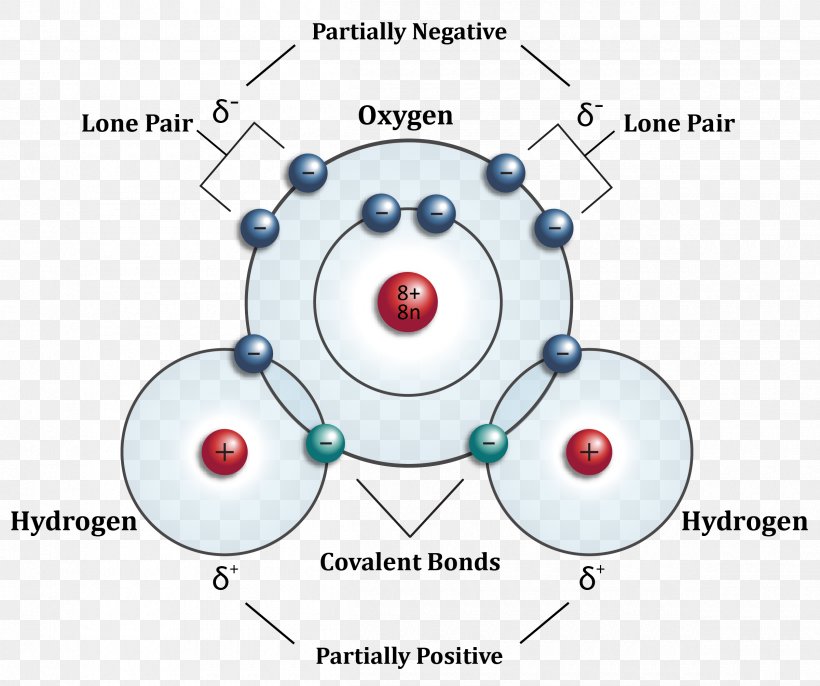
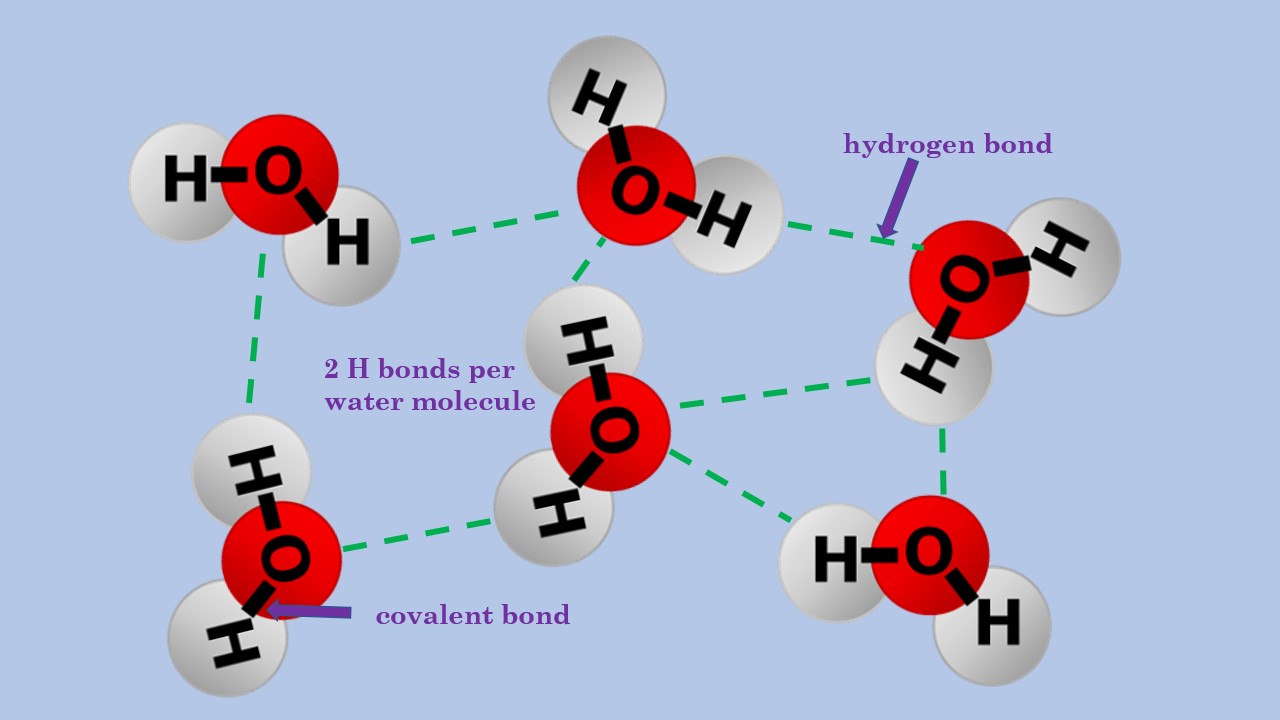
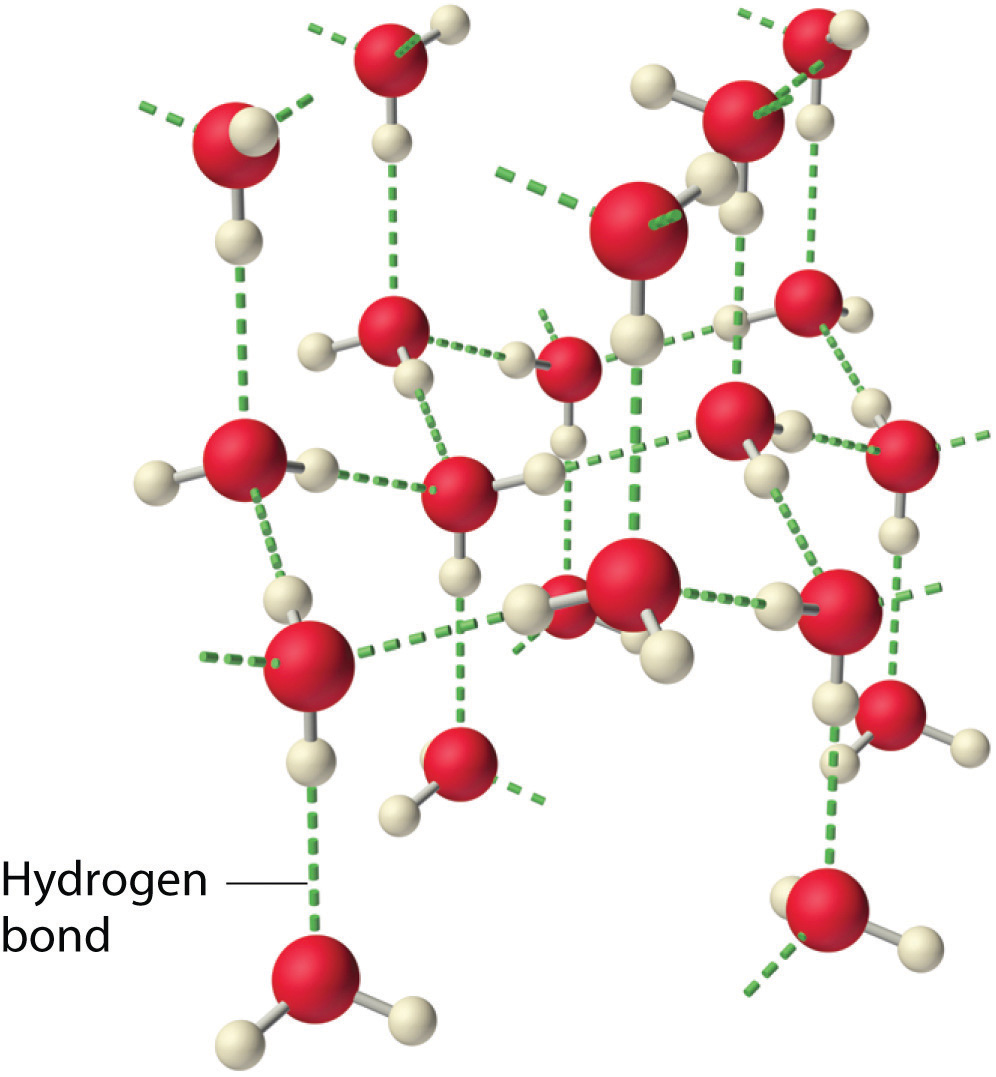
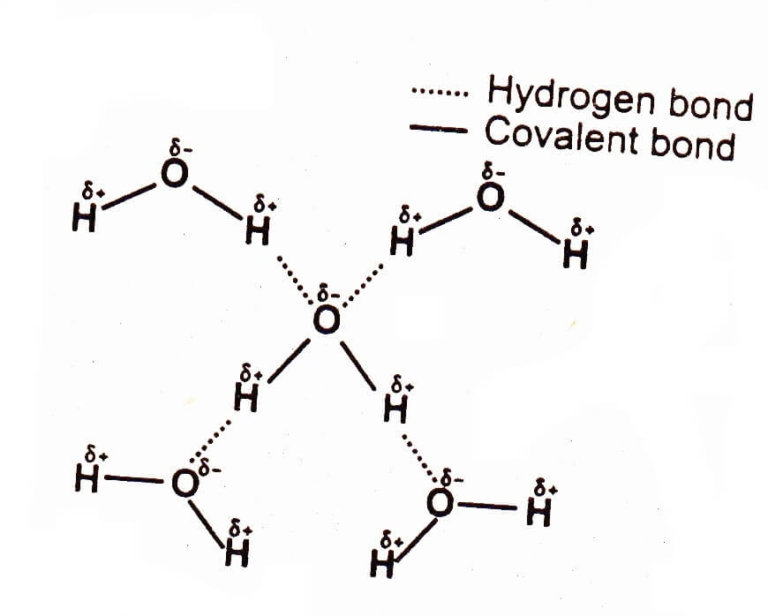
Hydrogen Bond Drawing
Hydrogen Bond Drawing - Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Web water owes these unique properties to the polarity of its molecules and, specifically, to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with other molecules. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. These interact to make a hydrogen bond, and it is still a hydrogen bond irrespective of which end you look at it from. These properties allow cells to regulate their internal temperature, provide lubrication, and facilitate nutrient uptake and waste removal. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat capacity, and surface tension. A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. Web this video shows three examples of drawing for the formation of hydrogen bond. Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat capacity, and surface tension. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded to. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains (intermolecular bonding); A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat capacity, and surface tension. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains (intermolecular bonding); Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded to. A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. These properties allow cells to regulate their internal temperature, provide lubrication, and facilitate nutrient uptake and waste removal. Web hydrogen bonding plays an essential role in natural polymers of biological origin in two ways: Web this video shows three examples of drawing for the formation of hydrogen bond. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Web hydrogen bonding plays an essential role in natural polymers of biological origin in two ways: The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. These interact to make a hydrogen bond, and it is still a hydrogen bond irrespective of which end you look at it from. Web water owes these. Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat capacity, and surface tension. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule.. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains (intermolecular bonding); Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded to. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Web water owes these unique properties to the polarity of its molecules and, specifically,. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded to. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Web water owes these unique properties to the polarity of its molecules and, specifically, to their. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. These properties allow cells to regulate their internal temperature, provide lubrication, and facilitate nutrient uptake and waste removal. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains (intermolecular bonding); A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Web this video shows three examples of drawing for the formation of hydrogen bond. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat. Web water owes these unique properties to the polarity of its molecules and, specifically, to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with other molecules. Web hydrogen bonding plays an essential role in natural polymers of biological origin in two ways: Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains (intermolecular bonding); Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Web hydrogen. Web hydrogen bonding plays an essential role in natural polymers of biological origin in two ways: Web this video shows three examples of drawing for the formation of hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded. These properties allow cells to regulate their internal temperature, provide lubrication, and facilitate nutrient uptake and waste removal. Web a hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Below, we'll look at how this hydrogen bonding works. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polymer chains. Web water owes these unique properties to the polarity of its molecules and, specifically, to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with other molecules. Hydrogen bond is an attraction force that formed between 2 molecules with hydrogen atoms that bonded to. These properties allow cells to regulate their internal temperature, provide lubrication, and facilitate nutrient uptake and waste removal. These interact to make a hydrogen bond, and it is still a hydrogen bond irrespective of which end you look at it from. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. Web hydrogen bonding plays an essential role in natural polymers of biological origin in two ways: Web hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its high boiling point, high heat capacity, and surface tension. A hydrogen bond be both intermolecular and intramolecular. Hydrogen bonding between different parts of. Web this video shows three examples of drawing for the formation of hydrogen bond. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge.Structure of hydrogenbond environments Schematic representation of the
How To Draw Hydrogen Bonds Askworksheet
Draw a diagram of water molecules, labeling the hydrogen bond and
Hydrogen Atom Water Molecule Molecular Orbital Diagram, PNG
Primary and Secondary Bonds Owlcation
Hydrogen Bonds — Overview & Examples Expii
Hydrogen Bonding in water Dr. M. Chemistry Tutor
11.5 Hydrogen Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Hydrogen Bonding Chemistry Skills
Hydrogen Bonding American Chemical Society
Below, We'll Look At How This Hydrogen Bonding Works.
Web A Hydrogen Bond Is The Attractive Force Between The Hydrogen Attached To An Electronegative Atom Of One Molecule And An Electronegative Atom Of A Different Molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding Between Adjacent Polymer Chains (Intermolecular Bonding);
Related Post: