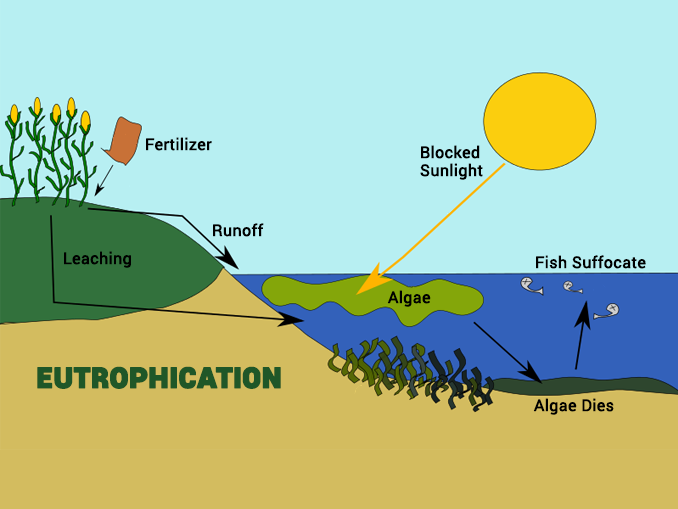
Eutrophication Drawing
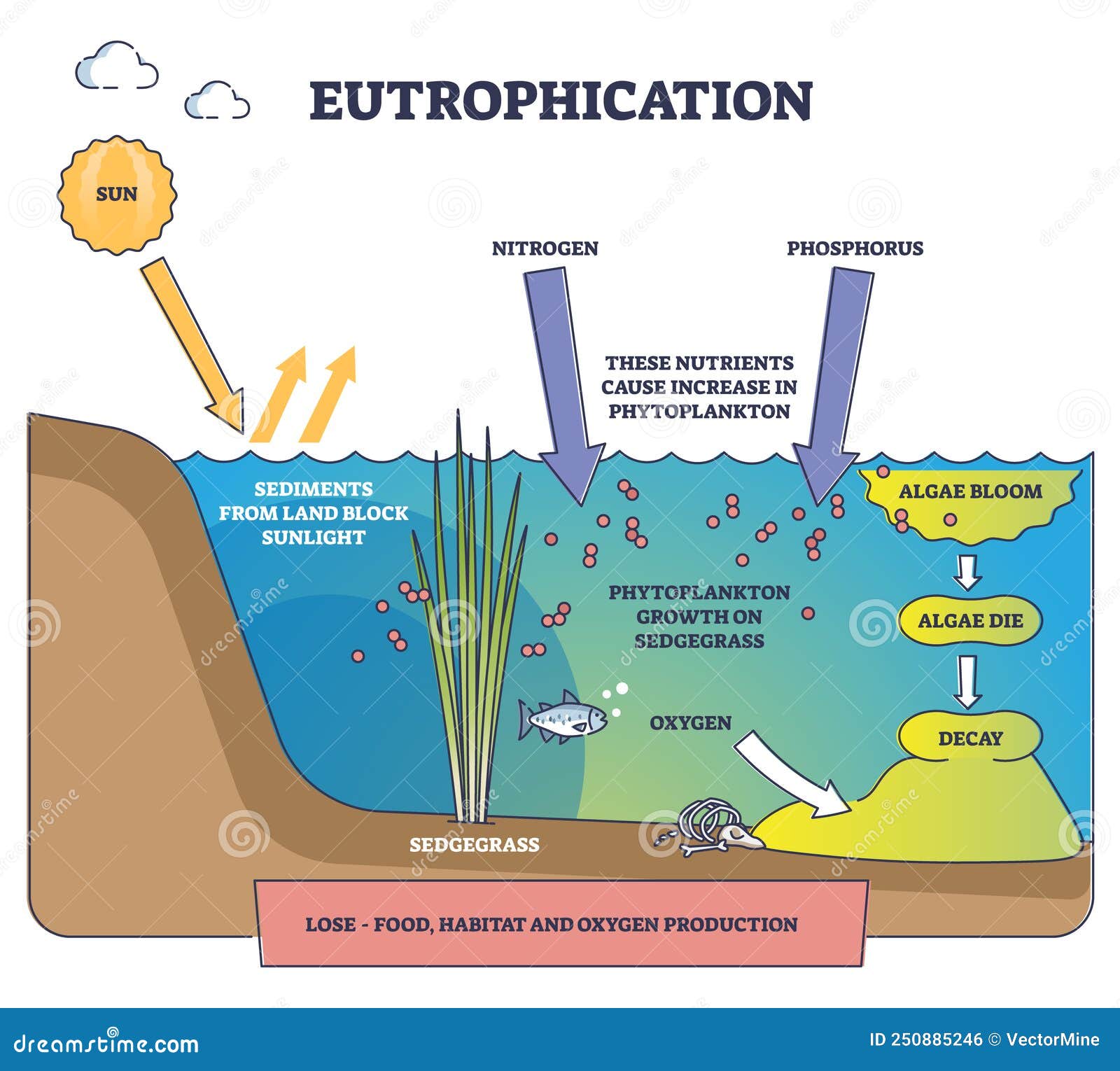
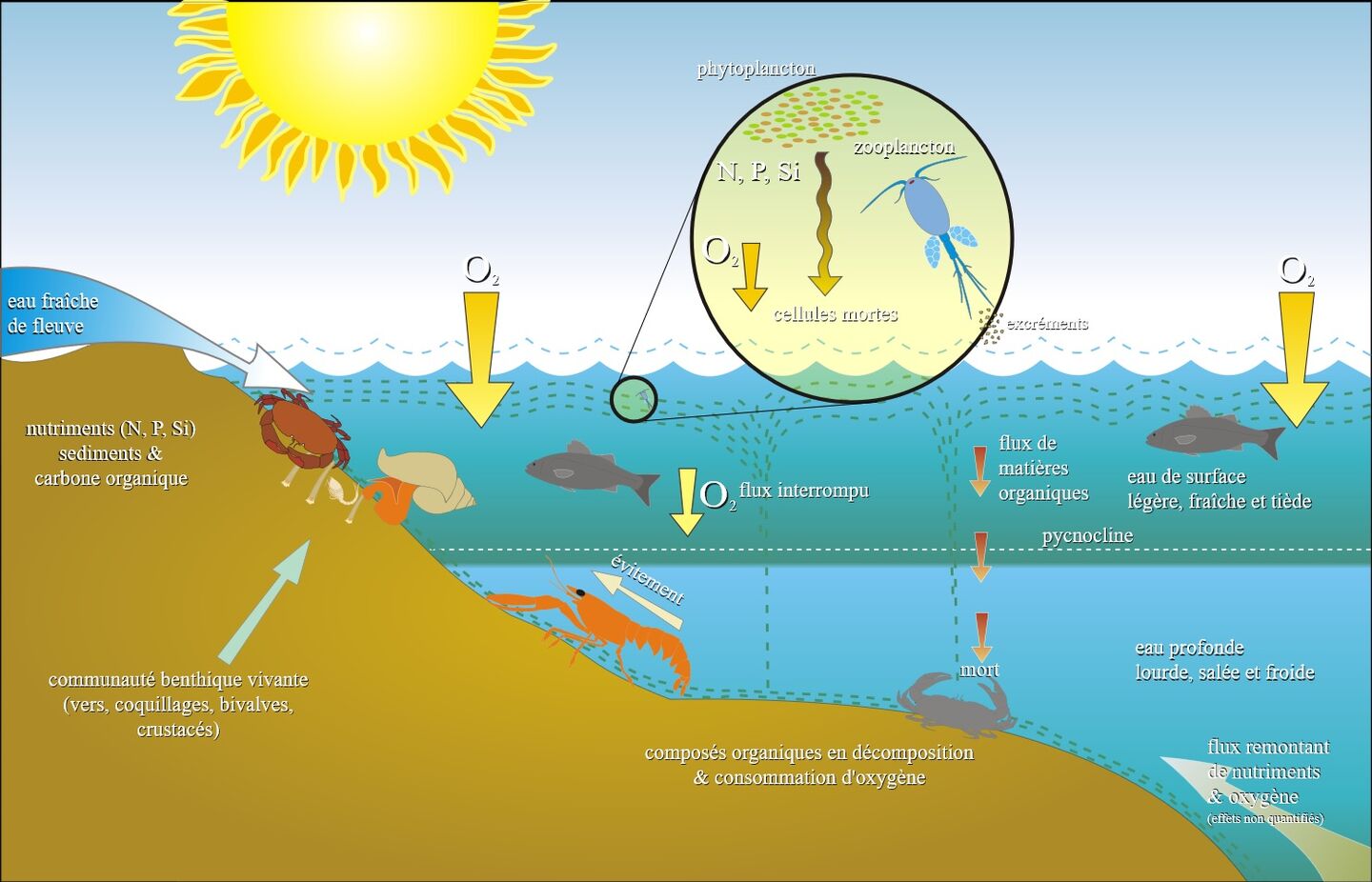
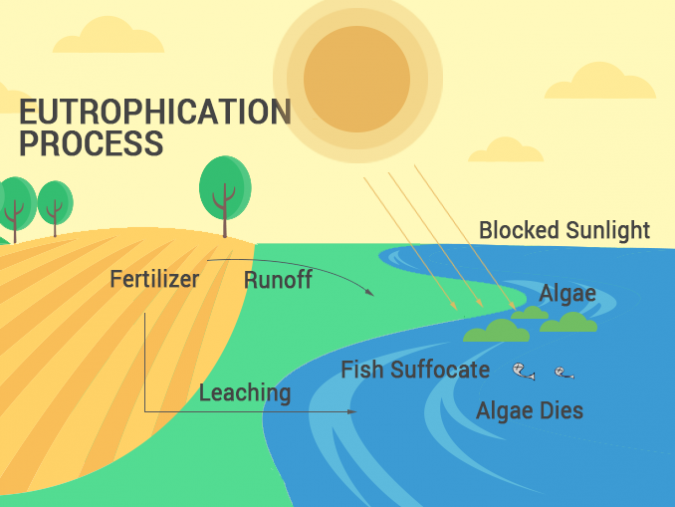
Eutrophication Drawing - Then, excess nutrients runoff from the field into the water. Eutrophication is the condition of a gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in a water body resulting in excessive plant and algal growth. Web eutrophication problems in the great lakes are caused by excessive nutrient inputs (primarily phosphorus, p, and nitrogen, n) from various sources throughout its basin. This resource works with html5 or flash. Eutrophication is the process where nutrient runoff enters bodies of water and increases algae production. This includes mobile devices such as ipads, kindle and android tablets as well as pcs or macs. In developing protection and restoration plans, it is important to know where and from what sources the nutrients originate. The process begins by adding excessive nutrients, particularly nitrogen, and phosphorus, into a water body. This elevated nutrient level leads to rapid growth and proliferation of algae and phytoplankton, often resulting in. Web eutrophication is an entirely natural process where excess nutrients such as phosphorous and nitrogen enter a water body and cause an algae bloom. Web eutrophication occurs in four steps. Here's an overview in a one minute video. For example, water in the great lakes was originally cool and clear. This elevated nutrient level leads to rapid growth and proliferation of algae and phytoplankton, often resulting in. The process begins by adding excessive nutrients, particularly nitrogen, and phosphorus, into a water body. This algae production covers the surface of the water, blocking sunlight from reaching below the surface. It can occur naturally, but is usually associated with human activity that releases nutrients into the environment. Web eutrophication is characterized by excessive plant and algal growth due to the increased availability of one or more limiting growth factors needed for photosynthesis (schindler 2006), such as. In developing protection and restoration plans, it is important to know where and from what sources the nutrients originate. Web eutrophication, the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in an aging aquatic ecosystem such as a lake. Web eutrophication describes the biological effects of an increase in the concentration of nutrients. The excess algae and plant matter eventually decompose, producing large amounts of carbon dioxide. This elevated nutrient level leads to rapid growth and proliferation of algae and phytoplankton, often resulting in. Eutrophication is the condition of a gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in a water body resulting in excessive plant and algal growth. Web eutrophication is the process by which a body of water becomes enriched in dissolved nutrients (such as phosphates) that stimulate the growth of aquatic plant life usually resulting in the. This addition can occur naturally or due to human activities such as agricultural drainage, sewage discharges, industrial waste, and atmospheric deposition. For example, water in the great lakes was originally cool and clear. As plants die off, they take up oxygen, causing other plants and organisms to die off. Web eutrophication is characterized by excessive plant and algal growth due to the increased availability of one or more limiting growth factors needed for photosynthesis (schindler 2006), such as. The collective term ‘nutrients’ refers to those elements that are essential for primary production by plants or other photosynthetic organisms. In other words, few biological materials (such as algae) lived there. Web eutrophication occurs in 4 simple steps: The collective term ‘nutrients’ refers to those elements that are essential for primary production by plants or other photosynthetic organisms. Eutrophication is the condition of a gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in a water body. This algae production covers the surface of the water, blocking sunlight from reaching below the surface. For example, water in the great lakes was originally cool and clear. The excess algae and plant matter eventually decompose, producing large amounts of carbon dioxide. Web in these experiments, pond water samples are enriched with varying levels of inorganic nutrients and are cultured. Harmful algal blooms, dead zones, and fish kills are the results of a process called eutrop. Web eutrophication animation process.link to other educational animation about kinetic energy: Web eutrophication occurs in 4 simple steps: Web eutrophication sets off a chain reaction in the ecosystem, starting with an overabundance of algae and plants. Anthropogenic eutrophication has caused a widespread loss of. Web eutrophication occurs in 4 simple steps: This addition can occur naturally or due to human activities such as agricultural drainage, sewage discharges, industrial waste, and atmospheric deposition. By looking at such parameters as time of day, turbidity, ph, and dissolved gases, the dynamics of eutrophic systems may be better understood. This resource works with html5 or flash. Cultural eutrophication. Eutrophication is the process where nutrient runoff enters bodies of water and increases algae production. Paerl) this page was last edited on. This resource works with html5 or flash. Anthropogenic eutrophication has caused a widespread loss of biodiversity in many systems. Here's an overview in a one minute video. Web eutrophication is characterized by excessive plant and algal growth due to the increased availability of one or more limiting growth factors needed for photosynthesis (schindler 2006), such as. Eutrophication is the process where nutrient runoff enters bodies of water and increases algae production. This activity will run on any browser that supports flash or a modern browser with html5. Paerl) this page was last edited on. This includes mobile devices such as ipads, kindle and android tablets as well as pcs or macs. Web eutrophication animation process.link to other educational animation about kinetic energy: This elevated nutrient level leads to rapid growth and proliferation of algae and phytoplankton, often resulting in. Web eutrophication describes the biological effects of an. Web eutrophication is an entirely natural process where excess nutrients such as phosphorous and nitrogen enter a water body and cause an algae bloom. Web eutrophication is the process by which a body of water becomes enriched in dissolved nutrients (such as phosphates) that stimulate the growth of aquatic plant life usually resulting in the. Web eutrophication occurs in four. This addition can occur naturally or due to human activities such as agricultural drainage, sewage discharges, industrial waste, and atmospheric deposition. Schematic diagram of the different pathways of nutrient deposition into coastal waters and ensuing processes leading to eutrophication (algal blooms) and hypoxia (photo credit: This leads to algal blooms, which, when they die and decompose, consume oxygen in the. Web eutrophication problems in the great lakes are caused by excessive nutrient inputs (primarily phosphorus, p, and nitrogen, n) from various sources throughout its basin. Web eutrophication, the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in an aging aquatic ecosystem such as a lake. It can occur naturally, but is usually associated with human activity. Web eutrophication is water pollution caused by excess nutrients. Web in these experiments, pond water samples are enriched with varying levels of inorganic nutrients and are cultured in the classroom under fluorescent lights. Web eutrophication is the process of excessively enriching a body of water in nutrients, primarily phosphorus and nitrogen. Web eutrophication is characterized by excessive plant and algal growth due to the increased availability of one or more limiting growth factors needed for photosynthesis (schindler 2006), such as. Then, excess nutrients runoff from the field into the water. Cultural eutrophication is caused by water pollution and is a serious threat to. The collective term ‘nutrients’ refers to those elements that are essential for primary production by plants or other photosynthetic organisms. Web eutrophication is an entirely natural process where excess nutrients such as phosphorous and nitrogen enter a water body and cause an algae bloom. Eutrophication is the condition of a gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in a water body resulting in excessive plant and algal growth. This lowers the ph of seawater, a process known as ocean acidification. Web eutrophication, the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in an aging aquatic ecosystem such as a lake. It can occur naturally, but is usually associated with human activity that releases nutrients into the environment. This leads to algal blooms, which, when they die and decompose, consume oxygen in the water, creating hypoxic or dead zones. Web eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of microorganisms that may deplete the oxygen of water. Here's an overview in a one minute video. Web eutrophication occurs in 4 simple steps:Eutrophication
Eutrophication Process Explanation and Water Pollution Stages Outline
L'eutrophisation d'un plan d'eau Alloprof
Diagram of eutrophication , drawing. Fotografía de noticias Getty Images
38 Eutrophic System Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
Eutrophication — Science Learning Hub
Concentrations of Dissolved Oxygen Near the Seafloor
How Does Eutrophication Work? Causes, Process and Examples Earth How
eutrofización, nutritivo sobrecargar en agua causando alga crecimiento
How Does Eutrophication Work? Causes, Process and Examples Earth How
This Resource Works With Html5 Or Flash.
Next, The Fertilizer Rich In Nitrate And Phosphate Sparks The Overgrowth Of Algae In Water Bodies.
Eutrophication Is The Process Where Nutrient Runoff Enters Bodies Of Water And Increases Algae Production.
Web Eutrophication Sets Off A Chain Reaction In The Ecosystem, Starting With An Overabundance Of Algae And Plants.
Related Post: