Flagellum Drawing
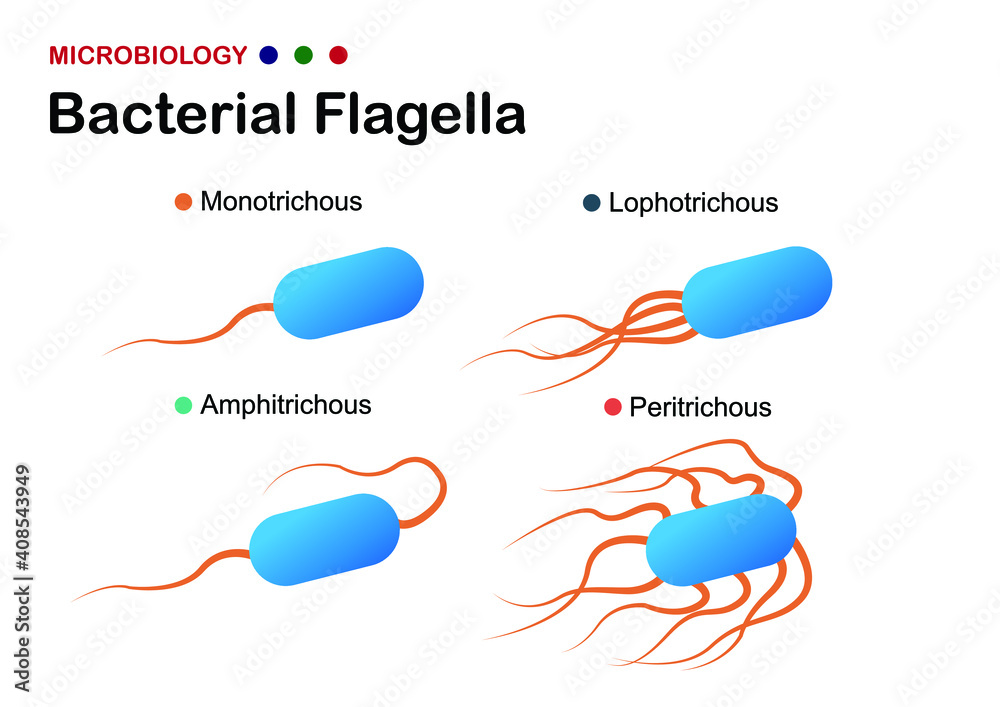
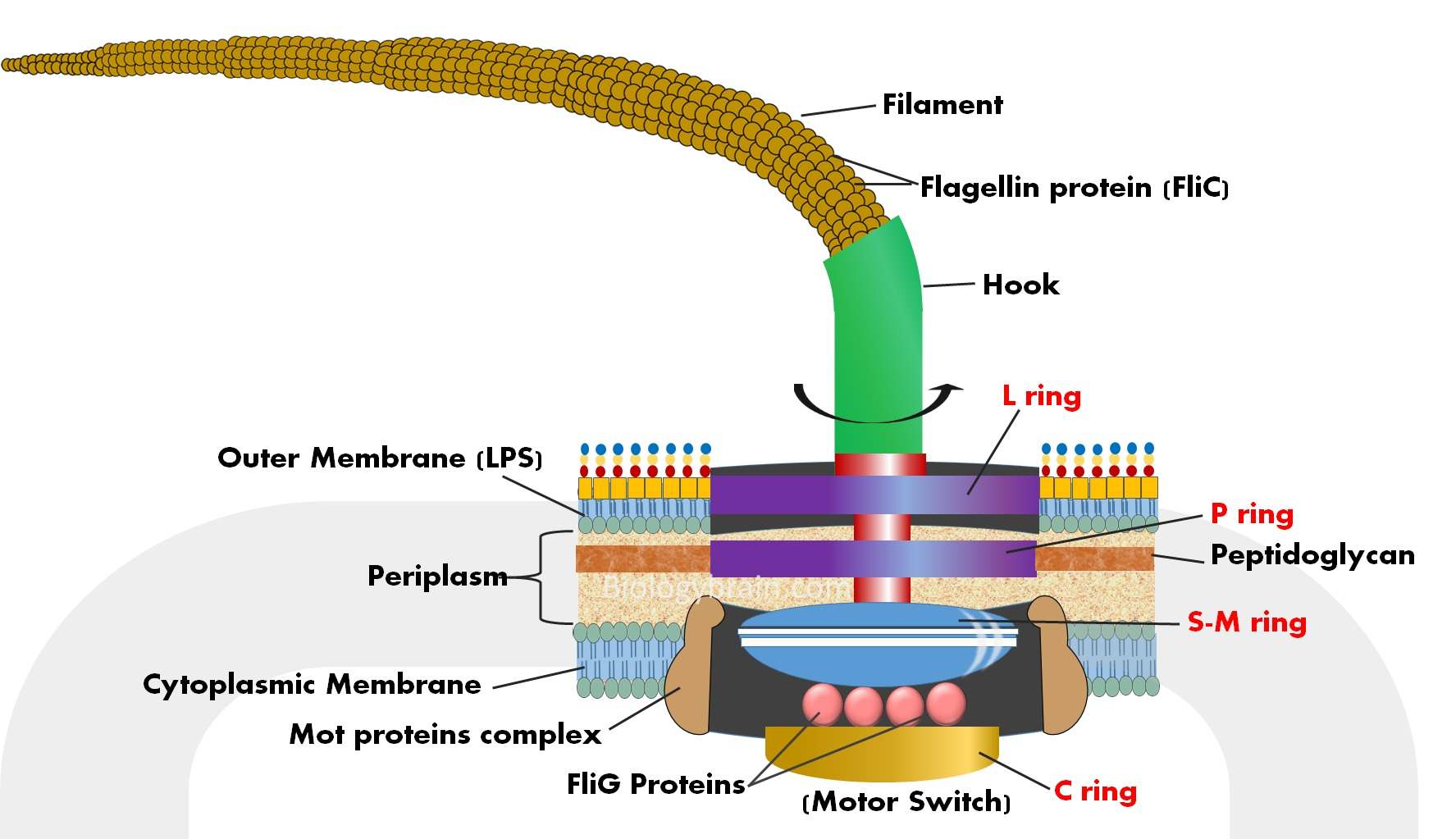
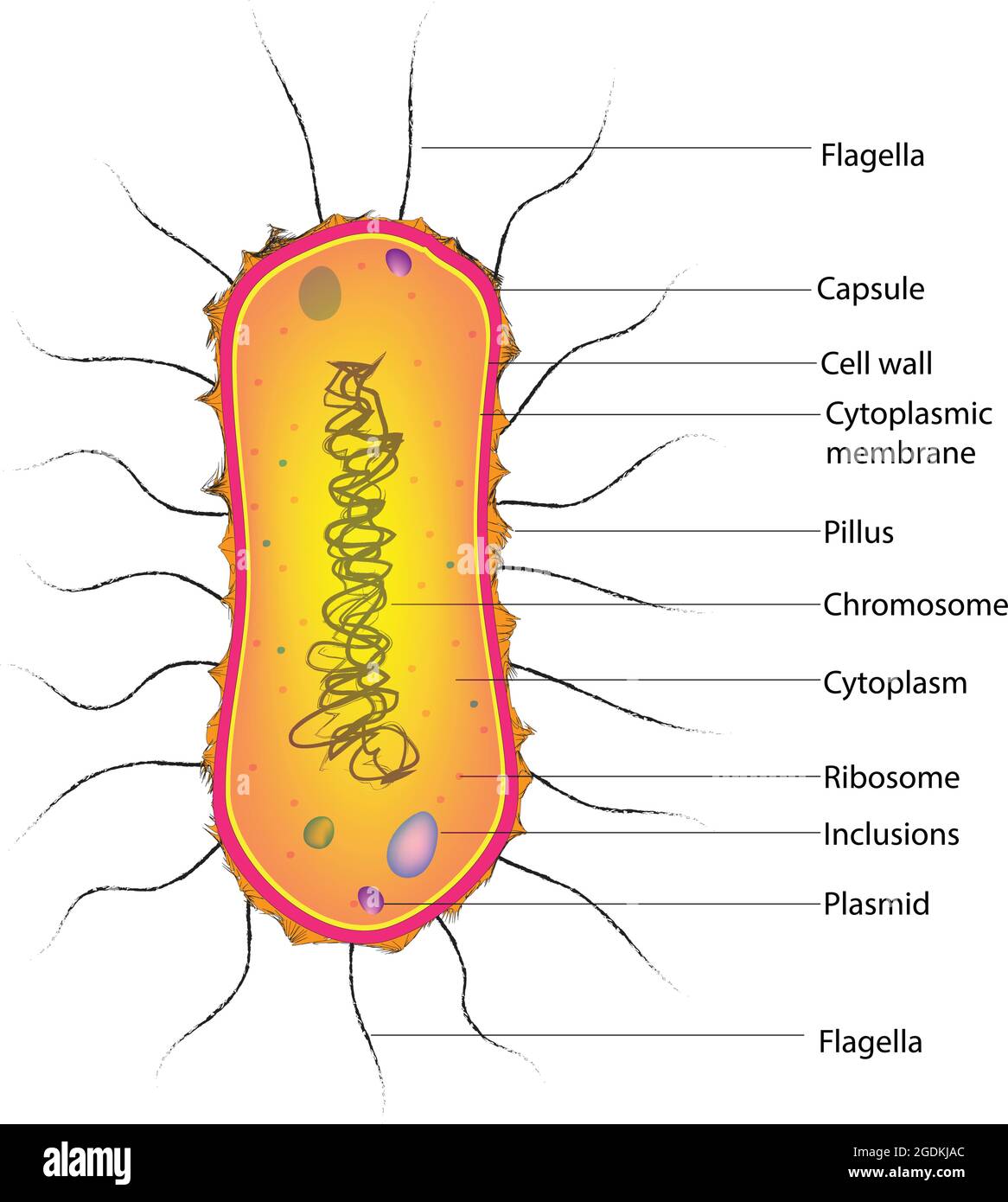
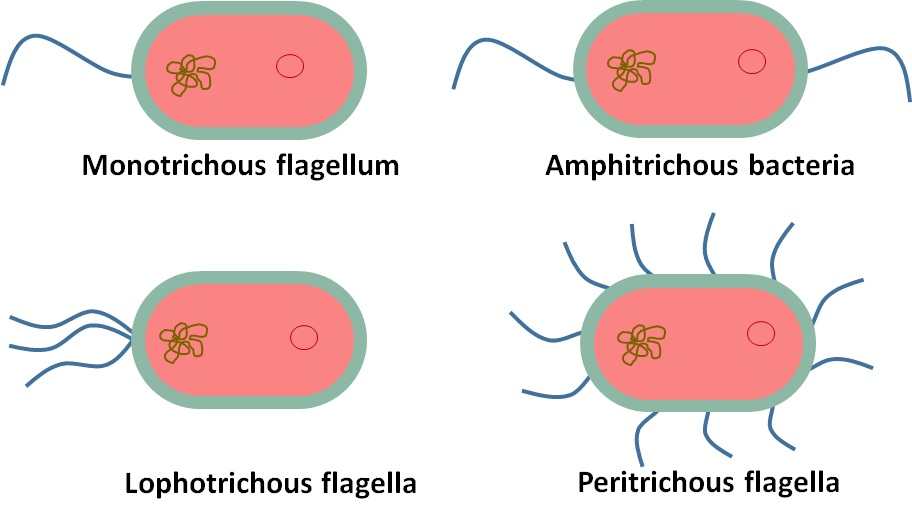
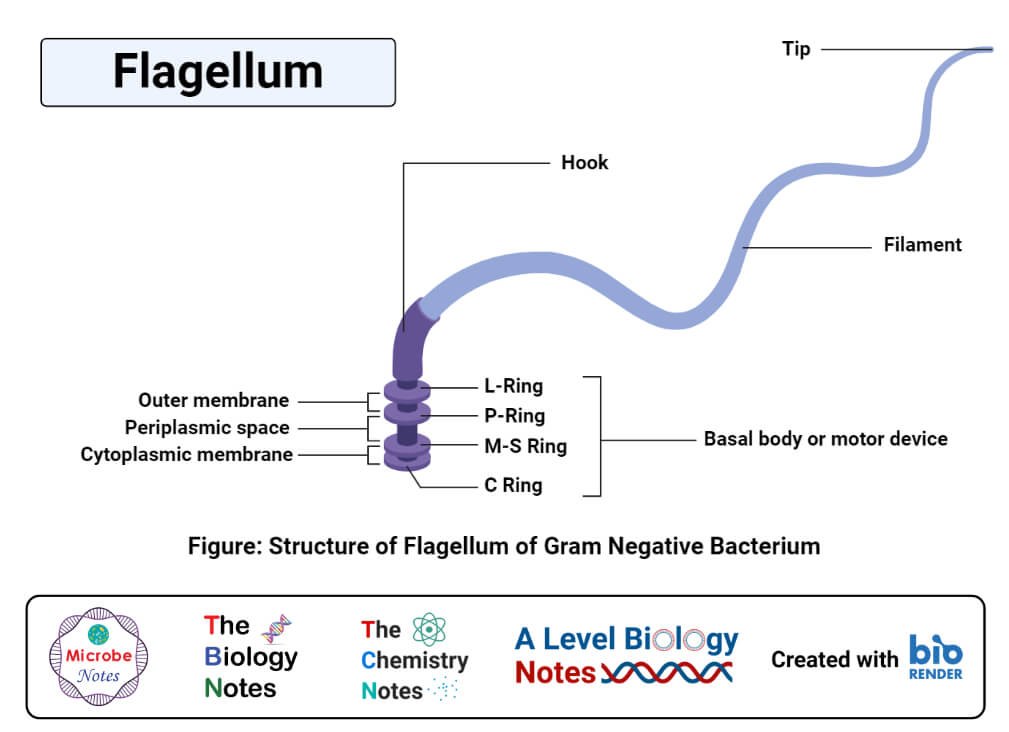
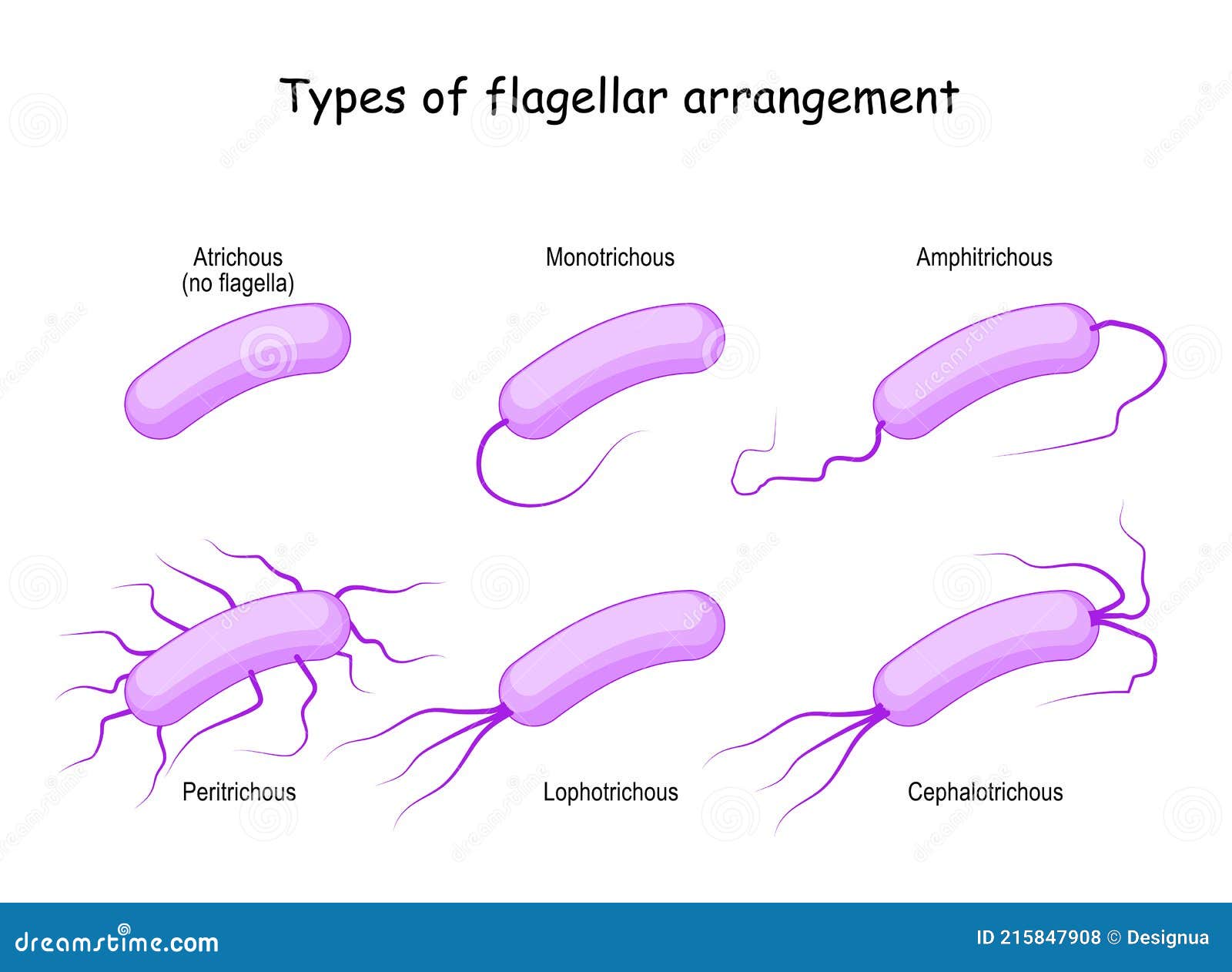
Flagellum Drawing - When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. Web introduction of flagella. In a flagellum, several symmetrical undulatory waves pass. Drawing of flagella stock illustrations. The bacterial flagellum is a locomotive organelle that propels the bacterial cell body in liquid environments. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A rotary motor embedded in their envelope that spins a long helical fiber called a flagellum (⇩). These are unbranched, long, thread like structures, mostly composed of the protein flagellin, intricately embedded in the cell envelope. Flagella) (latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores , and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Web microbiology | bacteriology. Take a microscopic look at how a eukaryotic flagellate's flagellum propels the organism through water. A universal joint called the hook connects the filament to the motor, translating the rotation. Movement of eukaryotic flagella in real time and slow motion. Web flagella perform independent undulatory movements while cilia show rowing type of sweeping motion either simultaneously (isochronic or synchronous) or one after the other (metachronic). Specialized flagella in some organisms are also used as sensory organelles that can detect changes in temperature. Four types of flagella and flagellar arrangements. Difference between cilia and flagella. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they are structurally very different from eukaryotic flagella. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. Take a microscopic look at how a eukaryotic flagellate's flagellum propels the organism through water. Web this technique is used to visualize the presence and arrangement of flagella for the presumptive identification of motile bacterial species. Protozoa use flagella, cilia, or pseudopods, whereas motile bacteria move only using flagella. A rotary motor embedded in their envelope that spins a long helical fiber called a flagellum (⇩). Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide. Difference between cilia and flagella. They are composed of a filament, hook, and basal body, which work together to generate torque and propel the bacterium forward. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. The depicted type of flagellum is found in bacteria such as e. Flagellum, hairlike structure that acts primarily as an organelle of locomotion in the cells of many. Web in this article we will discuss about the structure and kinds of fungal flagella. The word “flagellum” means “whip”. Web nearly all bacteria that swim use the same propeller: The term ‘flagellum’ is the latin term for whip indicating the long slender structure. Bacteria and archaea both have an organelle called the flagellum that resembles a filamentous thread. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. Take a microscopic look at how a eukaryotic flagellate's flagellum propels the organism through water. The word “flagellum” means “whip”. In a flagellum, several symmetrical undulatory waves pass. They are composed of a filament, hook, and basal body, which work together to generate torque and propel the bacterium forward. The word “flagellum” means “whip”. Take a microscopic look at how a eukaryotic flagellate's flagellum propels the organism through water. The term ‘flagellum’ is the latin term for whip indicating the long slender structure of the flagellum that resembles. Bacteria and archaea both have an organelle called the flagellum that resembles a filamentous thread. When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. Web this technique is used to visualize the presence and arrangement of flagella for the presumptive identification of motile bacterial species. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and. Coli and salmonella , and rotates like a propeller when the bacterium swims. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they are structurally very different from eukaryotic flagella. Most protozoa and some bacteria are motile. Flagella) (latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores , and from a wide. The depicted type of flagellum is found in bacteria such as e. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they are structurally very different from eukaryotic flagella. Flagella are the complex filamentous cytoplasmic structure protruding through cell wall. Web flagella (singular, flagellum) are the locomotory structures of many. Bacteria and archaea both have an organelle called the flagellum that resembles a filamentous thread. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. The depicted type of flagellum is found in bacteria such as e. Most protozoa and some bacteria are motile. Four types of flagella and flagellar arrangements. The word flagellum in latin means whip, just like the whipping motion flagella (plural) often use for locomotion. Web flagella perform independent undulatory movements while cilia show rowing type of sweeping motion either simultaneously (isochronic or synchronous) or one after the other (metachronic). Web a flagellum (/ f l ə ˈ dʒ ɛ l əm /; Web what are flagella?. Take a microscopic look at how a eukaryotic flagellate's flagellum propels the organism through water. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. The word flagellum in latin means whip, just like the whipping motion flagella (plural) often use for locomotion. Four types of flagella and flagellar arrangements. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum. Web nearly all bacteria that swim use the same propeller: A universal joint called the hook connects the filament to the motor, translating the rotation. Web flagella (singular, flagellum) are the locomotory structures of many prokaryotes. A rotary motor embedded in their envelope that spins a. Web nearly all bacteria that swim use the same propeller: Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. The bacterial flagellum is a locomotive organelle that propels the bacterial cell body in liquid environments. A universal joint called the hook connects the filament to the motor, translating the rotation. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they are structurally very different from eukaryotic flagella. Four types of flagella and flagellar arrangements. Flagellum, hairlike structure that acts primarily as an organelle of locomotion in the cells of many. They are composed of a filament, hook, and basal body, which work together to generate torque and propel the bacterium forward. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. Movement of eukaryotic flagella in real time and slow motion. Web flagella perform independent undulatory movements while cilia show rowing type of sweeping motion either simultaneously (isochronic or synchronous) or one after the other (metachronic). Difference between cilia and flagella. Most protozoa and some bacteria are motile. When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. The depicted type of flagellum is found in bacteria such as e. Movement and chemotaxis are made possible by the motile organelle known as the flagellum.Microbiology diagram shows the arrangement of bacterial flagella
Diagram of Flagella Definition, Types, Structure and Function
peritrichous bacteria, flagellum is a lashlike appendage that
Diagram of Flagella Definition, Types, Structure and Function
Flagella Diagram
Download Bacteria, Flagellum, Capsule. RoyaltyFree Vector Graphic
Overview of the structure of a flagellum. Schematic drawing of a
Flagella Structure, Types, Arrangement, Functions, Examples
Flagellum structure Diagram Quizlet
Types of Flagellar Arrangement. Bacteria Stock Vector Illustration of
Web This Technique Is Used To Visualize The Presence And Arrangement Of Flagella For The Presumptive Identification Of Motile Bacterial Species.
See All Videos For This Article.
Take A Microscopic Look At How A Eukaryotic Flagellate's Flagellum Propels The Organism Through Water.
All Prokaryotic Cells Are Encased By A Cell Wall.
Related Post: