Drawing Of Muscle Cell
Drawing Of Muscle Cell - The solid components include proteins and other organic and inorganic substances. Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. Web muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. Explain how smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle. They are the specialized cells that makeup muscle tissue of the body. Web skeletal muscle is formed by 75% of water and 25% of solids. Muscles work on a macro level, starting with tendons that attach muscles to bones. Learn about how a neuronal message is translated into a muscular action at the neuromuscular junction. Web a muscle cell is a long cell as compared to other kinds of cells, and many muscle cells connect with each other to create the long fibers present in muscle tissue. Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes). Explain the process of smooth muscle contraction. Web in this video, we will show you how to draw types of muscle cells step by step with easy drawing tutorial s. These layers cover muscle subunits, individual muscle cells, and myofibrils respectively. A muscle consists of fibers of muscle cells surrounded by protective tissue, bundled together many more fibers, all surrounded in a thick protective tissue. Web using mouse models, they discovered that two enzymes, dusp13 and dusp27, are crucial in regulating the transition of skeletal muscle stem cells from proliferation to differentiation. Muscle cells connect together and eventually to elements of the skeletal system. Web skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. Web the primary job of muscles is to move the bones of the skeleton, but muscles also enable the heart to beat and constitute the walls of other vital hollow organs. It’s here that neurons release a transmitter chemical called acetylcholine. These molecules bind to a protein receptor on the cells of muscles, triggering an opening in the cell membrane. Web this is what we wanted to get to, but we're going to go even within the muscle cell to see, understand how all the myosin and the actin filaments fit into that muscle cell. The solid components include proteins and other organic and inorganic substances. Web in this video, we will show you how to draw types of muscle cells step by step with easy drawing tutorial s. The muscular system is a set of tissues in the body with the ability to change shape. Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. Web describe the microanatomy of a smooth muscle cell. Learn about how a neuronal message is translated into a muscular action at the neuromuscular junction. Within muscles, there are layers of connective tissue called the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. It is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. Web this is what we wanted to get to, but we're going to go even within the muscle cell to see, understand how all the myosin and the actin filaments fit into that muscle cell. Web the primary job of muscles is. This article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. It’s here that neurons release a transmitter chemical called acetylcholine. Web a muscle is a group of muscle tissues which contract together to produce a force. Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. Web muscle tissue has a unique histological. Web a muscle is a group of muscle tissues which contract together to produce a force. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Learn about how a neuronal message is translated into a muscular action at the neuromuscular junction. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred. Web this is what we. Web anatomy of a skeletal muscle cell. Muscles work on a macro level, starting with tendons that attach muscles to bones. Web the muscle cell, or myocyte, develops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm. There are three main types of muscle: A muscle uses atp to contract and shorten, producing a force on the objects it is connected to. Web all skeletal muscle contractions originate at the junction between motor neurons, which originate in the spinal cord and brainstem, and muscle fibers. They are the specialized cells that makeup muscle tissue of the body. Web unlike cardiac and smooth muscle, the only way to functionally contract a skeletal muscle is through signaling from the nervous system. Web the structure. When the muscle cells contract, force is created as the muscles pull against the skeleton. Skeletal muscle tissue is arranged in bundles surrounded by connective tissue. These cells are responsible for generating force and movement throughout the body. Web the primary job of muscles is to move the bones of the skeleton, but muscles also enable the heart to beat. These molecules bind to a protein receptor on the cells of muscles, triggering an opening in the cell membrane. Web a muscle is a group of muscle tissues which contract together to produce a force. Web using mouse models, they discovered that two enzymes, dusp13 and dusp27, are crucial in regulating the transition of skeletal muscle stem cells from proliferation. Web a muscle cell is a long cell as compared to other kinds of cells, and many muscle cells connect with each other to create the long fibers present in muscle tissue. Web all skeletal muscle contractions originate at the junction between motor neurons, which originate in the spinal cord and brainstem, and muscle fibers. Under the light microscope, muscle. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Web muscle cells, also called myocytes, are the basic building blocks of the muscle tissues in the body. Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. Web skeletal muscle is formed by 75% of water and. Web the muscle cell, or myocyte, develops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm. These molecules bind to a protein receptor on the cells of muscles, triggering an opening in the cell membrane. Muscle cells connect together and eventually to elements of the skeletal system. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Web skeletal muscle is one. It is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. The muscular system is a set of tissues in the body with the ability to change shape. This article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. A muscle uses atp to contract and shorten, producing a force on the objects it is connected to. These molecules bind to a protein receptor on the cells of muscles, triggering an opening in the cell membrane. Web a muscle cell is a long cell as compared to other kinds of cells, and many muscle cells connect with each other to create the long fibers present in muscle tissue. So friends of you have. Web this is what we wanted to get to, but we're going to go even within the muscle cell to see, understand how all the myosin and the actin filaments fit into that muscle cell. Myocytes and their numbers remain relatively constant throughout life. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Web the muscle cell, or myocyte, develops from myoblasts derived from the mesoderm. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; Web how do neurons talk directly to muscle cells? Web skeletal muscle is formed by 75% of water and 25% of solids. Web the primary job of muscles is to move the bones of the skeleton, but muscles also enable the heart to beat and constitute the walls of other vital hollow organs. Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes).Skeletal Muscle Cell Structure
Human Physiology Muscle
Types of muscle cells vector illustration Biology Lessons, Teaching
Types of muscle cell diagram 1762350 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Diagram showing types of muscle cells illustration Stock Vector Image
Anatomy Of Muscle Cell The Anatomy Stories
How To Draw Muscle Cell Step by Step YouTube
Diagram showing types of muscle cells illustration Stock Vector
Labeled Diagram Of A Muscle Cell
Muscle cell diagram
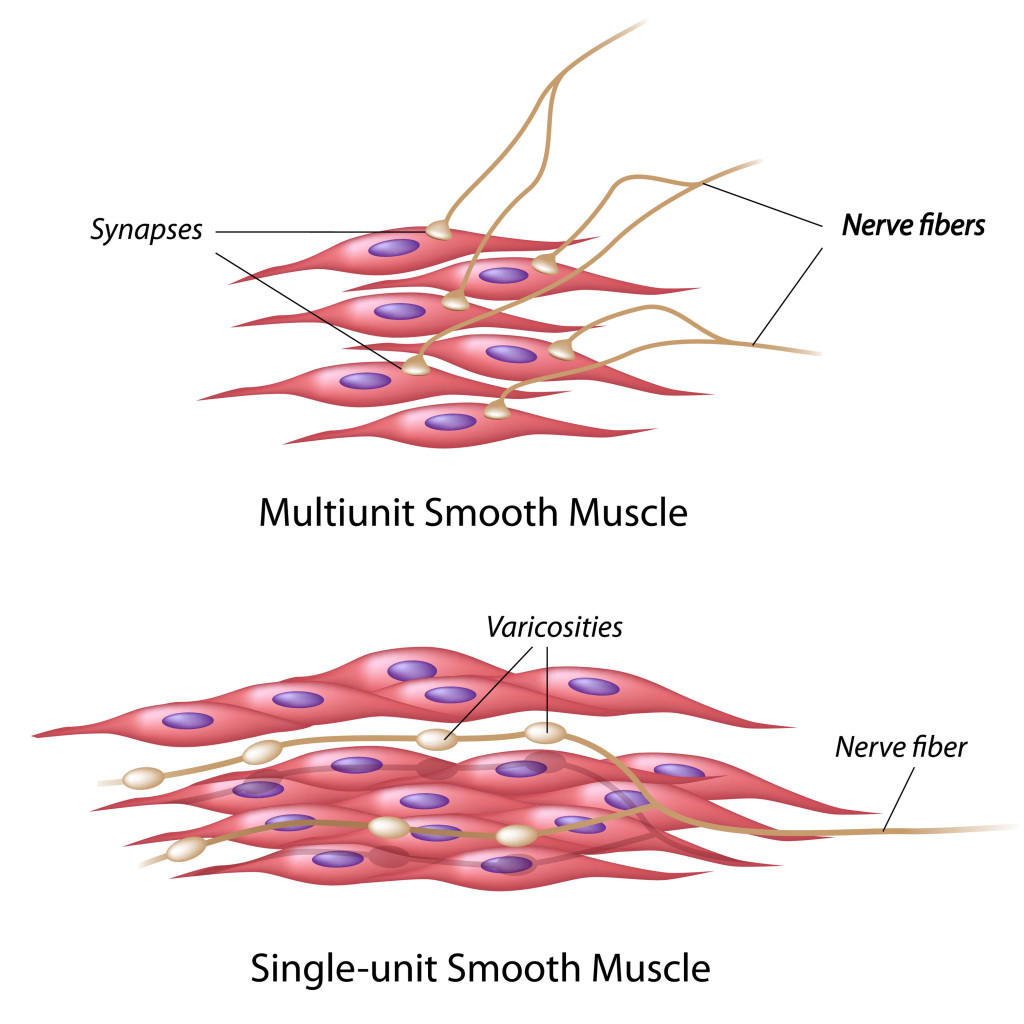
Explain How Smooth Muscle Differs From Skeletal Muscle.
There Are Three Types Of.
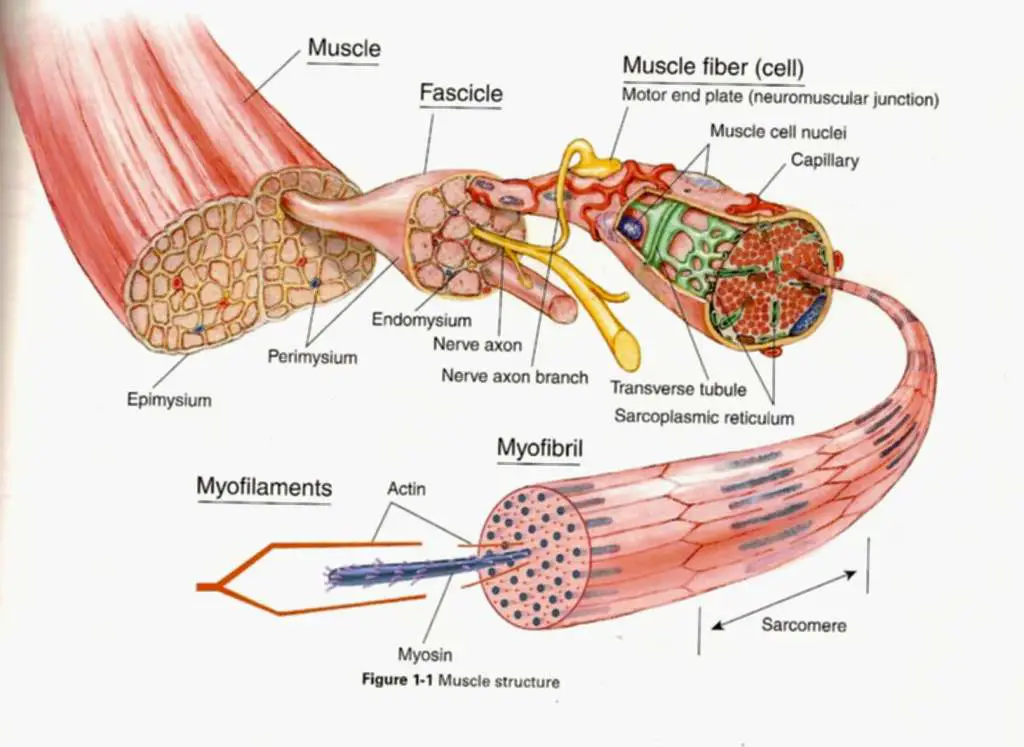
Within Muscles, There Are Layers Of Connective Tissue Called The Epimysium, Perimysium, And Endomysium.
These Molecules Bind To A Protein Receptor On The Cells Of Muscles, Triggering An Opening In The Cell Membrane.
Related Post: