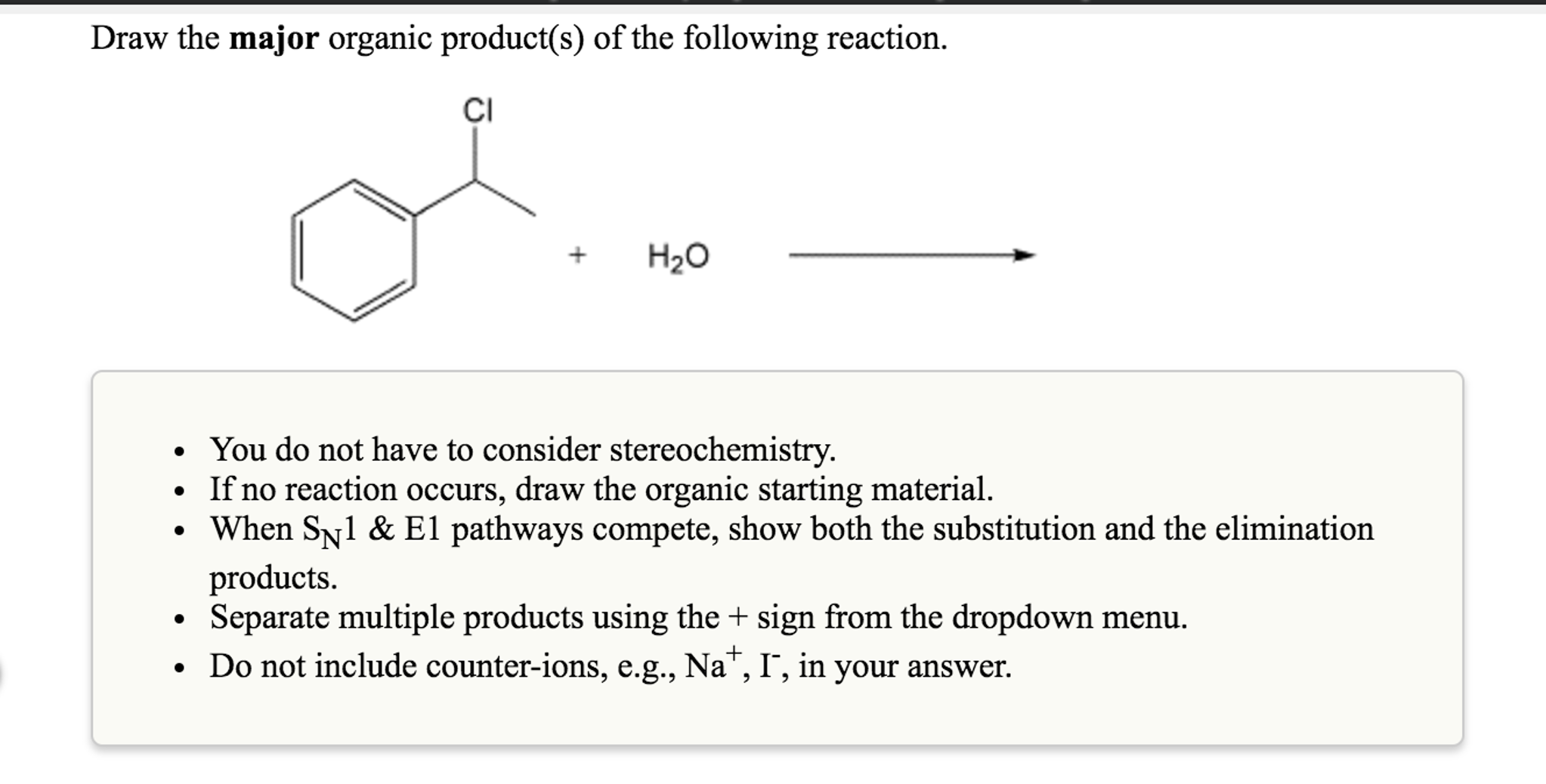
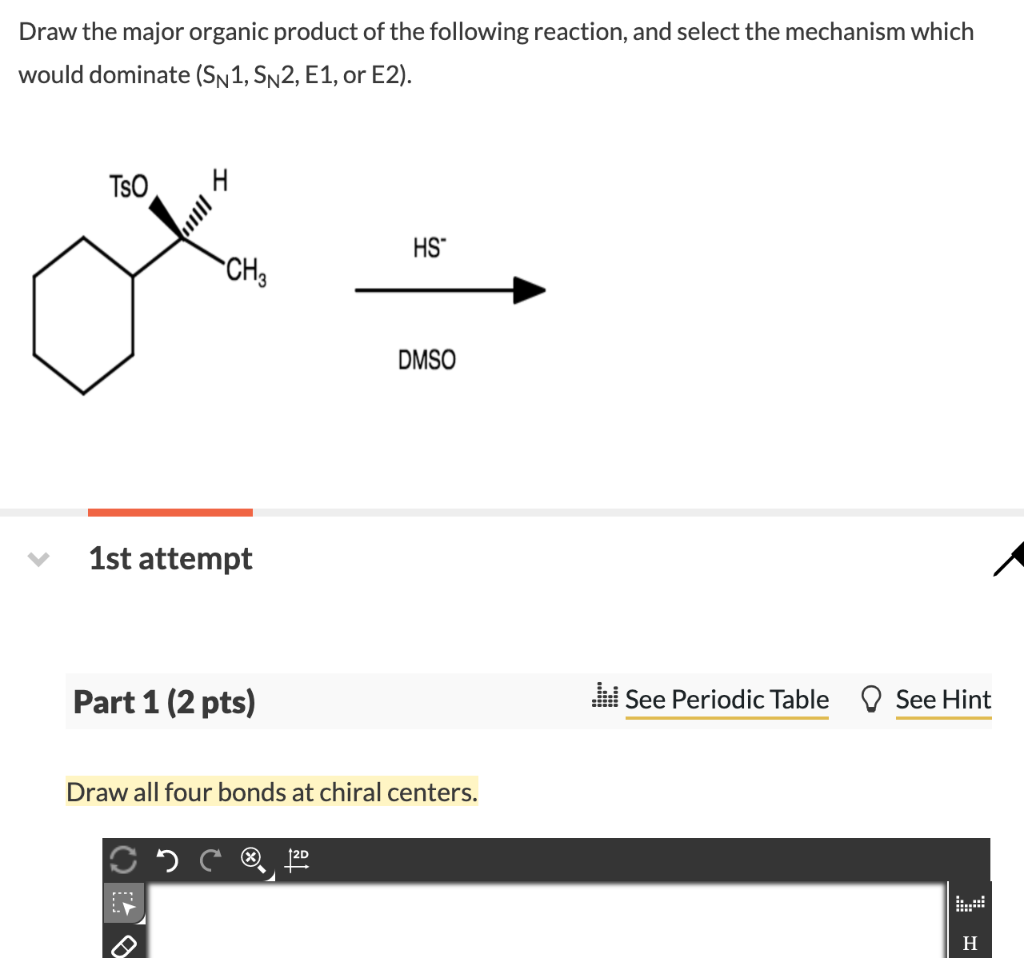
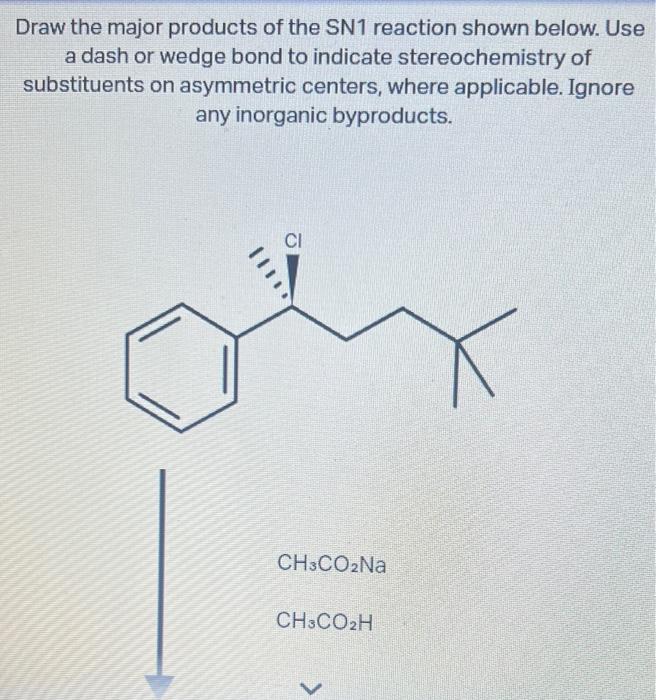
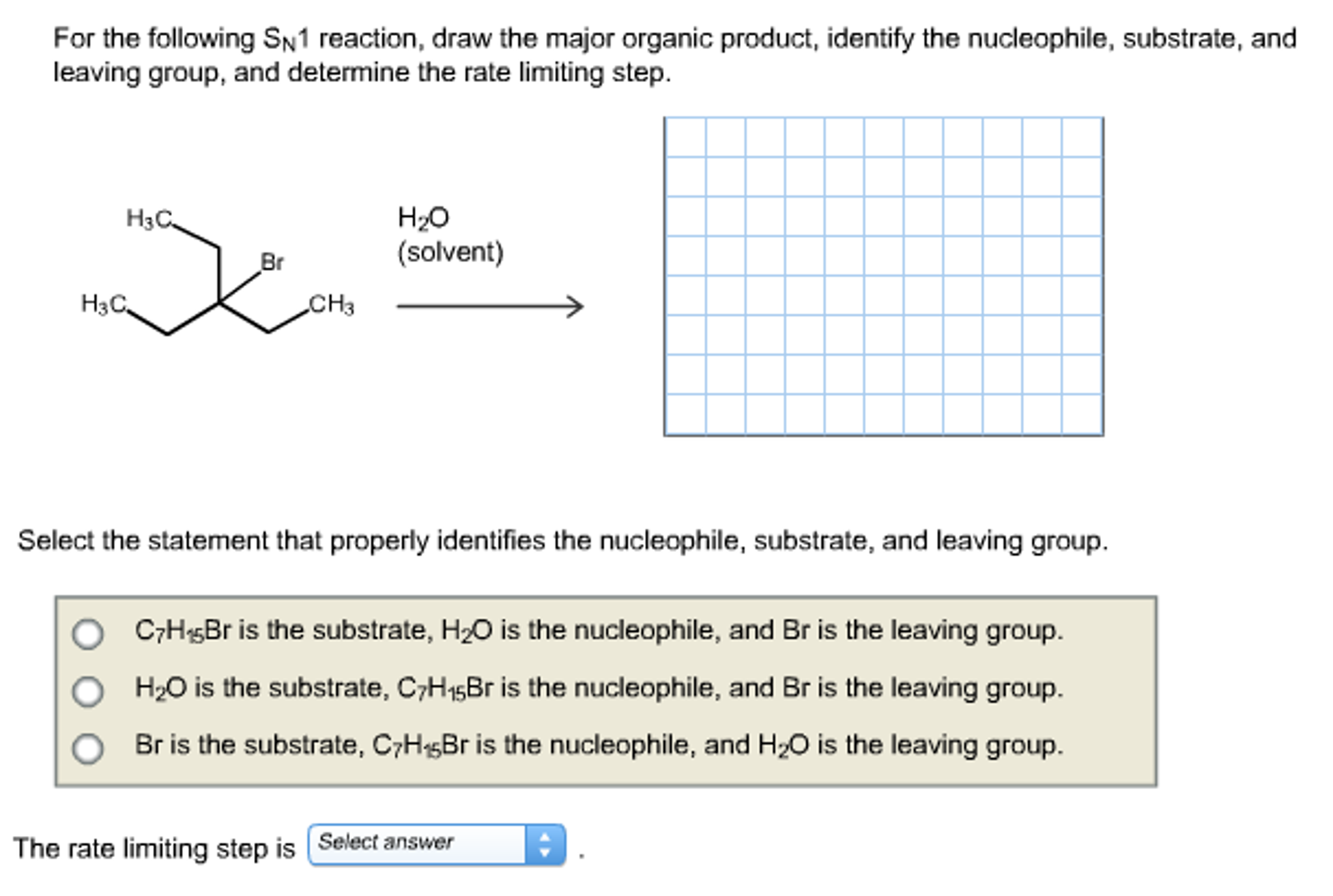
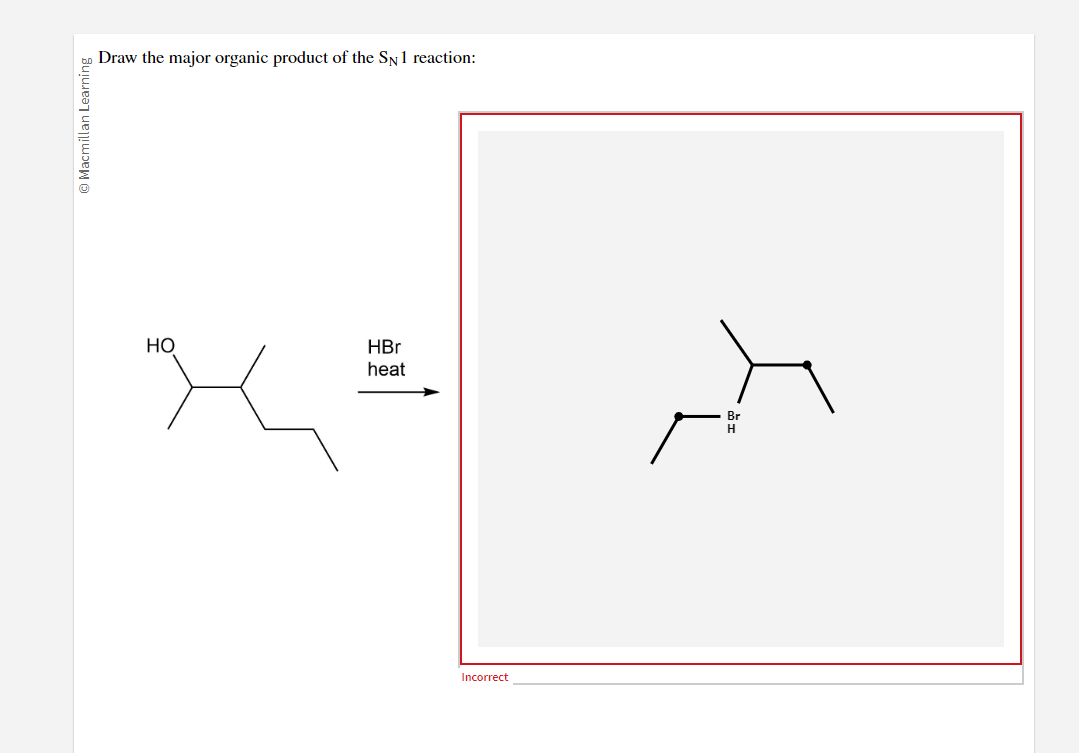
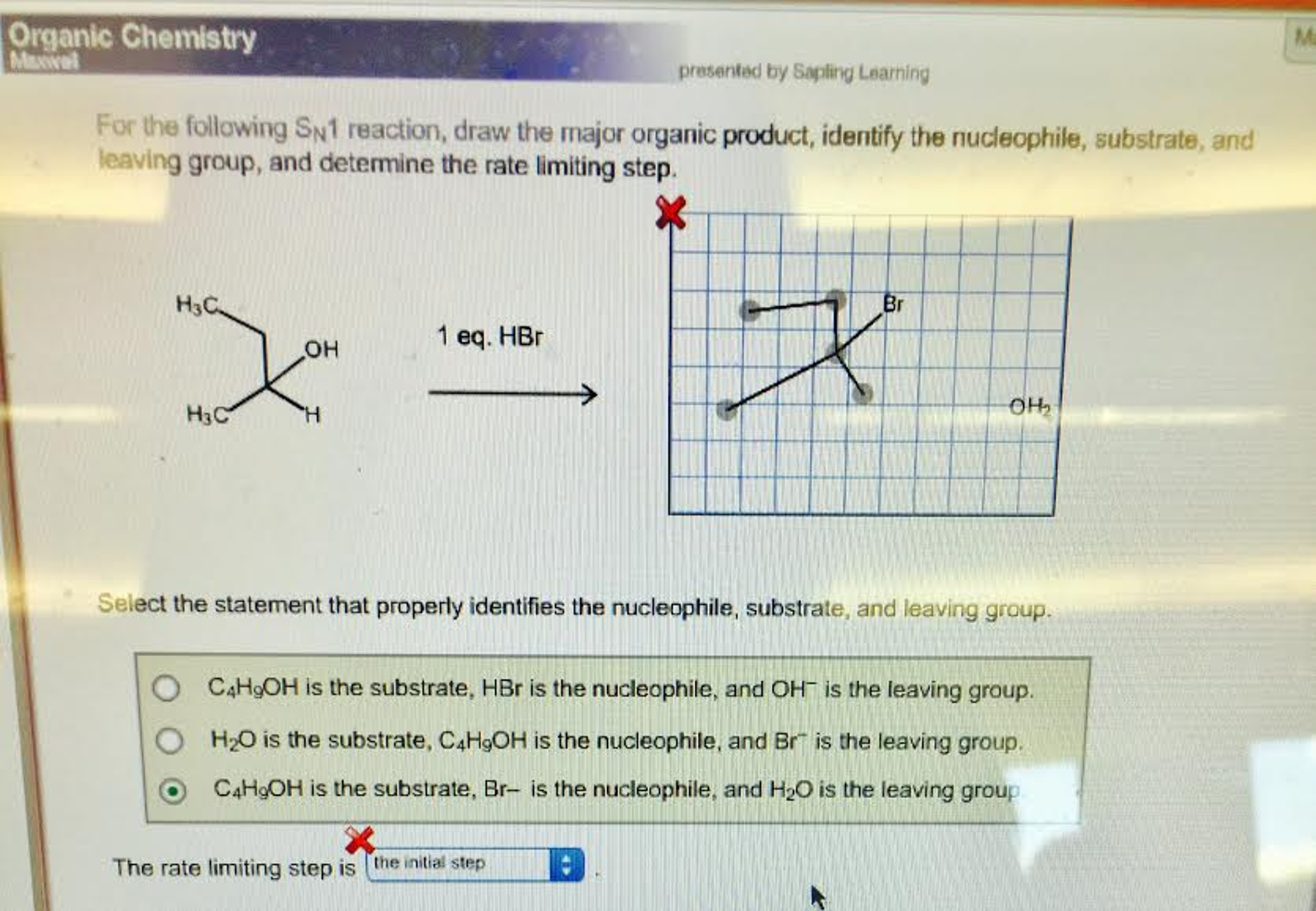
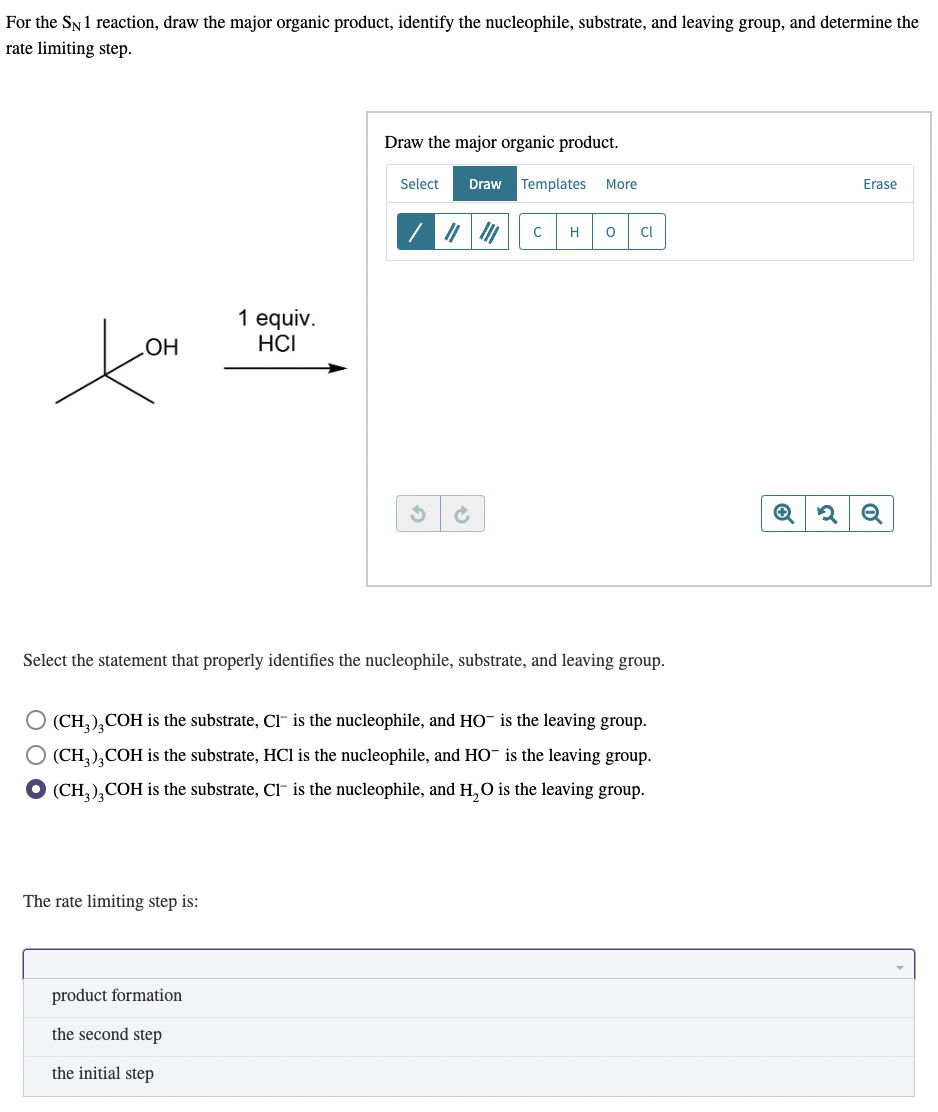
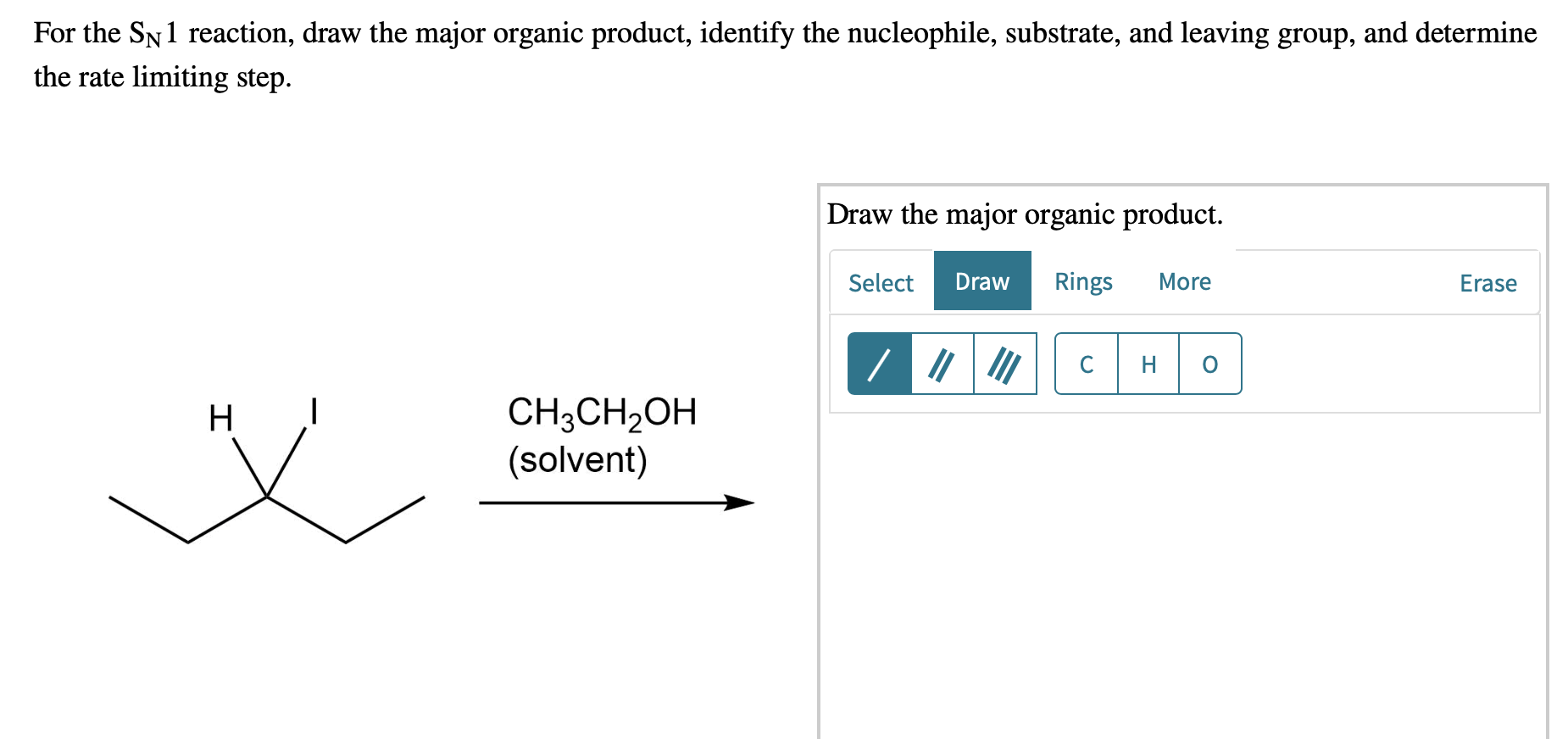
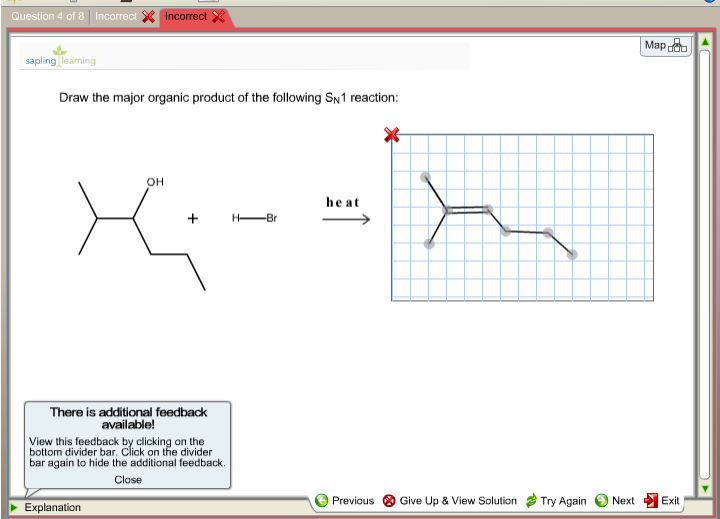
For The Sn1 Reaction Draw The Major Organic Product
For The Sn1 Reaction Draw The Major Organic Product - Web sn1 reactions give racemization at the α carbon atom. If there are other chiral centres, you get a pair of diastereomers. Web draw a mechanism for and organic products of the following sn1 reaction, and predict whether each product you draw is either major or minor. In this practice problem, you will need to determine the major organic product and the mechanism of each reaction. Web for the three‑step sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. If that is the only chiral centre, you get a racemic mixture. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web discuss how the structure of the substrate affects the rate of a reaction occurring by the s n 1 mechanism. Identify the substrate (molecule that is being reacted), the nucleophile (the reactant that donates an electron pair), and the leaving. Web select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate, including the r or s designation where appropriate, and draw the major organic product (s) for the sn1 reaction. Web so this might be an sn2 reaction, an sn1 reaction, an e2 reaction, or an e1 reaction. Web draw the major organic product of the sn1 reaction: Web sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. Web since tertiary carbocation is an electrophile and we are provided with a nucleophile ( methanol) , nucleophile will attack the carbocation which is on tertiary carbon. Web draw a mechanism for and organic products of the following sn1 reaction, and predict whether each product you draw is either major or minor. Arrange a given list of carbocations (including benzyl and allyl) in order. Include wedge/dash bonds and h on a stereocenter. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web for the three‑step sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web summary of sn1 and sn2 reactions and the types of molecules and solvents that favor each. We will learn about the reaction mechanisms, and how. The given reaction is a nu. If that is the only chiral centre, you get a racemic mixture. Draw the major organic product for the reaction shown. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Arrange a given list of carbocations (including benzyl and allyl) in order. Web summary of sn1 and sn2 reactions and the types of molecules and solvents that favor each. Identify the substrate (molecule that is being reacted), the nucleophile (the reactant that donates an electron pair), and the leaving. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. If that is the only chiral centre, you get a racemic mixture. In the presence of hbr, first lone pair on oxygen abstract then r…. Web sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. If there are other chiral centres, you get a pair of diastereomers. Web. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. We will learn about the reaction mechanisms, and how. Web discuss how the structure of the substrate affects the rate of a reaction occurring by the s n 1 mechanism. Web draw the major organic product of. Web summary of sn1 and sn2 reactions and the types of molecules and solvents that favor each. Do not draw counterions or byproducts. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web draw a mechanism for and organic products of the following sn1 reaction, and. Web for the three‑step sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web sn1 reactions give racemization at the α carbon atom. Web a potential energy diagram for an s n 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the. Web select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate, including the r or s designation where appropriate, and draw the major organic product (s) for the sn1 reaction. Web sn1 reactions give racemization at the α carbon atom. Web a substitution reaction is one in which one atom replaces the other atom. Web sn1, sn2, e1, and e2. Draw the major organic product of the following sn1 reaction: Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. In this practice problem, you will need to determine the major organic product and the mechanism of each reaction. Do not draw counterions or byproducts. The rate. Draw the major organic product for the reaction shown. Include wedge/dash bonds and h on a stereocenter. Here’s the best way to solve it. Draw the major organic product of the following sn1 reaction: Web select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate, including the r or s designation where appropriate, and draw the major organic product (s). Web a potential energy diagram for an s n 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than. Web discuss how the structure of the substrate affects the rate of a reaction occurring by the s n 1 mechanism. In the presence of hbr,. Draw the major organic product for the reaction shown. Web a potential energy diagram for an s n 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than. Web here’s how to approach this question. The rate limiting step of an sn1 reaction is the.. Web summary of sn1 and sn2 reactions and the types of molecules and solvents that favor each. Web sn1 sn2 e1 e2 practice problems. Do not draw counterions or byproducts. Web for the sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Web draw a mechanism for and organic. Web select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate, including the r or s designation where appropriate, and draw the major organic product (s) for the sn1 reaction. The given reaction is a nu. If that is the only chiral centre, you get a racemic mixture. In this practice problem, you will need to determine the major organic product and the mechanism of each reaction. Draw the major organic product of the following sn1 reaction: There are 3 steps to solve this one. Identify the substrate (molecule that is being reacted), the nucleophile (the reactant that donates an electron pair), and the leaving. Web summary of sn1 and sn2 reactions and the types of molecules and solvents that favor each. Web draw a mechanism for and organic products of the following sn1 reaction, and predict whether each product you draw is either major or minor. Web in an sn1 reaction, the major organic product is formed by the substitution of a leaving group with a nucleophile. Here’s the best way to solve it. Web sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. Web sn1 sn2 e1 e2 practice problems. Web so this might be an sn2 reaction, an sn1 reaction, an e2 reaction, or an e1 reaction. In the presence of hbr, first lone pair on oxygen abstract then r…. Web for the three‑step sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step.Solved Draw The Major Organic Product(s) Of The Following...
Draw The Major Organic Product Of The SN1 Reaction
Solved draw the major products of the SN1 reaction shown
Solved For the following SN1 reaction, draw the major
Solved Draw the major organic product of the SN1 reaction
Solved For The Following SN1 Reaction, Draw The Major Org...
Solved For the SN1 reaction, draw the major organic product,
Solved For the Sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product,
Solved Draw the major organic product of the following
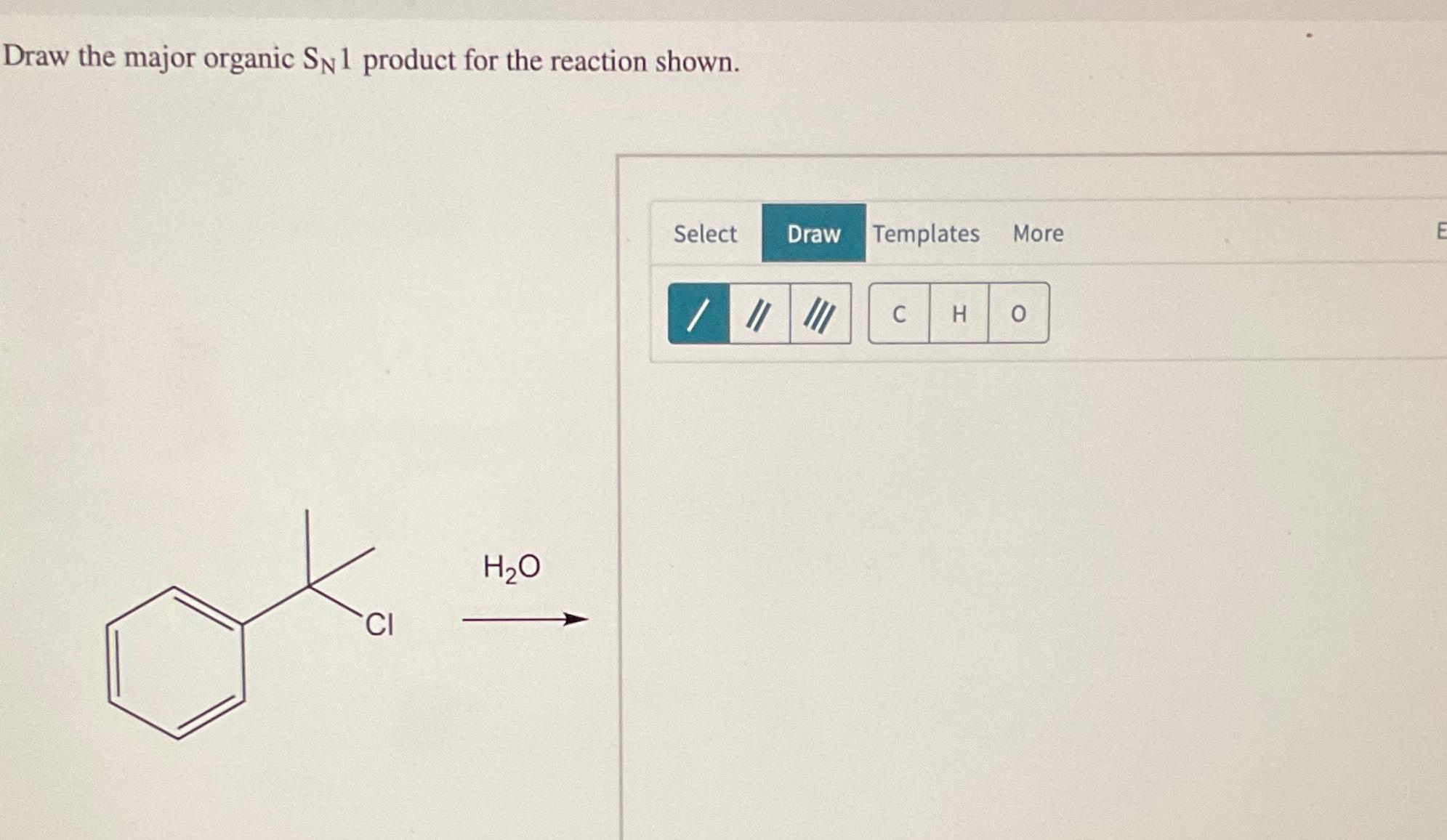
Solved Draw the major organic SN1 product for the reaction
We're Going To Look At All The Clues And Figure Out What's Likely To Occur, And Then Actually Draw.
The Rate Limiting Step Of An Sn1 Reaction Is The.
If There Are Other Chiral Centres, You Get A Pair Of Diastereomers.
Web Discuss How The Structure Of The Substrate Affects The Rate Of A Reaction Occurring By The S N 1 Mechanism.
Related Post: