Plasma Membrane Drawing Labeled
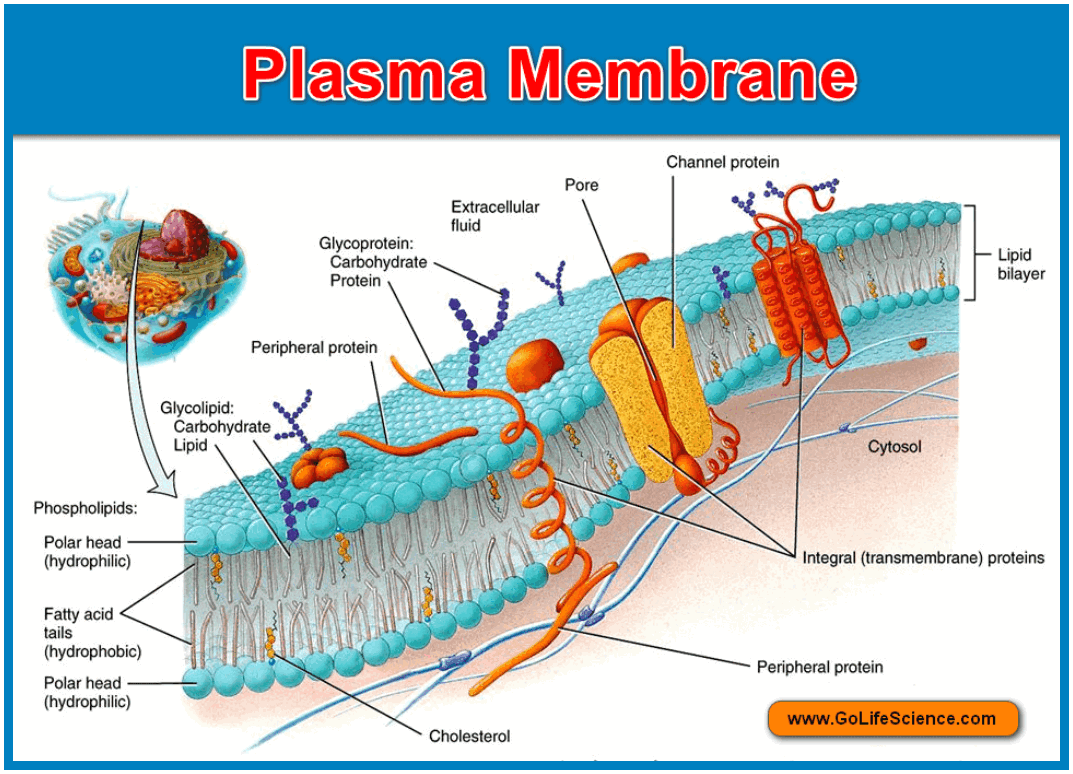
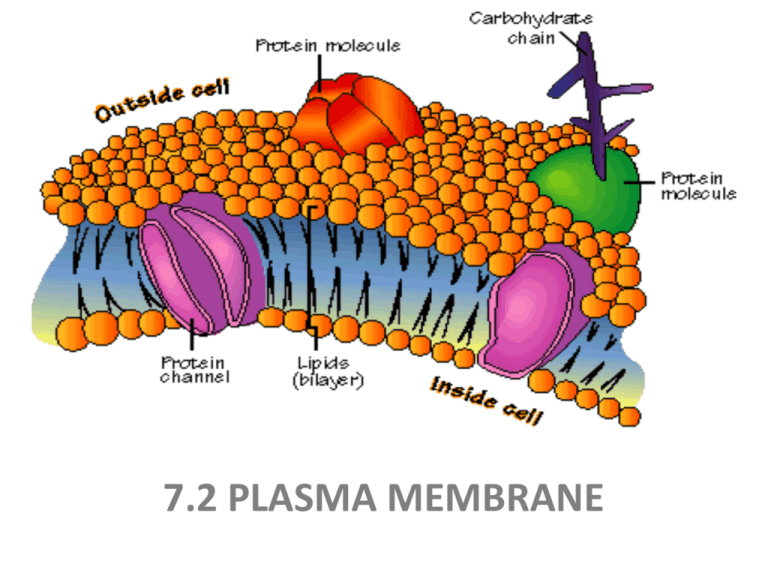
Plasma Membrane Drawing Labeled - The outer membrane contains porins, which form open aqueous channels allowing the free passage of ions and small molecules. Web the fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as comprised of diverse components—including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that are able to flow and change position, while maintaining the basic integrity of the membrane. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. Isolate cell’s contents from outside environment. Web the plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Web an animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Web the plasma membrane of some bacteria is surrounded by a cell wall and a distinct outer membrane. Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. Web a plasma membrane’s principal components are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Web the plasma membrane is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. Each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. Web the plasma membrane is a structure that forms a barrier between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment outside the cell. Organelles are structures that are themselves encased in membranes. Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). The membrane also protects and supports. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). The membrane also protects and supports. Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment. Web the plasma membrane is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell. Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Web like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. Web in eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane surrounds a cytoplasm filled with ribosomes and organelles. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. Web an animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Structure and function of the cell membrane. The membrane also protects and supports. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and. Structure and function of the cell membrane. Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Without the plasma membrane, there would be no cell. Web plasma membrane is selectively permeable to organic molecules and ions, it regulates the movement of particles in and out of organelles and cells. Web a plasma. The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'heads' of the phospholipids labelled. Image modified from openstax biology. Web the plasma membrane is a protective barrier that surrounds cells. Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Web the fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as comprised. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. Web plasma membrane is selectively permeable to organic molecules and ions, it regulates the movement of particles in and out of organelles and cells. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. The membrane also protects and supports.. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. Web plasma membrane is selectively permeable to organic molecules and ions, it regulates the movement of particles in and out of organelles and cells. Web the plasma membrane is a. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. The membrane also protects and supports. The outer membrane contains porins, which form open aqueous channels allowing the free passage of ions and small molecules. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. It is also simply called the cell membrane. Web a plasma membrane’s principal components are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Isolate cell’s contents from outside environment. Web the fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as comprised. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between the compartments inside and outside of the cell. Web as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. Web a. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. Web a plasma membrane’s principal components are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Web just as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane). Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Structure and function of the cell membrane. Web the fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as comprised of diverse components—including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that are able to flow. The outer membrane contains porins, which form open aqueous channels allowing the free passage of ions and small molecules. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. Phospholipids are the base of the plasma membrane because they have hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends that form a bilayer. Web the plasma membrane is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. Web a plasma membrane is a layer around a cell that prevents the cytoplasm from getting all mixed up with the outside environment. Each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. Web an animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Web the principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. Web just as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'heads' of the phospholipids labelled. Web the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like, because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Isolate cell’s contents from outside environment.Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology Wise
Plasma Membrane การศึกษา, ชีววิทยา
Cell Biology Glossary Membrane Structure Overview Draw It to Know It
Labeled Diagram Of Plasma Membrane Best Of Plasma Membrane Diagrams
Plasma membrane Basic structure, composition and Function
Plasma membrane. Molecular structure of plasma membrane, eps8 , Ad,
Plasma Membrane Diagrams 101 Diagrams
STRUCTURE of PLASMA MEMBRANE
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
5.4 Plasma Membrane Biology LibreTexts
Unlike The Animal Cell Lacking The Cell Wall, Plant Cells Have A.
Web Like All Other Cellular Membranes, The Plasma Membrane Consists Of Both Lipids And Proteins.
Web The Fluid Mosaic Model Describes The Structure Of The Plasma Membrane As Comprised Of Diverse Components—Including Phospholipids, Cholesterol, Proteins, And Carbohydrates—That Are Able To Flow And Change Position, While Maintaining The Basic Integrity Of The Membrane.
The Cell Membrane Is Semipermeable (Or Selectively Permeable).
Related Post:






/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
