of this experiment is to learn the techniques to separate and identify some common cations and to understand the principles for the equilibria of precipitation and complex formation. Web cations are ions that have a positive charge. Web principles of the qualitative analysis of cations. Web the cations and anions in an ionic solid are arranged in a lattice structure that maximizes the attractive forces between opposite charges and minimizes the repulsive forces between like charges. Many of the ions that form have eight electrons in their valence shell. If you haven't mastered the art of drawing lewis structures yet, you can check out. For anions, add one electron for each negative charge. Web for cations, subtract one electron for each positive charge. Explain the relative stability of methyl, primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations in terms of hyperconjugation and inductive effects. Web principles of the qualitative analysis of cations. One with a +3 charge is a. The structure of an ionic solid can be represented using a particulate model. Web now that you've mastered the art of drawing the lewis structures of neutral covalent compounds, it's time to draw the lewis structures of polyatomic ions. The total number of electrons does not change. The process of finding out how much of a compound is contained in a sample is called quantitative analysis. The flow of electrons b. Web the cations (cu +1 and hg +2) fill the tetrahedral holes in two adjacent cubic cells to provide a neutral compound with the correct molecular formula (cu 2 hgi 4). The process of finding out. The word cation comes from the greek word kato, which means down. a cation has more protons than electrons, giving it a net positive charge. Many of the ions that form have eight electrons in their valence shell. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. The crystal structure of sodium chloride, \(\ce{nacl}\), a typical. In section 4.7, we demonstrated that ions are formed by losing electrons to make cations, or by gaining electrons to form anions. The word “cation” comes from the greek word ánō, which means “up.” examples of cations include: Web draw lewis structures for ionic compounds. The structure of an ionic solid can be represented using a particulate model. Draw a. For anions, add one electron for each negative charge. The word cation comes from the greek word kato, which means down. a cation has more protons than electrons, giving it a net positive charge. If you haven't mastered the art of drawing lewis structures yet, you can check out. A negatively charged ion (an anion) has more electrons than protons.. Web for cations, subtract one electron for each positive charge. The flow chart shown below shows the summary of the separation of common cations in. Draw a skeleton structure of the molecule or ion, arranging the atoms around a central atom. Draw a point in the intersection of the perpendicular lines: The process of finding out how much of a. Cations with multiple charges may be given special names. An atom with an electric charge is called an ion. Web a cation is an ionic species with a positive charge. The crystal structure of sodium chloride, \(\ce{nacl}\), a typical ionic compound. Web cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms. Explain the relative stability of methyl, primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations in terms of hyperconjugation and inductive effects. What is the lewis electron dot symbol for each element? Web the cations and anions in an ionic solid are arranged in a lattice structure that maximizes the attractive forces between opposite charges and minimizes the repulsive forces between like charges. Web. Web the separation of cations in groups, along with the separation of ions within a group and their confirmation tests are described in detail in later chapters. Typically, in a cell drawing the anode is shown on the left and the cathode on the right. What is the lewis electron dot symbol for each element? For example, a cation with. Web the separation of cations in groups, along with the separation of ions within a group and their confirmation tests are described in detail in later chapters. Web now that you've mastered the art of drawing the lewis structures of neutral covalent compounds, it's time to draw the lewis structures of polyatomic ions. Indicate the direction of flow for each. The trick is called “frost circles”, or, sometimes, the “polygon method”. Many of the ions that form have eight electrons in their valence shell. Web a complete guide on how to draw the molecular orbitals of the allyl cation, allyl radical, and the allyl anion, including where to put the nodes. In section 4.7, we demonstrated that ions are formed. Indicate the direction of flow for each of the following in a cell illustration where the anode was placed on the right and the cathode on the left. The trick is called “frost circles”, or, sometimes, the “polygon method”. Web the purpose of this experiment is to learn the techniques to separate and identify some common cations and to understand the principles for the equilibria of precipitation and complex formation. Typically, in a cell drawing the anode is shown on the left and the cathode on the right. Web cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms gaining electrons. In section 4.7, we demonstrated that ions are formed by losing electrons to make cations, or by gaining electrons to form anions. The process of finding out how much of a compound is contained in a sample is called quantitative analysis. One with a +3 charge is a. Web draw a perpendicular line toward the diamond from the sample point in the cation triangle: Web the cations and anions in an ionic solid are arranged in a lattice structure that maximizes the attractive forces between opposite charges and minimizes the repulsive forces between like charges. Many of the ions that form have eight electrons in their valence shell. If you haven't mastered the art of drawing lewis structures yet, you can check out. What is the lewis electron dot symbol for each element? The structure of an ionic solid can be represented using a particulate model. Web now that you've mastered the art of drawing the lewis structures of neutral covalent compounds, it's time to draw the lewis structures of polyatomic ions. A negatively charged ion (an anion) has more electrons than protons.Chemical structure of cations and anions commonly used to form ionic
Basic Chemistry Ions, Cations, and Anions
Cations and Anions. Structure of Ions Stock Vector Illustration of
Cation Ap Chemistry, Protons, Anatomy And Physiology, Sodium, Physics
Ortep drawing of the molecular structure of cations in (a
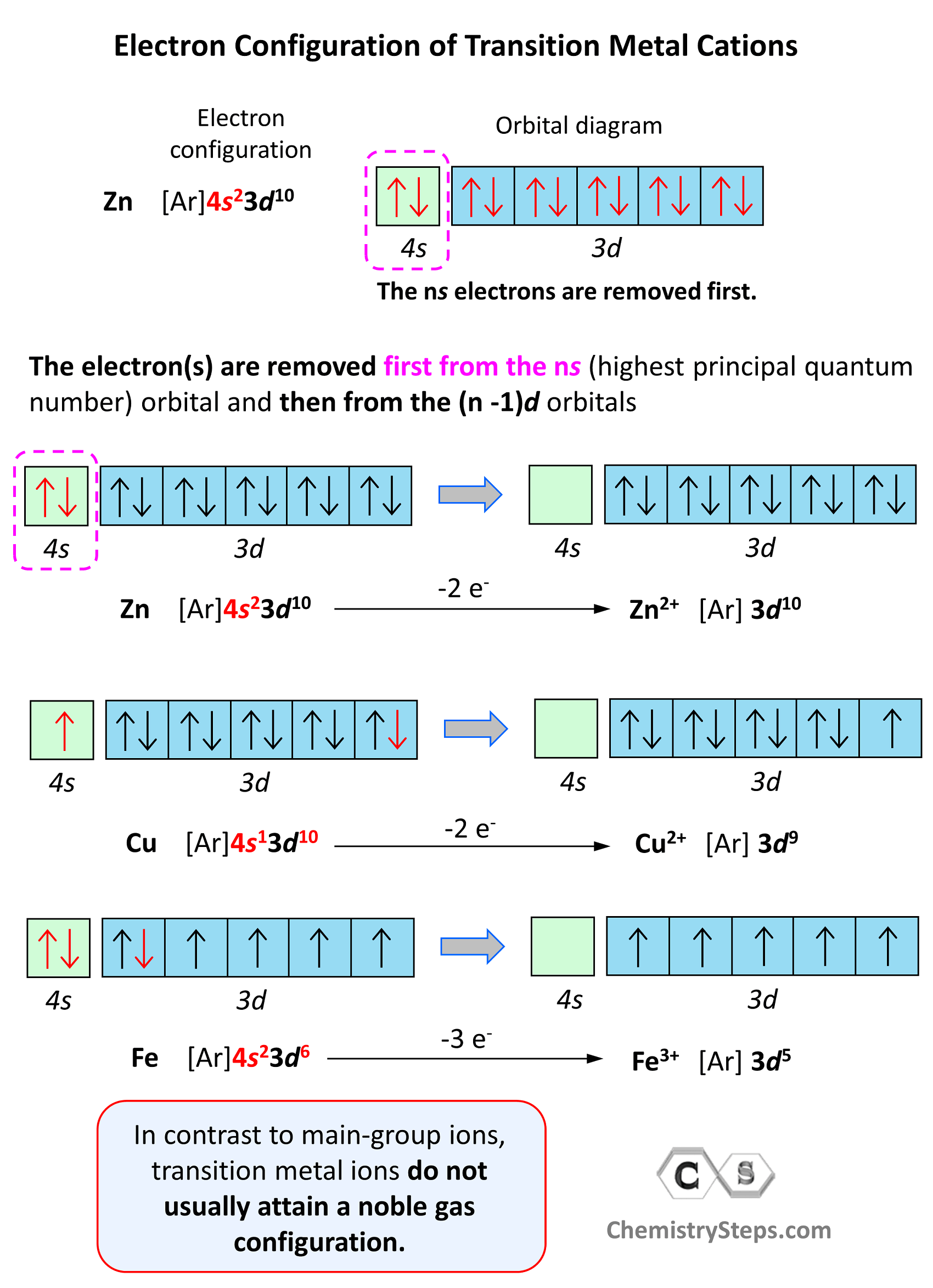
Electron Configurations of Ions Chemistry Steps
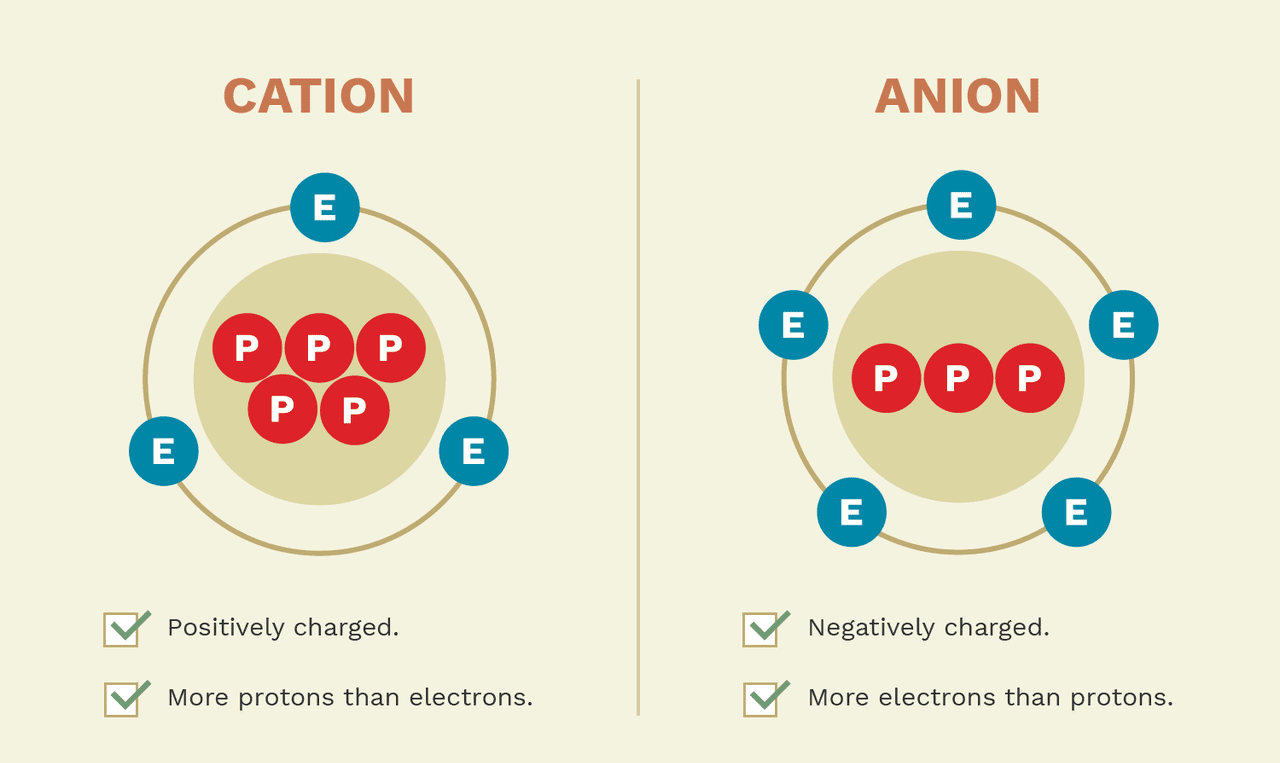
Cations and Anions Definitions, Examples, and Differences
ALevel Chemistry 1.6.1c draw electron configuration diagrams of
Spacefilling drawing of cations (A) and anions (B) of... Download
Ejemplos De Cationes Quimica Image to u
Web Draw Lewis Structures For Ionic Compounds.
Explain The Relative Stability Of Methyl, Primary, Secondary And Tertiary Carbocations In Terms Of Hyperconjugation And Inductive Effects.
The Smaller Purple Spheres Represent Sodium Cations, \(\Ce{Na^{+}}\), And The Larger Green Spheres Represent Chloride Anions, \(\Ce{Cl^{−}}\).
Web Cations Are Ions That Have A Positive Charge.
Related Post: