Vesicles Drawing
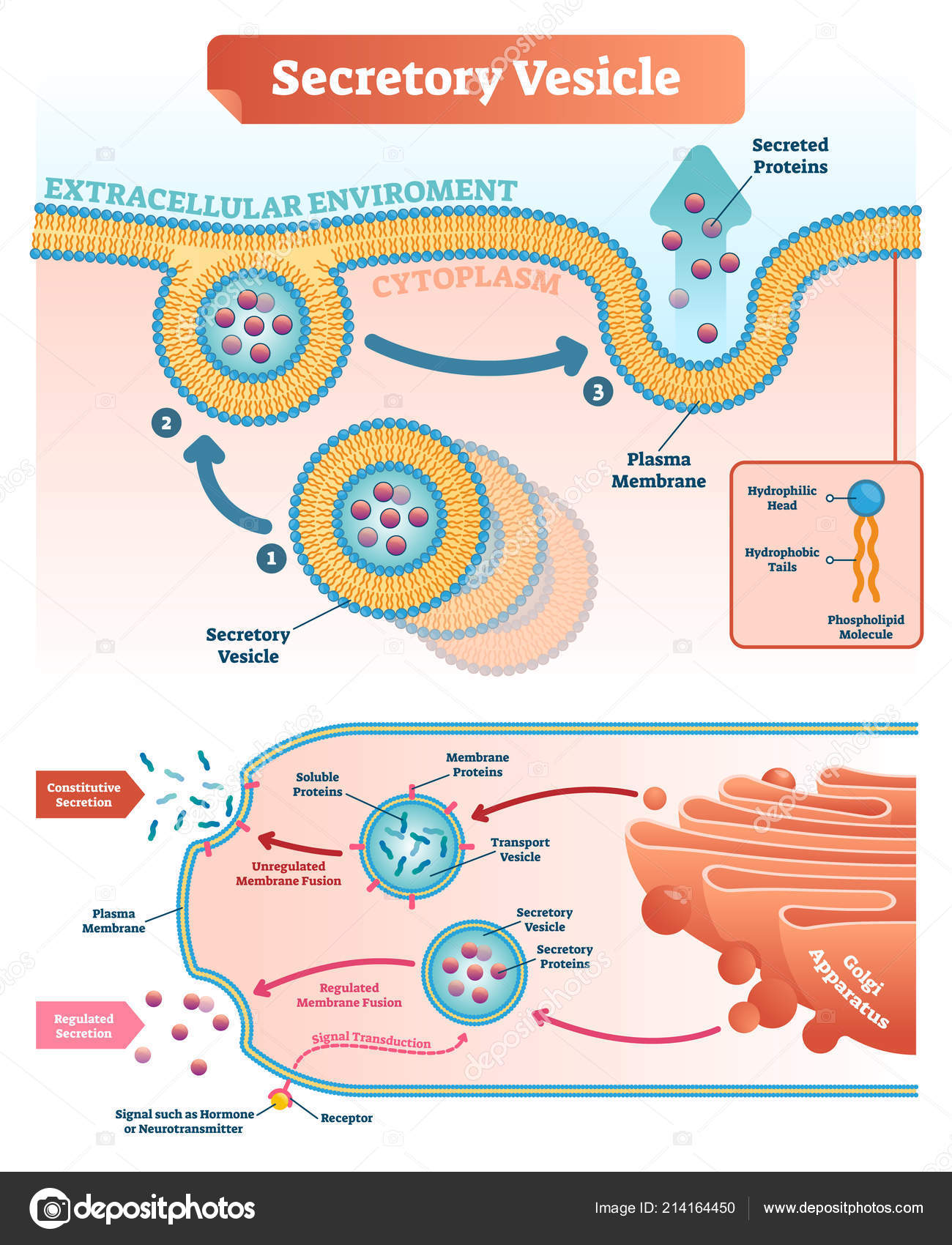
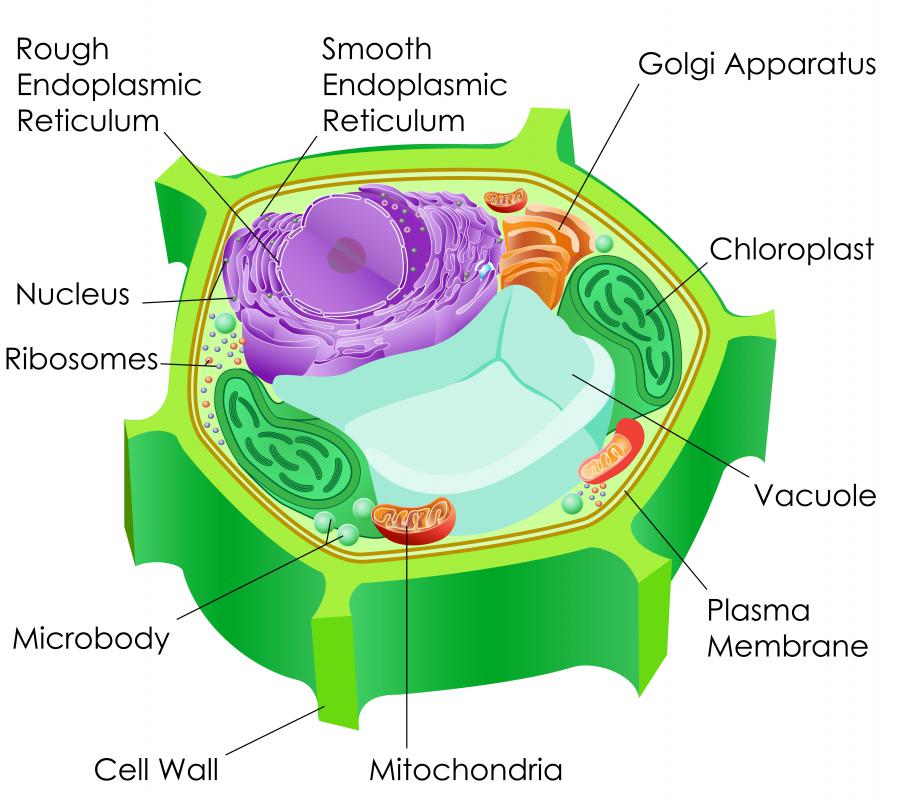
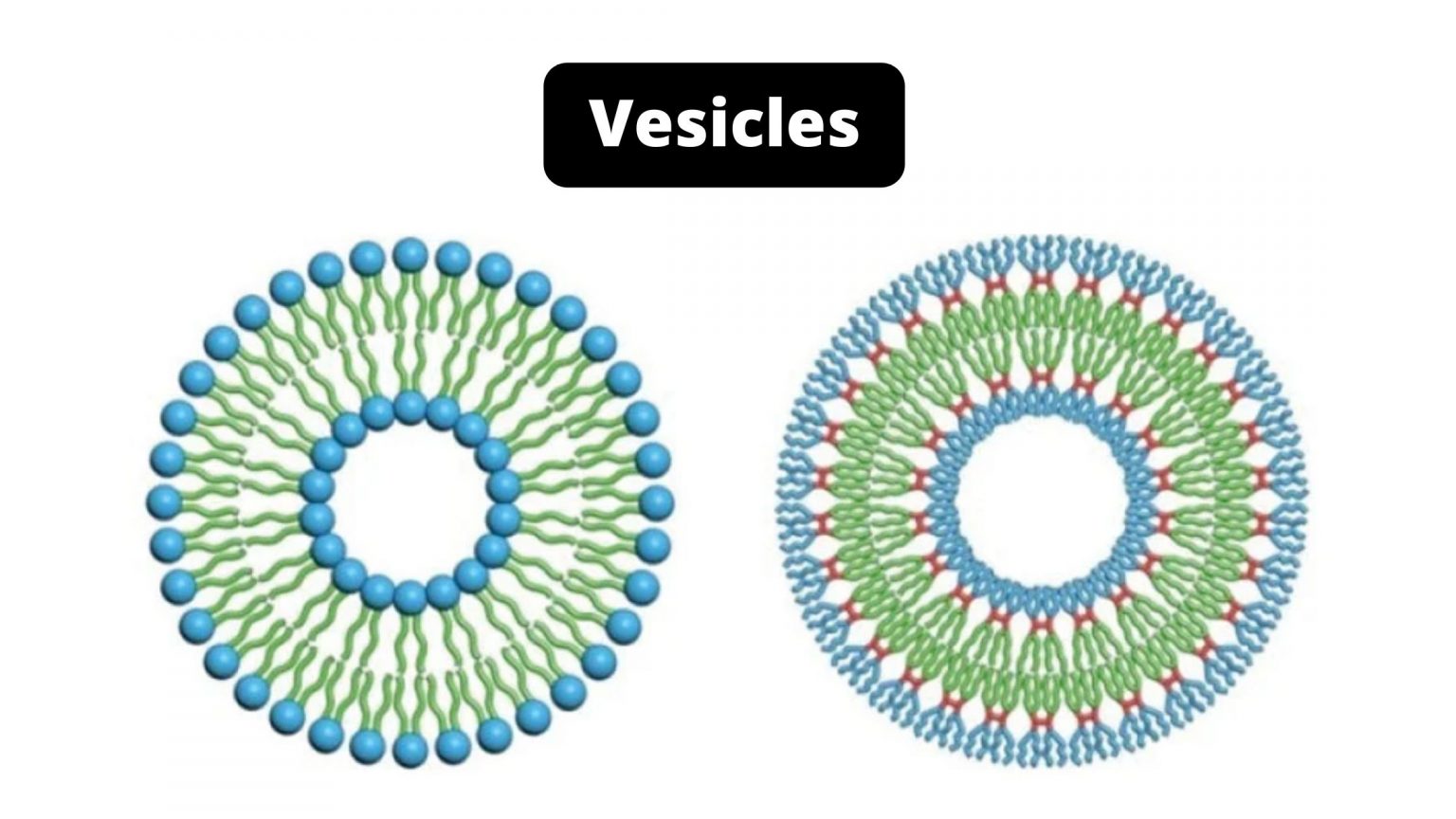
Vesicles Drawing - Web spherical bilayers that enclose an aqueous compartment are called vesicles or liposomes. Web vesicles are important for the survival of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Web learn how transport vesicles form and fuse with their target membranes. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Web in cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Four main vesicles within the cells are: Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and can be moved along cytoskeletal elements by motor proteins. Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are. Web a vesicle consists of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Web a synthetic vesicle, called a liposome, can be created by mixing phospholipid molecules in an aqueous environment. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and can be moved along cytoskeletal elements by motor proteins. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Click the info button at the top right corner to find more tutorials, quiz questions and an interactive drawing pad!. Web expert insights on laboratory developed tests, the consequences of ending abortion protection, health equity, and more draw 18,000 attendees to adlm 2024. They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. No covalent steps are required. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Web vesicles are important for the survival of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. As you've learned already, cells are the basic unit of life. Web in this short tutorial, learn how to draw an endosome fusing with a lysosome. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. They are needed for every system of the body. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. A vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Web a synthetic vesicle, called a liposome, can be created by mixing phospholipid molecules in. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Web vesicles perform a wide range of functions within cells, such as the transport of proteins and lipids between the different parts of a cell. Alternatively, they may be prepared. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall. An overview of prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Each vesicle is coated with a. Web a synthetic vesicle, called a liposome, can be created by mixing phospholipid molecules in an aqueous environment. An overview of prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells. Web vesicles perform a wide range of functions within cells, such as the transport of proteins and lipids between the different parts of a cell. Web secretory vesicles definition. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is. Web a vesicle consists of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. Web we describe a general vesicle modeling tool that has been designed for wide application to a variety of cell models, implemented within our software stochastic engine for pathway simulation. An animal. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion ( exocytosis ), uptake ( endocytosis ), and the transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of. They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. Web in this short tutorial, learn how to draw an endosome fusing with a lysosome. Cells contain parts called organelles. The space inside the vesicle can be. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is. Web a vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Definition, structure & function (with analogy & diagram) updated june 24, 2019. Web in cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Web expert insights on laboratory developed. As you've learned already, cells are the basic unit of life. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and. Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are. Web vesicles are important for the survival of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Does the er become smaller and smaller every time? Click the info button at the top right corner to. Web in cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Web we describe a general vesicle modeling tool that has been designed for wide application to a variety of cell models, implemented within our software stochastic engine for pathway simulation. Web spherical bilayers that enclose an aqueous compartment are called vesicles or liposomes. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Web a synthetic vesicle, called a liposome, can be created by mixing phospholipid molecules in an aqueous environment. Certain functions are specified for each type of vesicle and are crucial for the cells. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall. Cells contain parts called organelles. Definition, structure & function (with analogy & diagram) updated june 24, 2019. Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and can be moved along cytoskeletal elements by motor proteins. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. An overview of prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells. They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. The space inside the vesicle can be. Each vesicle is coated with a protein complex, and understanding the structure and function of these complexes is a central challenge in cell biology.Secretory vesicle vector illustration. Labeled closeup infographic
Biochemistry Glossary Transport Vesicle Draw It to Know It
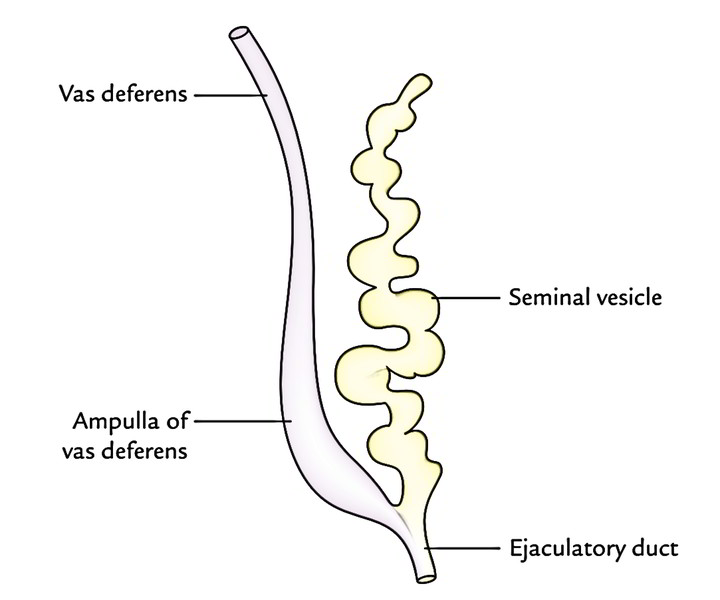
Anatomy Of Seminal Vesicle Anatomy Book
In Cell Biology, what are Vesicles? (with picture)
Functions of Vesicles Biology Wise
Vesicles Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
Vesicles Definition, Structure, Types, and Functions Microbiology Notes
Vesicle anatomy Britannica
Good Morning Kids on emaze
2.4.7 Explain how vesicles are
We Also Discuss How Vesicles Interact With Other Cells And Pathogens.
They Essentially Help Clean Up And Recycle Cellular Debris And Wastes.
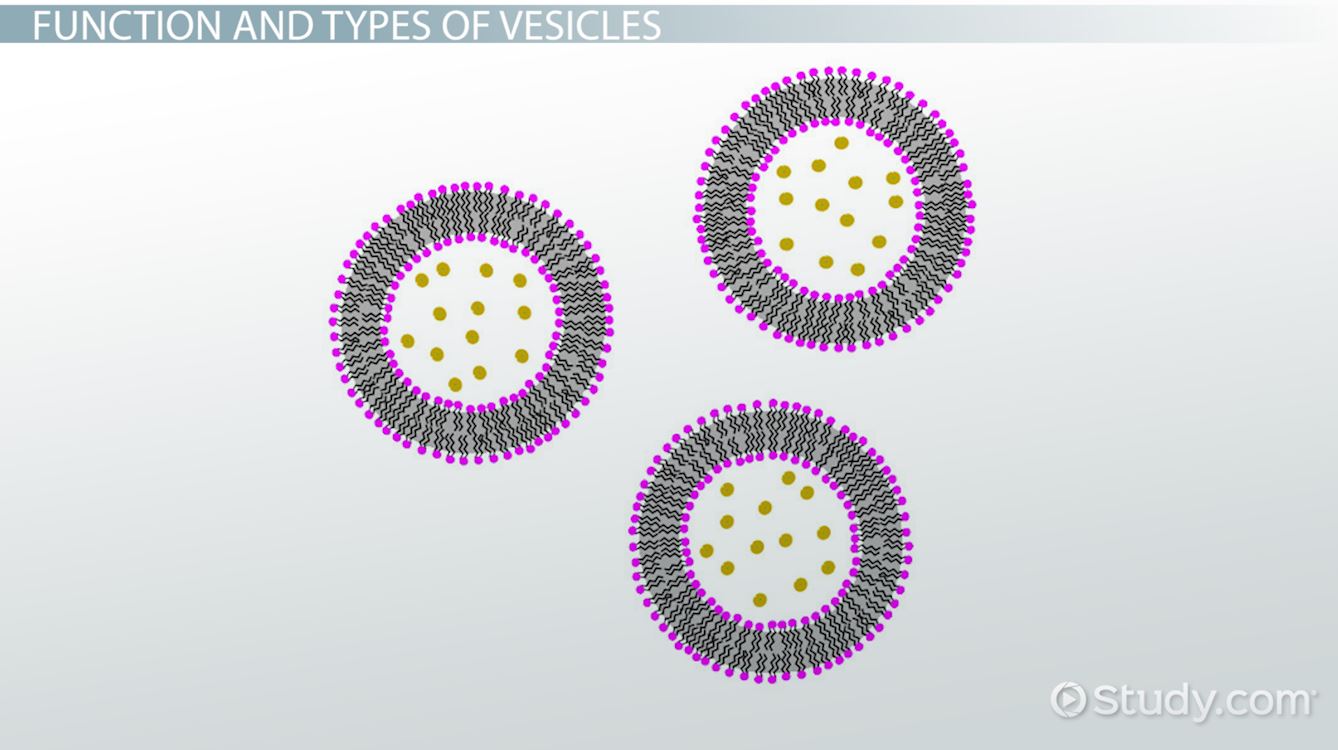
The Small, Spherical Compartment Of Vesicles Is Separated From The Cytosol By At Least One Lipid Bilayer.
Web Vesicles Are Important For The Survival Of Both Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells.
Related Post: