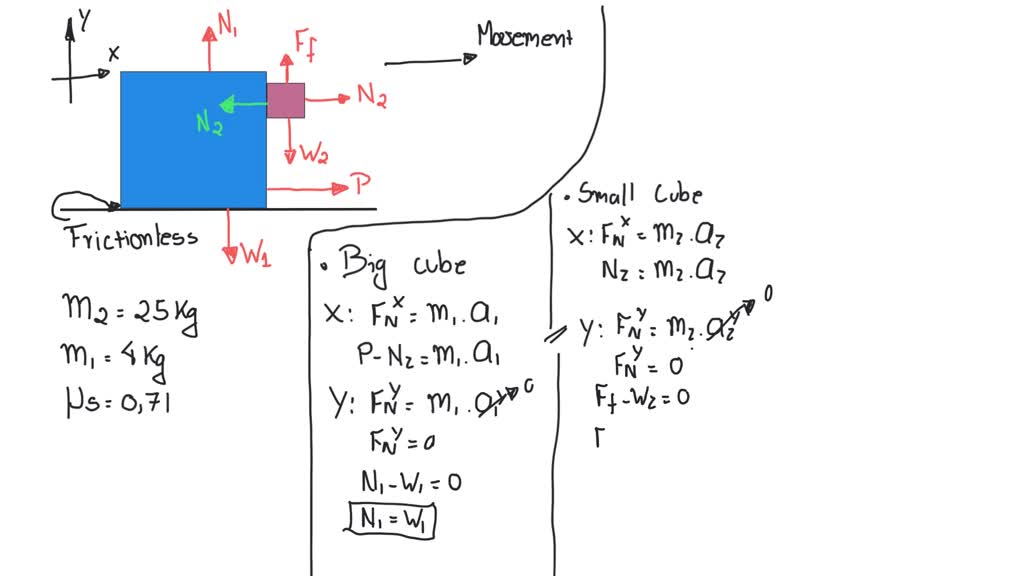
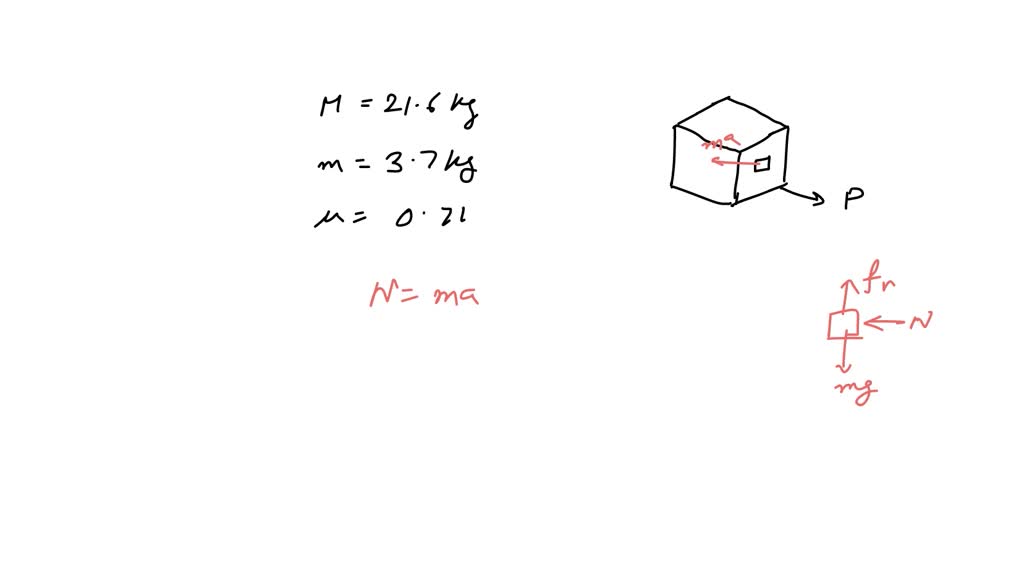
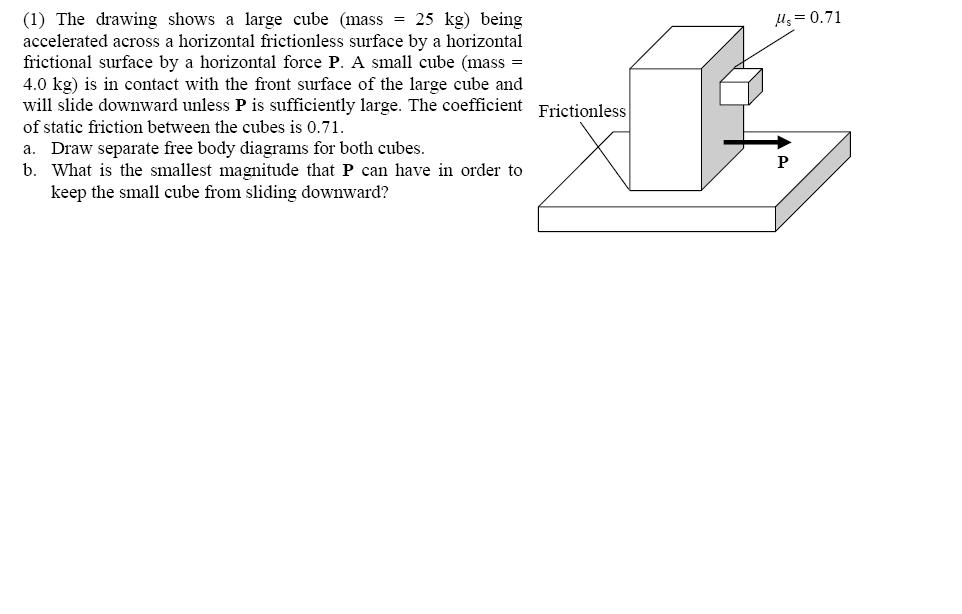
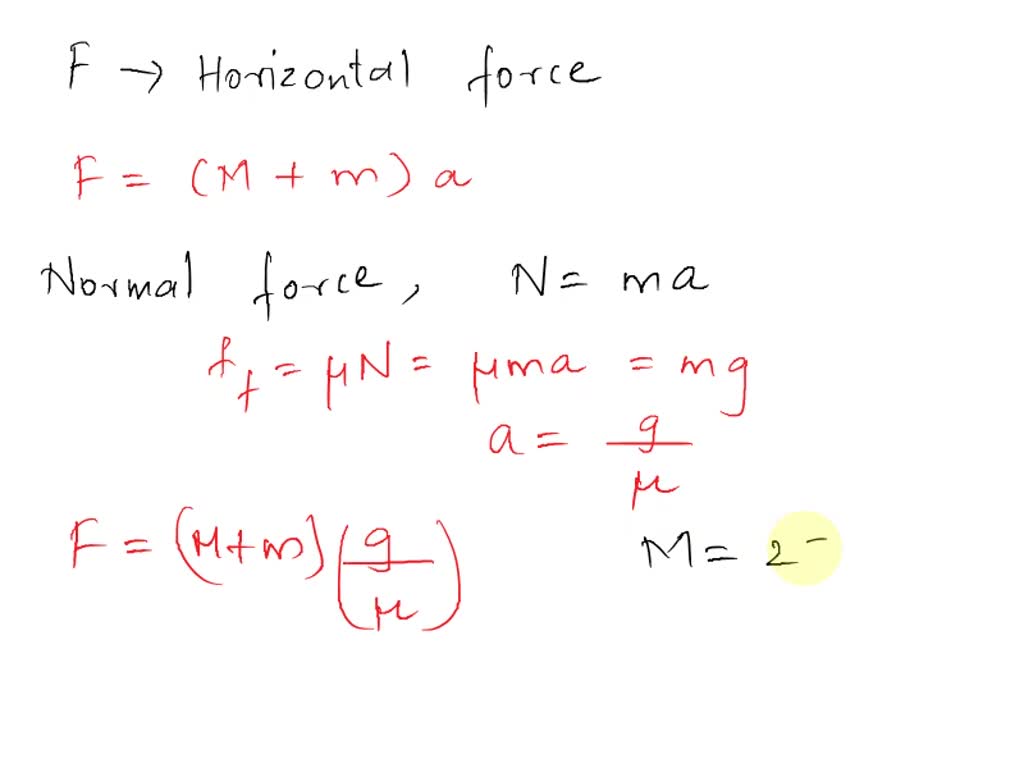The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated - Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 48 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web the drawing shows a large cube mass is 25kg, being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass 4.1 kg) is in contact with. A small cube (mass =. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\vec{p}$. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. A small cube (mass 4.1 kg) is in contact with. Web the drawing shows a large cube mass is 25kg, being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube(mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p →. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.1 kg) is in. A small cube (mass = 3.6 kg) is in contact. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. The big cube tends to move the right when there is a force p on it. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. Web the drawing shows a large cube mass is 25kg, being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p →. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated. The action off the. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. The action off the weight force is suffered. Web a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p → is sufficiently large.. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is. There is one big cube and one smaller cube. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. The coefficient of static friction between. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 48 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p → is sufficiently large. A small cube (mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 48 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The action off the weight force is suffered. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass 22.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. There is one big cube and one small cube in this. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. A small cube (mass = 4.5 kg) is. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p is. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass 22.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows. A small cube(mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with. There is one big cube and one smaller cube. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\vec{p}$. The coefficient of static friction between. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. A small cube (mass =. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is. A small cube mass is 4.0 kg is in contact with. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p.SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
mmh The drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
Answered *44. The drawing shows a large cube… bartleby
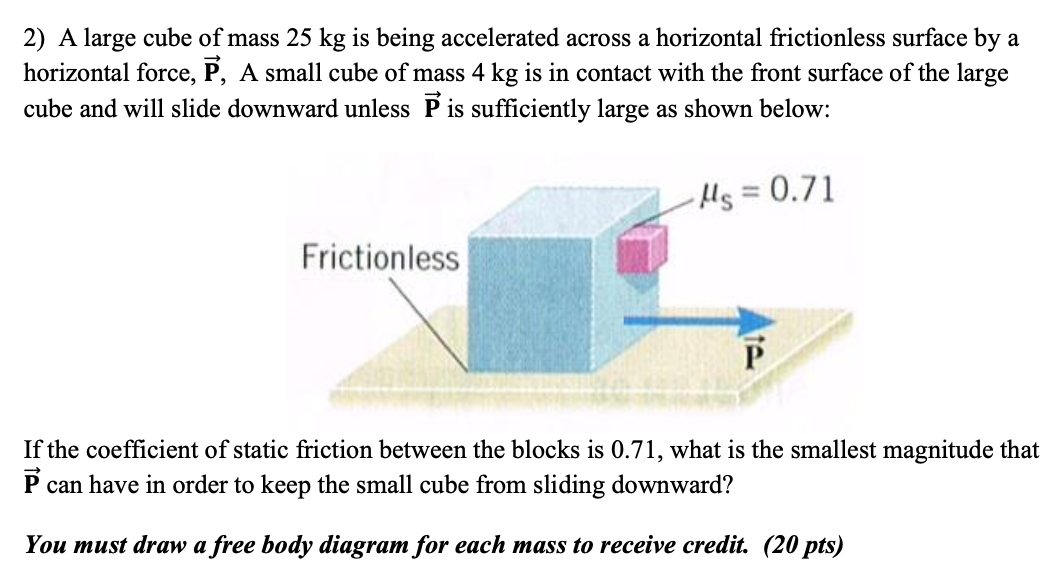
Solved 2) A large cube of mass 25 kg is being accelerated
SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
SOLVED The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.6 kg) being
The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being
SOLVED The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated
SOLVED The figure below shows large cube (mass 30kg) being accelerated
Solved 2) A large cube of mass 25 kg is being accelerated
A Small Cube (Mass = 4.0 Kg) Is In.
Web The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 25 Kg) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force.
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 28.6 Kg) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force P.
Web The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 48 Kg) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force.
Related Post: