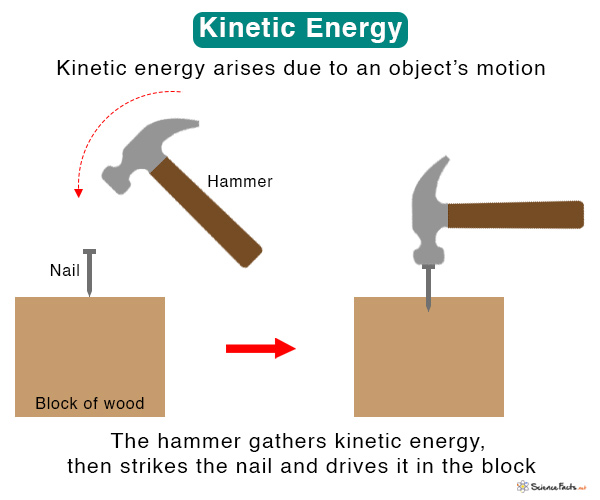
Kinetic Energy Drawing
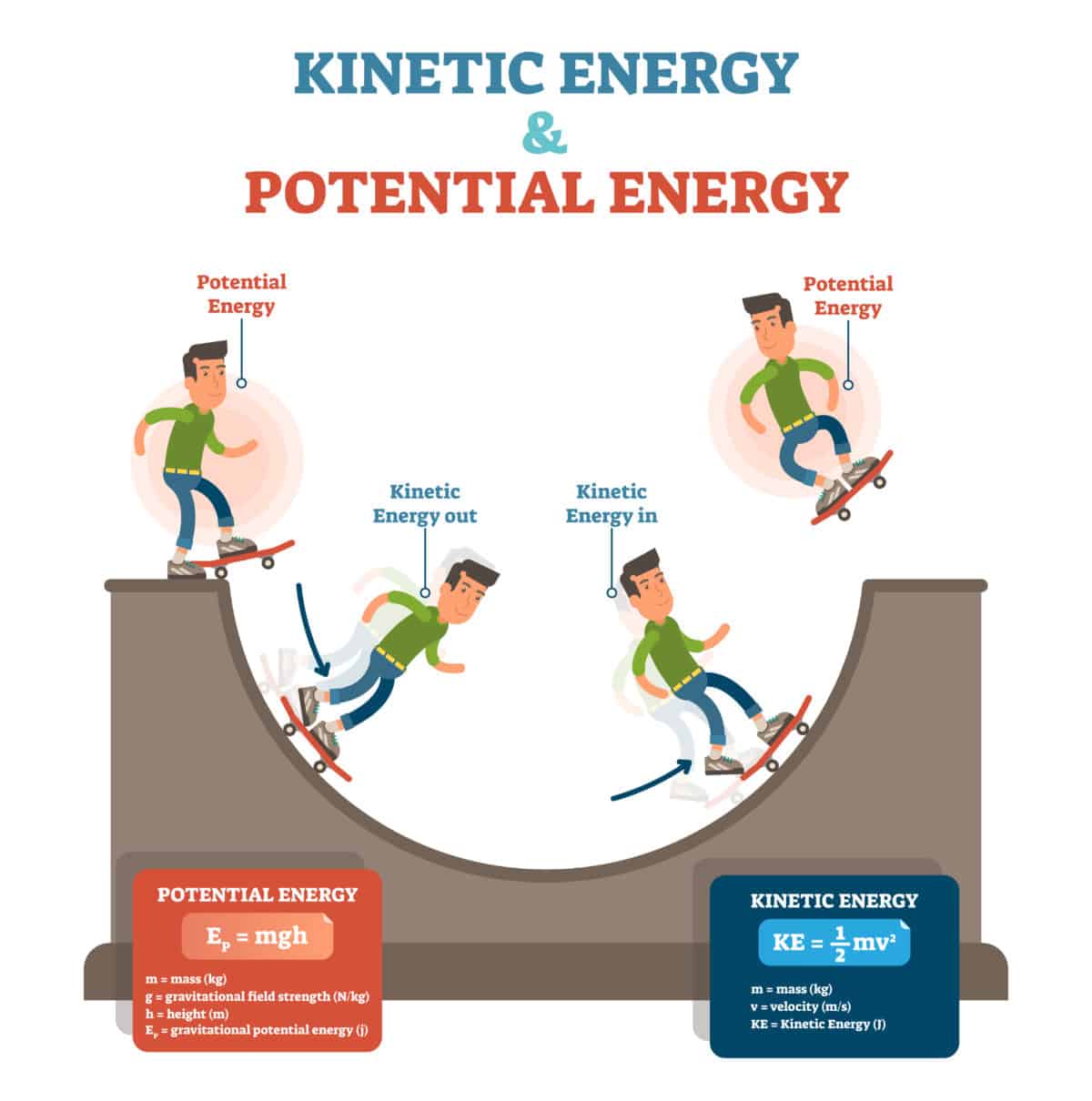
Kinetic Energy Drawing - We’ll also dive into the differences between kinetic and potential energy. Web kinetic energy is a form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion. The energy that a moving object has in addition to its rest energy. Animations present in the video are transformed into a single static screen image in the slides. 1 k j = 1000 j. Kinetic energy is k on an energy graph. Web energy is an important concept in physics that is used to understand large and small processes. At \(x=\pm d\), the potential energy is equal to \(e\), so the kinetic energy is zero. To draw the energy graph of a system, the. Web so the formula for kinetic energy is that it's equal to 1/2 times the mass of the object, times the magnitude of its velocity squared, or another way to think about it, its speed squared. Ke = ½ m v 2. Some students profit from reviewing the slides of the presentation. For example, a flying squirrel might collide with a stationary chipmunk. They are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. Objects in motion have energy associated with them. With the paper roller coasters: Kinetic and potential energy lesson (or activity ), students build their own model paper roller coasters and explore how conservation of energy applies in terms of gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, and friction. M is the object's mass (kg) v is the object's speed (m/s) Web so the formula for kinetic energy is that it's equal to 1/2 times the mass of the object, times the magnitude of its velocity squared, or another way to think about it, its speed squared. Kinetic energy, often abbreviated as ke, is usually given in the standard s.i. We’ll also dive into the differences between kinetic and potential energy. Here, we’ll begin with the energy of a moving object by exploring examples of kinetic energy and how to calculate it. Kinetic and potential energy lesson (or activity ), students build their own model paper roller coasters and explore how conservation of energy applies in terms of gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, and friction. Kinetic energy, potential energy, and the kinetic plus potential energy line. Ke is also given in units of kilo joules (kj). Web an energy diagram provides us a means to assess features of physical systems at a glance. It’s plausible to suppose that the greater the velocity of a body, the greater effect it could have on other bodies. An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass. Web the kinetic energy of an object is the energy associated with the object which is under motion. Web choose from 178,770 kinetic energy drawing stock illustrations from istock. M is the object's mass (kg) v is the object's speed (m/s) Discover examples, formulas, and more in this comprehensive article on kinetic energy. ² ² 1 j = 1 k g ∗ ( m ² / s ²). Imagine two objects moving at the same speed. The energy that a moving object has in addition to its rest energy. The energy that a moving object has in addition to its rest energy. Web these graphs consist of three main components: Ke = ½ m v 2. You can view this video on youtube or here on our website: Discover examples, formulas, and more in this comprehensive article on kinetic energy. The equation for kinetic energy is 1/2 m v squared. We’ll also dive into the differences between kinetic and potential energy. Web the kinetic energy of an object is the energy associated with the object which is under motion. Kinetic and potential energy lesson (or activity ), students build their own model paper roller coasters and explore how conservation of. A few things to note: [2] the kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, force ( f) times displacement ( s ), needed to achieve its stated velocity. Web the kinetic energy of an object is the energy associated with the object which is under motion. They are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy. So as mass increases, kinetic energy increases, like the more massive cheddar versus the swiss, and as velocity increases, kinetic energy increases even more, like the speedy swiss versus the slower cheddar. Here is a look at kinetic energy, including its definition, examples, units, formula, and how to calculate it. If work , which transfers energy, is done on an. 1 k j = 1000 j. Web kinetic energy is the energy that any object with mass has simply because it is moving. M is the object's mass (kg) v is the object's speed (m/s) You can view this video on youtube or here on our website: To draw the energy graph of a system, the. To draw the energy graph of a system, the. Web slides from the video tutorial. Kinetic energy is k on an energy graph. Ke is also given in units of kilo joules (kj). Some students profit from reviewing the slides of the presentation. To draw the energy graph of a system, the. Web so the formula for kinetic energy is that it's equal to 1/2 times the mass of the object, times the magnitude of its velocity squared, or another way to think about it, its speed squared. At \(x=\pm d\), the potential energy is equal to \(e\), so the kinetic energy is. M is the object's mass (kg) v is the object's speed (m/s) Web choose from 178,770 kinetic energy drawing stock illustrations from istock. Evaluate the kinetic energy of a body, relative to different frames of reference. Kinetic energy, often abbreviated as ke, is usually given in the standard s.i. They are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy. We provide them here on our website. It is defined as “the energy required by a body to accelerate from rest to stated velocity.” it is a scalar quantity. So as mass increases, kinetic energy increases, like the more massive cheddar versus the swiss, and as velocity increases, kinetic energy increases even more, like the speedy swiss versus the slower. A few things to note: Web learn about kinetic energy and its types, including translational, rotational, vibrational, thermal, and electrical. View drawing of kinetic energy videos. If an object is not moving, it has no kinetic energy. We will examine a couple of simple examples, and then show how it can be used for more advanced cases in physics and chemistry. The energy that a moving object has in addition to its rest energy. You can view this video on youtube or here on our website: Web the energy transferred is known as kinetic energy, and it depends on the mass and speed achieved. Web kinetic energy is the energy that any object with mass has simply because it is moving. Web the kinetic energy of an object is the energy associated with the object which is under motion. Here, we’ll begin with the energy of a moving object by exploring examples of kinetic energy and how to calculate it. Kinetic energy, potential energy, and the kinetic plus potential energy line. Web slides from the video tutorial. Kinetic energy can be transferred between objects and transformed into other kinds of energy. Web an energy diagram provides us a means to assess features of physical systems at a glance. ² ² 1 j = 1 k g ∗ ( m ² / s ²).Energy Definition, Formula, Examples Teachoo
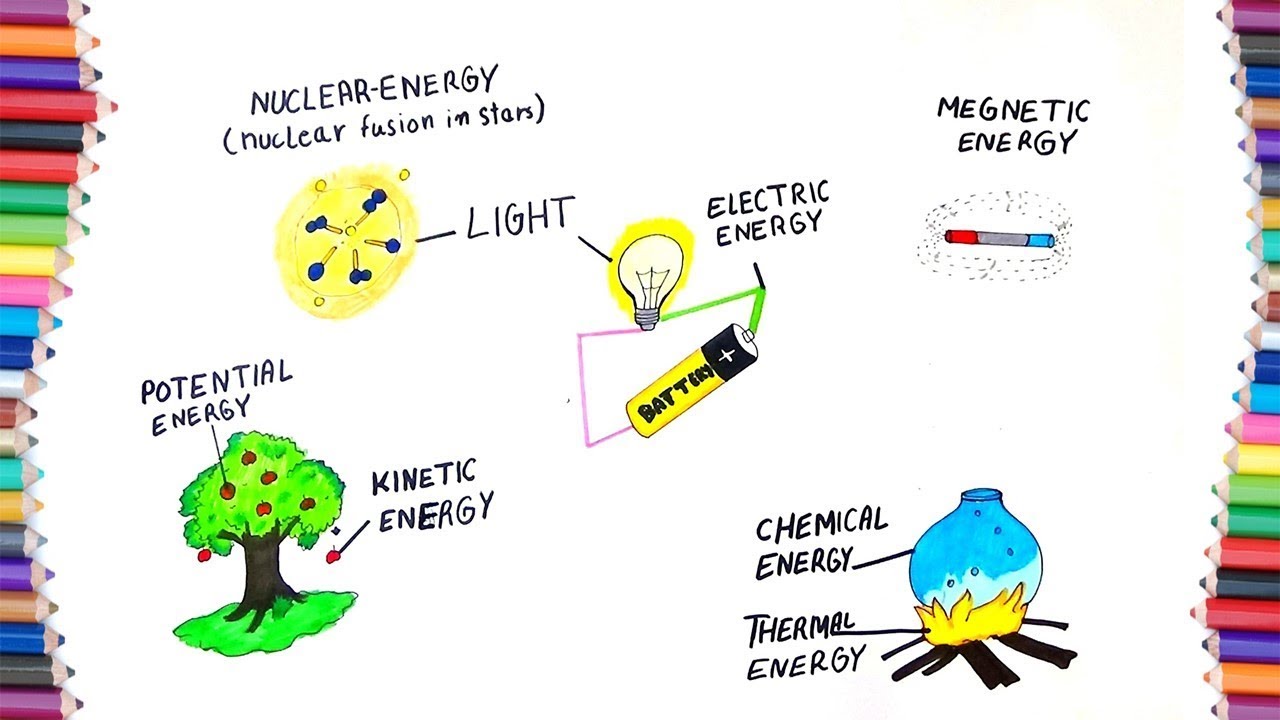
10 Examples Of Energy
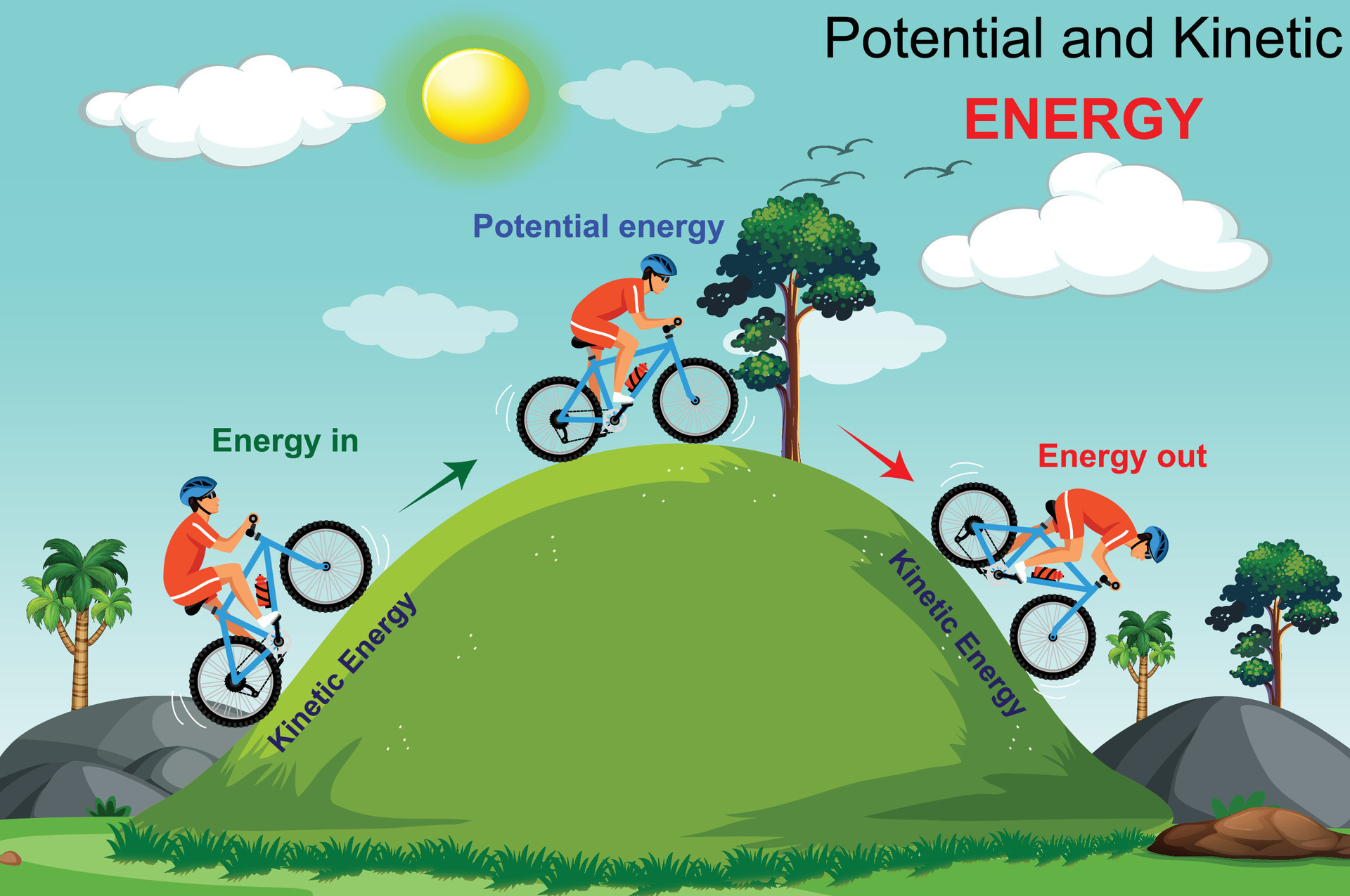
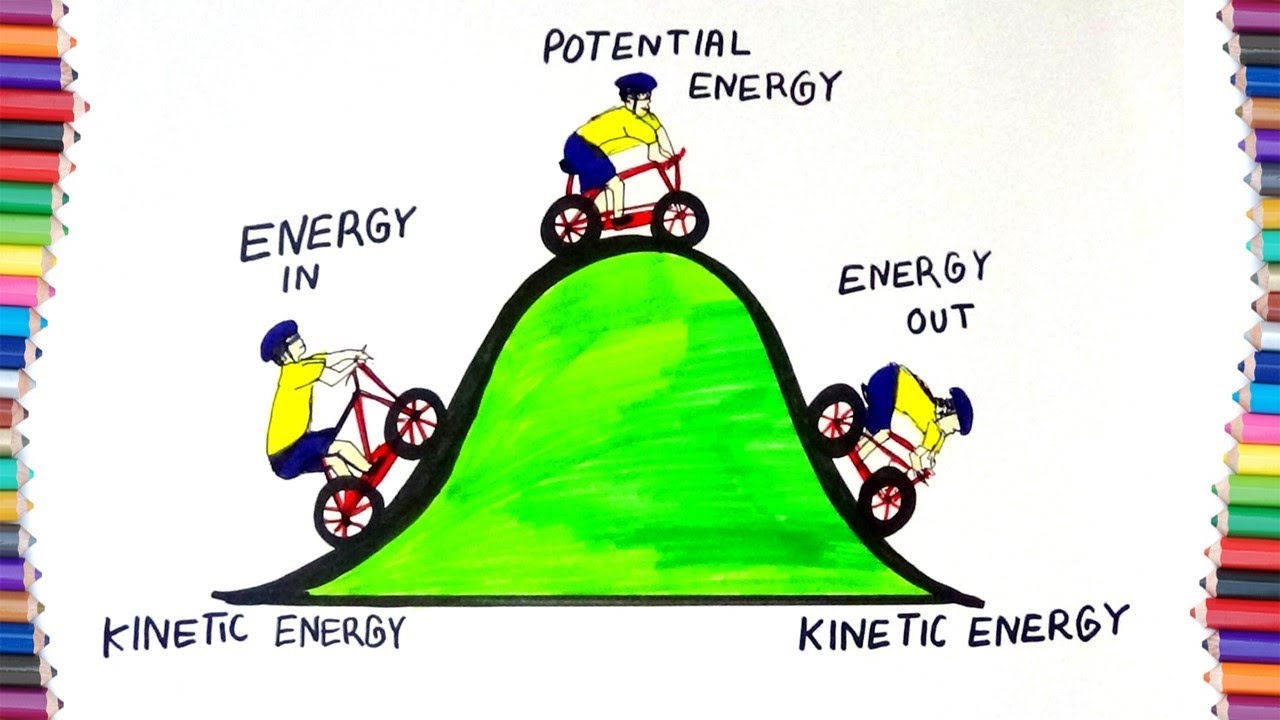
And Potential Energy For Kids Kids Matttroy
Vector illustration about mechanic energy. Scheme with potential
Potential and energy diagram. 27798551 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Examples Of Energy With Pictures Assessment And Video Edu
Potential And Energy Diagram Clip Art Cycle Drawing Vector
Energy Diagram For Kids
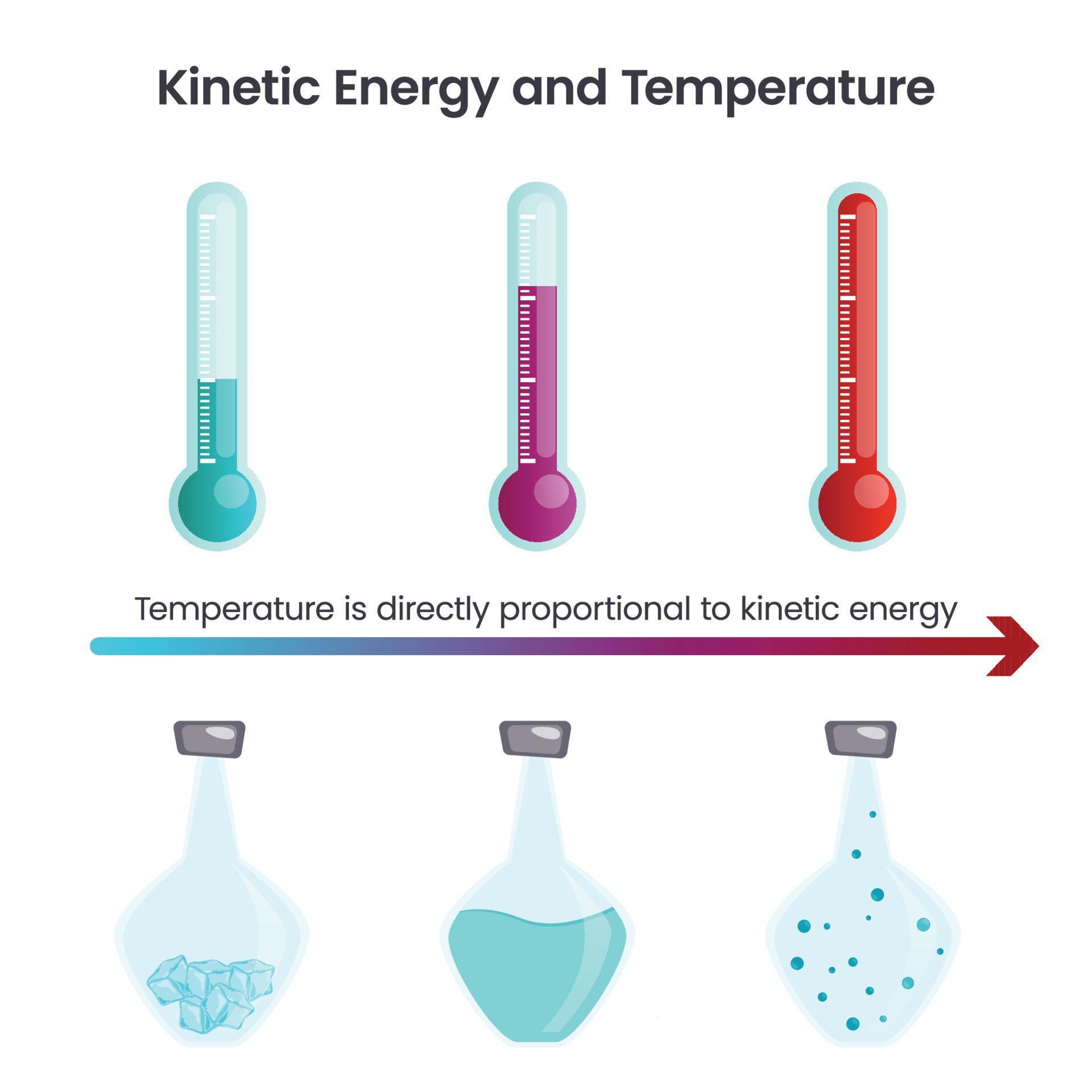
Energy and Temperature science vector graphic 21790106 Vector
List 96+ Pictures Energy Is Energy That An Object Possesses
Ke Is Also Given In Units Of Kilo Joules (Kj).
[2] The Kinetic Energy Of An Object Is Equal To The Work, Force ( F) Times Displacement ( S ), Needed To Achieve Its Stated Velocity.
Kinetic Energy Is K On An Energy Graph.
Web The Energy Diagram Allows Us To Describe The Motion Of The Object Attached To The Spring In Terms Of Energy.
Related Post: